AP World History Syllabus
advertisement

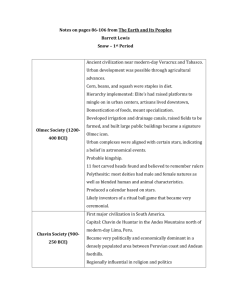
AP World History Course Syllabus Miss Beck The following is a tentative course outline for AP World History. Chapters listed below assigned reading, section and unit. YOU are responsible for the content and reading, even if it is not covered in great detail during a class period. World history content covered in this course spans over 10,000 years and requires a great amount of diligence, discipline and reading in order to fully grasp content and concepts. Please note you will always be ahead with textbook reading than with actual lessons in class. Please do not fall behind with reading so you will be prepared for the AP World History exam in May. The textbook will be used for the majority of reading; however, several other sources will be utilized as well throughout the course. Textbook: Earth & Its Peoples. Fifth Edition Bulliet, Professor, Pamela Crossley, Daniel Headrick, Steven Hirsch, Lyman Johnson, and David Northrup.. Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2011. Unit I: Foundations- 8000 BCE-600 CE (Weeks 1-6) 1. World Geography 2. Civilizations- Emphasis on “What is a “Civilization?” 3. Chapter 1: The Origins of Agriculture to the First River Valley Civilizations a. Before Civilization b. Mesopotamia c. Egypt d. Indus River Valley 4. Chapter 2: New Civilizations in the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. 2200-250 BCE a. Early China, 2000-221 BCE b. Nubia, 3100BCE-350 CE c. Celtic Europe, 1000-50 BCE 5. Chapter 3: The Mediterranean and the Middle East, 2000-300 BCE a. Cosmopolitan Middle East, 1700-1100 BCE b. Aegean World, 2000-1100 BCE c. Assyrian Empire, 911-612 BCE d. Israel, 2000-500 BCE e. Phoenicia and the Mediterranean, 1200-500 BCE 6. Chapter 4: Greece and Iran, 1000-30 BCE a. Ancient Iran, 1000-486 BCE b. Rise of the Greeks ,1000-500 BCE c. Struggle for Persia and Greece, 546-323 BCE d. Hellenistic Age, 323-30 BCE 7. Chapter 5: Age of Empires: Rome and Han China, 753 BCE-600 CE a. A Mediterranean Empire, 753 BCE-600 CE b. Origins of Imperial China, 221 BCE-220 CE 8. Faith and Religions: a. Hinduism b. Buddhism c. Judaism d. Christianity 9. Chapter 7: Networks of Communication and Change, 300 BCE-600 CE a. Silk Road b. Indian Ocean Maritime c. Trading Across the Sahara Sub-Saharan Africa d. Cultural Borrowing and Spread of Ideas UNIT EXAM: Multiple Choice and Comparison Writing Unit II: 600-1450 CE (Weeks 7-13) 1. Chapter 8: The Rise of Islam, 600-1200 a. Origins of Islam b. Rise and Fall of Caliphate, 632-1258 c. Islamic Civilization 2. Chapter 9: The Christian Societies Emerge in Europe, 600-1200 a. Byzantine Empire, 600-1200 b. Early Medieval Europe, 600-1000 c. Western Church d. Kievian Russia, 900-1200 e. Western Europe Revives, 1000-1200 f. Crusades, 1095-1204 3. Chapter 10: Inner and East Asia, 600-1200 a. Emergence of East Asia, to 1200 b. Kingdoms of East Asia and Southeast Asia 4. Chapter 11: Peoples and Civilizations of the Americas, 600-1200 a. Classic-Era Culture and Society in Mesoamerica, 200-900 b. Postclassical Period in Mesoamerica, 900-1500 c. Northern American Peoples d. Andean Civilizations, 200-1500 5. Chapter 12: Mongol Eurasia and Its Aftermath, 1200-1500 a. Rise of the Mongols, 1200-1260 b. Mongols and Islam,1260-1500 c. Regional Responses in Western Eurasia d. Mongol Domination in China, 1271-1368 e. Centralization and Militarism in East Asia, 1200-1500 6. Chapter 13: Tropical Africa and Asia, 1200-1500 a. Tropical Lands and Peoples b. New Islamic Empires c. Indian Ocean Trade d. Social and Cultural Change UNIT EXAM: Multiple Choice and Document Based Question Writing Unit