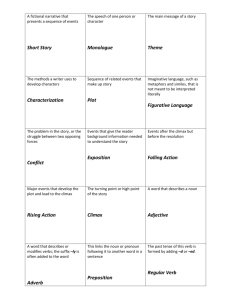
Welcome Back! Grammar Warm Up In your notebooks please take
advertisement
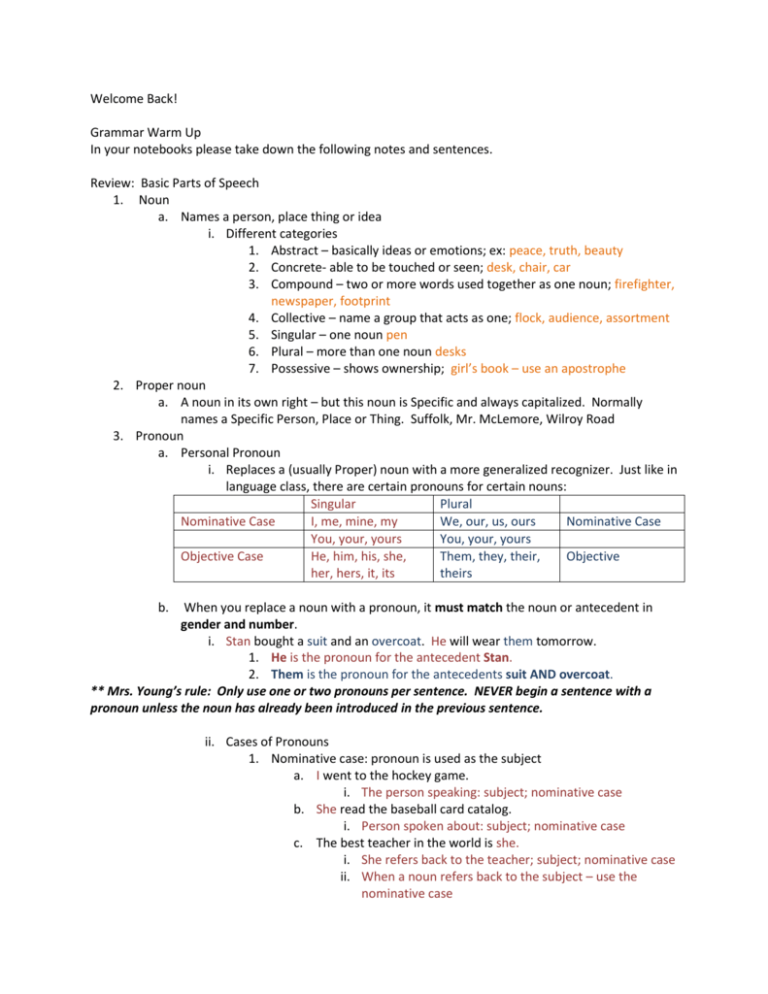
Welcome Back! Grammar Warm Up In your notebooks please take down the following notes and sentences. Review: Basic Parts of Speech 1. Noun a. Names a person, place thing or idea i. Different categories 1. Abstract – basically ideas or emotions; ex: peace, truth, beauty 2. Concrete- able to be touched or seen; desk, chair, car 3. Compound – two or more words used together as one noun; firefighter, newspaper, footprint 4. Collective – name a group that acts as one; flock, audience, assortment 5. Singular – one noun pen 6. Plural – more than one noun desks 7. Possessive – shows ownership; girl’s book – use an apostrophe 2. Proper noun a. A noun in its own right – but this noun is Specific and always capitalized. Normally names a Specific Person, Place or Thing. Suffolk, Mr. McLemore, Wilroy Road 3. Pronoun a. Personal Pronoun i. Replaces a (usually Proper) noun with a more generalized recognizer. Just like in language class, there are certain pronouns for certain nouns: Singular Plural Nominative Case I, me, mine, my We, our, us, ours Nominative Case You, your, yours You, your, yours Objective Case He, him, his, she, Them, they, their, Objective her, hers, it, its theirs b. When you replace a noun with a pronoun, it must match the noun or antecedent in gender and number. i. Stan bought a suit and an overcoat. He will wear them tomorrow. 1. He is the pronoun for the antecedent Stan. 2. Them is the pronoun for the antecedents suit AND overcoat. ** Mrs. Young’s rule: Only use one or two pronouns per sentence. NEVER begin a sentence with a pronoun unless the noun has already been introduced in the previous sentence. ii. Cases of Pronouns 1. Nominative case: pronoun is used as the subject a. I went to the hockey game. i. The person speaking: subject; nominative case b. She read the baseball card catalog. i. Person spoken about: subject; nominative case c. The best teacher in the world is she. i. She refers back to the teacher; subject; nominative case ii. When a noun refers back to the subject – use the nominative case 2. Objective Case a. When a pronoun is used as an object of the verb (direct object) b. Answers the questions “What” or “whom” after the verb. Also receives the action of the verb. i. His family visited her in the hospital. ii. HIS IS AN ADJECTIVE in this sentence – tells whose family it was that went to see her. iii. HER is the pronoun that is being visited. c. Dr. Nina explained it. i. It is the objective case pronoun. Answers the question explained what? ii. Write these in your notebook and make sure they are correct! Choose the correct case for each pronoun in the sentences below. 1. Maria and (me, I) are planning a vacation to Florida. 2. I have never been as skillful with computers as (him, he). 3. My mother invited Jill and (her, she) to our Thanksgiving dinner. 4. The worker (who, whom) left the empty soda can on the computer table should not have been so thoughtless. 5. When Chaz and I chose a builder, we chose one (whom, who) we believed was reputable. 6. (Who, Whom) do you think won the lottery this week 7. I was (he, him), my father, who first noticed the trouble in my marriage. 8. I would not like to be (him, he) when the boss comes in this morning. 9. We were taken in by a charlatan (whom, who) we thought was an honest man. 10. Between you and (me, I), who and whom are confusing. CHECK YOUR WORK!! Choose the correct case for each pronoun in the sentences below. 