Math III - NC Mathematics
advertisement

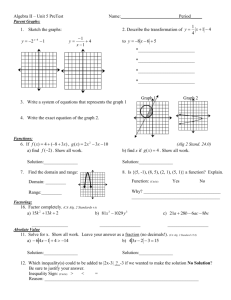
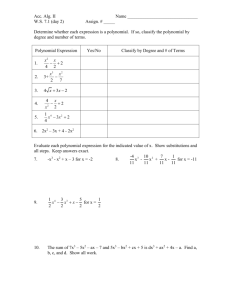
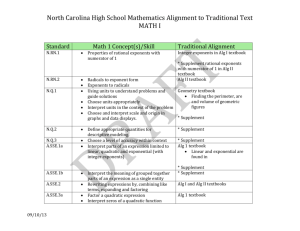
North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Traditional Text MATH III Standard N.RN.3 Math III Concept (s) N.Q.1 N.Q.2 N.Q.3 N-CN.1 N.CN.2 N.CN.7 N.CN.9 (+) A.SSE.1a A.SSE.1b 09/10/13 Sum or product of two rational numbers is rational Sum of rational and irrational numbers is irrational Product of a nonzero and irrational number is irrational Use units to understand problems and guide solutions Choose units appropriately Interpret units in context Choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays Define appropriate quantities for descriptive modeling Chose a level of accuracy within context Know and represent complex numbers Add, subtract, and multiply complex numbers Solve quadratics that have complex solutions Know the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra and show it’s true for quadratic polynomials Interpret parts of an expression Traditional Alignment * Supplement Geo textbook Finding perimeter, area, and volume of geometric figures * Supplement *Supplement *Supplement Alg II textbook Alg II textbook Alg II textbook Alg II textbook Alg I textbook Only linear and exponential *Supplement other functions * Supplement Interpret the meaning of grouped together parts of an expression as single entity 1 A.SSE.2 A.SSE.3b A.SSE.4 A-APR.1 A.APR.2 A.APR.3 A.APR.4 A.APR.6 A.APR.7 (+) A.CED.1 A.CED.2 A.CED.3 Alg I and Alg II text Foundations in Alg II and advanced problems in Alg II Alg I and Alg II textbooks Produce equivalent forms of Foundations in Alg I and advanced expressions to reveal key features problems in Alg II Complete the square to reveal vertex Derive the formula for a finite geometric Alg II textbook series and use the formula to solve problems Add, subtract, and multiply polynomials Alg I and Alg II textbooks Foundations in Alg I and advanced problems in Alg II Alg II textbook Know and apply the Remainder Theorem Alg II textbook Identify zeros of polynomials from factored forms Only factoring to reveal zeros Use zeros to construct rough graph * Supplement constructing rough graphs * Supplement Prove polynomial identities and use them to describe numerical relationships Rewrite rational expressions using long Alg II textbook division, synthetic division, or technology Alg II textbook Perform operations with rational expressions and understand properties Alg I and Alg II textbooks Create and solve equations and Foundations in Alg 1 and advanced in Alg inequalities with one variable II Create and graph equations with two or Alg I, Alg II, and Geo textbooks more variables Foundations in Alg 1 and advanced in Alg II, trig in Geo Alg I and Alg II textbooks Represent constraints by equations or Only linear systems inequalities and by systems of equations and/or inequalities Rewriting expressions by combining like terms, expanding, and factoring 2 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Traditional Text MATH III A.CED.4 A.REI.1 A.REI.2 A.REI.4.a A.REI.4.b A.REI.10 A.REI.11 F.IF.2 F.IF.4 Interpret solutions Rearrange formulas Construct an argument for solving simple equations Solve rational equations with one variable Solve radical equations with one variable Show how extraneous solutions may arise Complete the square to write quadratics in vertex form Derive the quadratic formula by completing the square Solve quadratics in all ways Graph of an equation represents all the solutions Solving systems using function notation Use, evaluate, and interpret statements written in function notation Interpret key features of graphs and tables Given verbal description, sketch graphs *Supplement for all other functions Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks Foundations to solving are in Alg I and advanced solving is in Alg II Alg II textbook Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks Alg I and Alg II textbooks Concepts * Must supplement for all types of functions Alg I and Alg II textbooks * Supplement interpreting the rules and numbers Alg I and Alg II Foundations in Alg 1 and advanced in Alg II * Supplement identifying key features of a