Polar Molecule

The Science of Water in the Living World
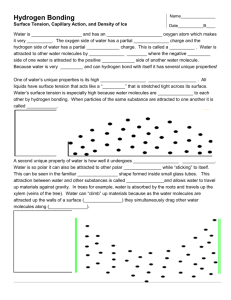
Water is a polar molecule.
• Polar Molecule: _____________________________________
___________________________________________________
– The are more electrons surrounding the oxygen atom than the hydrogen atoms.
– Oxygen atom has a slightly negative charge.
– Hydrogen atoms has a slightly positive charge.
• Hydrogen Bonds: ____________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
• How is a hydrogen bond different than a covalent bond?
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Properties of Water
• Adhesion: __________________________
____________________________________
____________________________________
– Cohesion makes water have high
surface tension – it is difficult to break the surface of a body of water.
– Cohesion makes water a viscous
liquid – it is difficult to move through.
• Cohesion: ___________________________
____________________________________
____________________________________
• Capillary Action: ____________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
___________________________________________________
Examples of Capillary Action:
– Water flowing into the spores of a sponge
– Water flowing into plant roots and up the plant stem.
– Groundwater moving up through soil.
Water: The (Almost) Universal Solvent
Water can mix other polar/ionic molecules.
– Polar molecules can be referred to as hydrophilic (water
loving)
– Solute : ______________________________________
_____________________________________________
– Solvent: ______________________________________
_____________________________________________
Ex: Salt (solute) dissolves in water (solvent).
– ____________________________________________________________________
– ____________________________________________________________________
– ____________________________________________________________________
Water does not mix with nonpolar molecules.
– Non polar molecules can be referred to as hydrophobic (water fearing).
– Water (polar) and oil (nonpolar) do not mix.
Heat and Water
Water molecules are in constant motion. The higher the temperature the faster the molecules are moving.
The Three States of Water:
• Gas (vapor): _____________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
– Water molecules are spread much further apart than in liquid water.
– Increasing temperature, increases the rate of evaporation.
• Liquid: _______________________________
______________________________________
______________________________________
– Hydrogen bonds are constantly being broken and reformed.
– Cold Water: ______________________
_________________________________
_________________________________
– Warm Water: ____________________
________________________________
________________________________
• Ice: ____________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
– In ice, the water molecules are further apart than in liquid water.
– Ice is less dense than liquid water.
– Why is it important that ice floats in the ocean?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
Heat Capacity: ________________________________________________________________
• Water has the highest heat capacity of any natural substance.
• Heat energy must be used to break hydrogen bonds between water molecules before the molecules are able to move faster and increase temperature.
• A relatively constant water temperature helps organisms maintain
homeostasis
:
________________________________________________________________________
• It takes a long time and a lot of energy for water to heat up or cool down.
• Water’s high heat capacity protects organisms from drastic changes in temperature.
Acid, Bases and pH
• Water molecules sometimes split apart to from ions.
• What is an ion?
__________________________
__________________________
__________________________
• Pure water is neutral:
__________________________
__________________________
Acids Bases
pH: (power of Hydrogen) as in Hydrogen ions
• Measures the H+ concentration in solution: [H+]
• It is a log scale, so it increases by powers of ten.
• Ex: pH 2 = [H+] of 0.01M, pH 3 = [H+] of 0.001M
• Ex: A solution with a pH of 2 is ten times more acidic then a solution with a pH of 3.
1.
According to the scale, what substance is neutral?
2.
What solution has an [H+] of 0.0001M?
3.
Which substance produce the most OH- ions in solution?
4.
How many more times acidic is tomato juice compared to pure water.
Buffer: ________________________________
_______________________________________
_______________________________________
• Many land animals have buffers in their blood that maintain a constant pH.
• Ocean water acts as a buffer and resists changes in pH.
• If the pH of an organism changes, it will affect the chemical reactions inside their cells.
• Buffers help organisms maintain homeostasis with respect to pH.