III: 1450-1750 CE (Weeks 14-19) 1. Chapter 14: The Latin West, 1200-1500 a. Rural Growth and Crisis b. Urban Revival c. Learning, Literature, and the Renaissance d. Political and Military Transformations 2. Chapter 15: The Maritime Revolution, to 1550 a. Maritime Expansion, before 1450 b. European Expansion ,1400-1550 c. Encounters with Europe, 1450-1550 3. Chapter 16: Transformation in Europe, 1500-1750 a. Culture and Ideas b. Social and Economic Life c. Political Innovations 4. Chapter 17: The Diversity of American Colonial Societies, 1530-1770 a. Columbian Exchange b. Spanish America and Brazil c. English and French Colonies in North America 5. Chapter 18: The Atlantic System and Africa, 1550-1800 a. Plantations in the West Indies b. The Atlantic Economy 6. Chapter 19: Southwest Asia and the Indian Ocean, 1500-1750 a. Ottoman Empire, to 1750 b. Safavid Empire ,1502-1722 c. MughalEmpire ,1526-1761 7. Chapter 20: Northern Eurasia, 1500-1800 a. Japanese Reunification b. Later Mind and Early Qing Empires c. Russian Empire UNIT EXAM: Multiple Choice and Continuity and Change over Time Essay Unit IV: 1750-1914 CE (Weeks 20-25) 1. Chapter 21: Revolutionary Changes in the Atlantic World, 1750-1850 a. Eighteenth Century Crisis b. American Revolution, 1775-1800 c. French Revolution, 1789-1815 d. Revolution Spreads, Conservatives Respond 2. Chapter 22: The Early Industrial Revolution, 1760-1851 a. Causes of Industrialization b. Technological Revolution c. Impact of the Early Industrial Revolution d. New Economic and Political Belief Systems 3. Chapter 24: Land of Empires in the Age of Imperialism, 1800-1870 a. Ottoman Empire b. Russian Empire c. Qing Empire 4. Chapter 25: Africa, India, and the New British Empire, 1750-1870 a. Changes and Exchanges in Africa b. British Mandate in India c. Britain’s Eastern Empire 5. Chapter 26: The New Power Balance, 1850-1900 a. New Technologies and the World Economy b. Social Changes c. Socialism and Labor Movements d. Nationalism and the Rise of Italy, Germany, and Japan e. Great Powers of Europe f. China, Japan, and Western Powers 6. Chapter 27: The New Imperialism, 1869-1914 a. New Imperialism: Motives and Methods b. Scramble for Africa c. Imperialism in Asia and the Pacific d. Imperialism in Latin America UNIT EXAM: Multiple Choice and Writing Assignment TBD (Based on need) Unit V: 1914 to present (Weeks 26-31) 1. Chapter 28: The Crisis of the Imperial Order, 1900-1929 a. Origins of Crisis in Europe and the Middle East b. The “Great War” and Russian Revolutions, 1914-1918 c. Peace and Dislocation in Europe, 1919-1929 d. China and Japan: Contrasting Destinies e. New Middle East 2. Chapter 29: The Collapse of the Older Order, 1929-1949 a. Stalin Revolution b. The Depression c. Rise of Fascism d. East Asia, 1931-1945 e. Second World War 3. Chapter 30: Striving for Independence: India, Africa, and Latin America, 1900-1949 a. Indian Independence Movement, 1905-1947 b. Sub-Saharan Africa, 1900-1945 c. Mexico, Argentina and Brazil, 1900-1949 4. Chapter 31: The Cold War and Decolonization, 1945-1979 a. The Cold War b. Decolonization and Nation Building 5. Chapter 32: The End of the Cold War and the Challenge of Economic Development and Immigration, 1975-2000 a. Postcolonial Crises and Asian Economic Expansion b. Challenges of Population Growth c. Growth of Cities 6. Chapter 33: New Challenges in a New Millennium a. Globalization and Economic Crisis b. Global Culture UNIT EXAM: Multiple Choice and Writing Assignment TBD (Based on need) Please Note: AP Exam Review will take place from the conclusion of content coverage until the exam date. Projects and other forms of learning will be assigned thereafter.