1. Maria and (me, I) are planning a vacation to Florida. Nominative 2. I have never been as skillful with computers as (him, he). (As he is.) Objective 3. My mother invited Jill and (her, she) to our Thanksgiving dinner. Objective 4. The worker (who, whom) left the empty soda can on the computer table should not have been so thoughtless. Nominative 5. When Chas and I chose a builder, we chose one (whom, who) we believed was reputable. (Who is the subject of the verb "was.") Nominative 6. (Who, Whom) do you think won the lottery this week? (Who is the subject of the verb "won.") 7. I was (he, him), my father, who first noticed the trouble in my marriage. 8. I would not like to be (him, he) when the boss comes in this morning. 9. We were taken in by a charlatan (whom, who) we thought was an honest man. (Who is the subject of the verb "was.") 10. Between you and (me, I), who and whom are confusing. iii. Additional Pronouns 1. Indefinite Pronouns a. Pronoun that does not define or stand for something particular. b. All, either, each, one, everyone, several, some, other, another, both, none, many c. Sometimes used as adjectives – make sure you know how it is being used. d. Must agree in number (singular or plural) use a singular pronoun for a singular antecedent: i. Singular antecedent : another, anybody, anyone, each, either, everybody, everyone, neither, nobody, one, somebody, someone e. Many try for office but few succeed in being elected. i. Many – indefinite pronoun used as subject of the verb try – doesn’t refer to anyone in particular. ii. Few – indefinite pronoun used as subject of the verb succeed. f. Several friends entered the race, and all runners received a ribbon. i. Several – indefinite pronoun used as a subject for the verb entered. ii. All – indefinite pronoun used a subject for the verb received. iii. Practice: Handout #25 and 26 – both sides. Due now! 2. Demonstrative Pronouns a. Used to point out, designate or demonstrate the antecedent for which they are standing in. i. This is my country. 1. This is a demonstrative pronoun – can point to it. 2. This, that, these and those a. Demonstrative pronouns. 3. Possessive Pronouns a. Used to show ownership or possession. b. Singular Plural mine, my our, ours your, yours your, yours his, her, hers, its their, theirs c. Mine is the nicest car on the block. i. Mine: possessive pronoun – shows to whom the car belongs. d. Yours is the oldest car in the neighborhood. i. Yours shows possession belongs to someone else. 4. Relative Pronouns a. Relate or refers to nouns or other pronouns in a sentence. The nouns referred to are called antecedents. i. Who and Whom: refer to people. 1. Who is used as a subject or Nominative case. 2. Whom is used as an Objective case. ii. Which refers to animals and things iii. That and Whose refers to persons, animals or things iv. Complete practice # 27 & 28 – turn in before you leave!! 5. Interrogative Pronouns a. Used in asking a question. i. Who – nominative ii. Whom – objective iii. Which – referring to persons, things and telling one thing from another iv. What referring to things v. Whose – referring to persons or things. 1. Which is safer – an airplane or a ship? a. Which asks a question about a thing 2. Whose is it? a. Whose asks a question referring to a person 3. Thomas Edison, who had little formal schooling, invented the electric bulb. a. Who – refers to Thomas Edison, subject of the sentence i. Complete practice # 29 & 30. Turn in before you leave!