graph within context 09/10/13 3 F.IF.5 F.IF.7c F.IF.7e F.IF.8a F.IF.9 F.BF.1a F.BF.1b F.BF.2 F.BF.3 F.BF.4a F.LE.3 F.LE.4 F.TF.1 F.TF.2 F.TF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph Graph polynomial functions, identifying zeros and showing end behavior Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features Use factoring and completing the square to show key features Compare properties of two functions expressed in different ways Given context, write a function using an explicit expression, a recursive process, or showing steps for calculations Combine standard functions using arithmetic operation Model situations to write arithmetic and geometric sequences both recursively and explicitly Identify the effects of algebraic transformations to include translations, reflections, and dilations Solve for f(x) = c and find the inverse of the function Understanding that a quantity increasing exponentially will eventually exceed all others For exponential models, express as a logarithm and evaluate Understand radian measure of an angle as the length of the arc on the unit circle Explain how the unit circle enables the extension of trig functions, interpreted as radian measures of angles Choose trig functions to model periodic phenomena with specified amplitude, Alg I and Alg II textbook * Supplement Alg I and Alg II textbook Alg I and Alg II textbook * Supplement comparison of different forms Geo and Alg II textbooks *Supplement recursive process Alg II textbook Geo and Alg II textbooks *Supplement for informal recursive Alg II textbook Alg II textbook *Supplement Alg II textbook Alg II textbook Alg II textbook * Supplement radian measures Alg II textbook 4 North Carolina High School Mathematics Alignment to Traditional Text MATH III F.TF.8 G.CO.1 G.CO.9 G.CO.10 G.CO.11 G.CO.12 G.SRT.2 G.SRT.3 G.SRT.4 G.SRT.5 G.C.1 G.C.2 G.C.3 G.C.5 09/10/13 frequency, and midline Prove the Pythagorean identity sin2(θ) + cos2(θ) =1 and use it to find trig ratios Define angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment Prove theorems about lines and angles Prove theorems about triangles Prove theorems about parallelograms Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods Define similarity by using geometric transformations Explain using similarity transformations the meaning of similarity for triangles Establish the AA criterion for two triangles to be similar Prove theorems about triangles Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships Prove all circles are similar Relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle Prove properties of angles for a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle Derive using similarity that the length of the arc intercepted is proportional to the radius Define the radian measure of the angle * Supplement Alg I and Geo textooks Geo textbook Geo textbook Geo textbook *Supplement Geo textbook Geo textbook Geo textbook Geo textbook * Supplement Geo textbook * Supplement Geo textbook *Supplement deriving on their own and defining radian measure 5 G.GPE.1 G.GPE.2 G.MG.3 S.ID.4 S.IC.1 S.IC.3 S.IC.4 S.IC.5 S.IC.6 S.MD.6 (+) S.MD.7 (+) as the constant of proportionality Derive the formula for the area of a sector Derive equation of a circle from Pythagorean Theorem Complete the square to find the center and radius of circle Derive the equation of a parabola give a focus and directrix Apply geometric methods to solve design problems Use mean and standard deviation to analyze and estimate Estimate areas under the normal curves Process for make inferences about populations based on random samples Purposes of and differences among sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies and explain how randomization relates to each Use data from a sample survey to estimate a population mean or proportion Develop a margin of error Use data from a randomized experiment to compare Use simulations to decide if differences are significant Evaluate reports based on data Use probabilities to make fair decisions Analyze decisions and strategies using probability concepts Alg II textbook Only completing the square * Supplement deriving equation of circle * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement * Supplement 6