Addition of Decimals using Base 10 blocks Word
advertisement

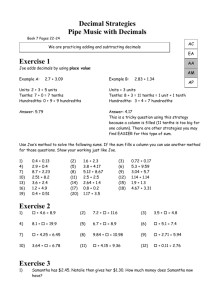
Addition with Decimals using Base 10 Blocks Refer to Everyday Math Grade 4: Unit 4, Lesson 4.4 and 4.5 Refer to Everyday Math Grade 5: Unit 2, Lessons 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, and 2.4 Objective/Goal: Using Base-10 blocks, students will understand how to add decimals. Benchmarks Touched On 5.1.3.1 (M) 5.1.3.2 (L) 5.1.3.3 (L) 5.1.3.4 (H) Benchmark Emphasized 5.1.3.1 Add and subtract decimals and fractions, using efficient and generalizable procedures, including standard algorithms. 5.1.3.2 Model addition and subtraction of fractions and decimals using a variety of representations. 5.1.3.3 Estimate sums and differences of decimals and fractions to assess the reasonableness of results. 5.1.3.4 Solve real-world and mathematical problems requiring addition and subtraction of decimals, fractions and mixed numbers, including those involving measurement, geometry and data. Misconceptions The first error revealed is related to naming decimals. Rank the value based solely on the number of digits – the longer the number, the greater the value. Treat all the numbers as whole numbers in assigning value, ignoring the decimal completely. An emphasis on digits and procedures rather than values and number sense. Deficiencies in understanding place value. Materials: Base -10 blocks (3 flats, 20 longs, 25 units) Adding Decimals worksheet Math notebook Addition real-world problems (see sheet) Student Language Frames Pencil Stages: 1. Estimate and build concrete representation, add and read correctly. (Math Notebook) 2. All of above and Part of a Whole Representation 10 x 10 board to represent addition; write answers in word form. (Adding Decimals recording sheet) 3. All of the above and base ten representation 4. All of the above and the standard algorithm Directions: Each student has a bag of base-10 blocks, and the Adding Decimals page or a math notebook. Ask students to estimate the answer to the problem: 0.28 + 0.6. Have students write down the estimate and share their answer with a partner. Ask Student A to estimate the answer and explain how the estimate was made. Students write the numbers under where it says Part of a Whole Representation on the Adding Decimals page. Create with base-10 blocks and have students point to each digit 2 tenths and 8 hundredths then 6 tenths. Teachers and students are checking students’ work to make sure that the number is represented correctly. Ask Student A to find the sum and to explain the value of each digit. (88 hundredths 8 tenths and 8 hundredths) Was our estimate reasonable? Why? Record on the Adding Decimals sheet with a drawing to represent each number in the Part of a Whole Representation. Shade in 2 columns one color and 8 squares another color. Shade in 6 columns the same color as the 2 in the first grid. The bottom grid will be the sum of 8 columns and 8 squares for 88 hundredths. Students write the answer in word form under the grid (eighty-eight hundredths). Ask students to represent the Base-10 blocks on their paper and make the connection to the standard algorithm. Continue with this process, giving a problem, creating the Base-10 model and finding the sum until each student has explained his/her thinking. Note: If students have difficulty with this activity or their explanations, they need to return to decimal concepts rather than focus on how to add or subtract decimals. Variation For students who are not ready for the pictorial representation and need more practice with the Part of a Whole Representation, use the 10 x 10 addition boards to see more decimal concepts. Ask Student A to estimate the answer to the problem 37 hundredths plus 3 tenths and explain how the estimate was made. Students use the addition board to record the addition problem 0.37 + 0.3. Create with Base-10 blocks and write the digits in decimal form on the addition board over the representation. 0.37 + 0.3. Ask Student A to find the sum and to explain the value of each digit. (0.67) Was our estimate reasonable? Why? Record in the addition board using two different colors to represent the Base-10 blocks. Students write the standard algorithm and draw the Base-ten blocks. Variation For students who are ready for the pictorial representation with a problem in context. Ask Student A to estimate the answer and explain how the estimate was made. (7.46 + 6.2 + 0.08) Students write Adding Decimals at the top of the page in their math notebooks and record the addition problem 7.46 + 6.2 + 0.08. Create with Base-10 blocks and write the digits in decimal form over the grid in their notebook and pictorial representation; 7 over (7 flats) 46/100 over the base-ten blocks (4 longs and 6 units), 6 over (6 flats) 2/10 over the (2 longs), and 8/100 over the (8 units) explaining the value of each digit. Ask Student A to find the sum and to explain the value of each digit. Was our estimate reasonable? Why? Record in the math notebook with a drawing to represent the base-10 blocks showing the sum. Students write the standard algorithm and represent the base-ten blocks. Purposefulness of Chosen Problems: Chapin and Johnson (2000) state, “Finding examples of decimals (5.2 on an odometer for example) explaining what the decimal numeral means in the context of its use (I walked 5.2 miles to work) indicating the general value of the decimal numeral (I live a little more than 5 miles to work) and then stating what two whole numbers the decimal is between (5.2 miles is between 5 miles and 6 miles) helps students recognize that the decimal amount is the sum of a whole number and a number less than one.” This approach reaffirms the importance of avoiding “naked” mathematics and instead teaching skills and concepts within context. Decimal number sense should be a focus during instruction so that students recognize an unreasonable answer (Sherman, Richardson, and Yard 2005). In addition, the decimals used in computation problems should be authentically – examples include money, the radio dial, linear measures and digital speedometers. …we need to strive for conceptual understanding that connects the notation with the value being represented. Additionally, we want to help students make generalizations regarding decimal computation. To that end, we can have students name the decimal correctly and use a variety of concrete models to represent decimals. (Book: Math Misconceptions pages 43-48) #1) 0.28 + 0.6 #2) 0.37 + 0.3 #3) 0.37 + 0.4 #4) 0.15 + 0.07 #5) 1 + 0.08 #6) 1.46 + 1.2 + 0.08 Student Math Notebook Samples Title written at the top of the page: "Adding Decimals" Directions for Partner Work: Once all students in the flex group have explained their thinking, students continue the activity with their partner. Students decide who is Partner A and who is Partner B. Give a stack of cards using only cards 0-9. Partner A chooses three cards to represent a whole number with decimal fractions to the hundredths place. Partner B chooses three more cards to represent another whole number with decimal fractions to the hundredths place. Once the numbers are chosen, students need to estimate the answer first and explain why this is their answer. Students create the base-10 model of the problem. Partner A and B check their partner’s model to verify they are the same. Partner A describes the estimation and then finding the sum using the Student Frames below. Both draw the representation in their math notebook and record the regrouping. Continue the process with Partner B starting first and explaining his/her thinking. Math notebooks are checked for student understanding of the process. Student Language Frames (what the students say to each other): “I made the decimals ______________ and _______________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) “The sum of _____________ and _____________ is _____________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (Students make sure to check and agree with your partner’s work and that the sum is the same.) Addition Real-World Problems 1.) Alyssa’s parents gave birth to twins and named them Betty and Debbie. When they were first born, Debbie weighed 5.2 pounds and was 21.5 inches tall, and Betty weighed 6.3 pounds. How much did the babies weigh in total? 2.) Michael rode his bicycle to a farm that sold baskets of mangos for $7.42 each and baskets of oranges for $6.20 each, and a bag for 8 cents. Michael decided to buy a basket of mangos and a basket of oranges and he needed a bag to carry them on his bicycle. How much did Michael need to pay for his purchase? 3.) Nathan is wondering which pair of shoes he should wear to be tall enough to ride the roller coaster at MOA this weekend. His favorite ride requires 4.5 feet tall. Nathan is 3.99 feet tall and with his baseball cap he is 0.02 inches taller. Will his tennis shoes with soles that are .35 inches tall make him tall enough for the ride? 4.) Erin rode her bike 3.5 miles on Monday. She rode her bike 2.75 miles on Wednesday and 5.12 miles on Saturday. How far did she ride her bike in all three days? Addition Real-World Problems 1.) Alyssa’s parents gave birth to twins and named them Betty and Debbie. When they were first born, Debbie weighed 5.2 pounds and was 21.5 inches tall, and Betty weighed 6.3 pounds. How much did the babies weigh in total? 2.) Michael rode his bicycle to a farm that sold baskets of mangos for $7.42 each and baskets of oranges for $6.20 each, and a bag for 8 cents. Michael decided to buy a basket of mangos and a basket of oranges and he needed a bag to carry them on his bicycle. How much did Michael need to pay for his purchase? 3.) Nathan is wondering which pair of shoes he should wear to be tall enough to ride the roller coaster at MOA this weekend. His favorite ride requires 4.5 feet tall. Nathan is 3.99 feet tall and with his baseball cap he is 0.02 inches taller. Will his tennis shoes with soles that are .35 inches tall make him tall enough for the ride? 4.) Erin rode her bike 3.5 miles on Monday. She rode her bike 2.75 miles on Wednesday and 5.12 miles on Saturday. How far did she ride her bike in all three days? Student Language Frames Student Language Frames: “I made the decimals ______________ and _______________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) “The sum of _____________ and _____________ is _____________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (Students make sure to check and agree with your partner’s work and that the sum is the same.) Student Language Frames: “I made the decimals ______________ and _______________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) “The sum of _____________ and _____________ is _____________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (Students make sure to check and agree with your partner’s work and that the sum is the same.) Student Language Frames: “I made the decimals ______________ and _______________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) “The sum of _____________ and _____________ is _____________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (Students make sure to check and agree with your partner’s work and that the sum is the same.) Student Language Frames: “I made the decimals ______________ and _______________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) “The sum of _____________ and _____________ is _____________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (Students make sure to check and agree with your partner’s work and that the sum is the same.) Student Language Frames: “I made the decimals ______________ and _______________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) “The sum of _____________ and _____________ is _____________. (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (tenths, hundredths) (Students make sure to check and agree with your partner’s work and that the sum is the same.) Estimate Adding Decimals Part of a Whole Representation Base-10 Representation Standard Algorithm Sum written in words: Estimate Part of a Whole Representation Base-10 Representation Standard Algorithm Base-10 Representation Standard Algorithm Sum written in words: Estimate Part of a Whole Representation Sum written in words: Estimate Adding Decimals Part of a Whole Representation Base-10 Representation Standard Algorithm Sum written in words: Estimate Part of a Whole Representation Base-10 Representation Standard Algorithm Base-10 Representation Standard Algorithm Sum written in words: Estimate Part of a Whole Representation Sum written in words: