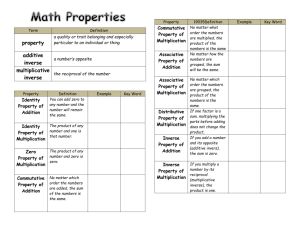
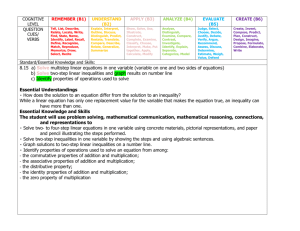
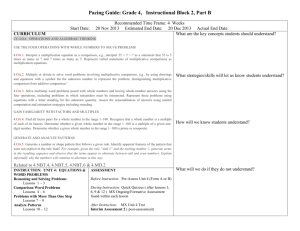
math_612_619
advertisement
Lesson Plan Template (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) 0 Teacher: Ms. Meek and Mrs. Valentine/ Ms. Betts Date(s): May 4 - 8, 2015 Content or Unit: Remediation Monday 6.13 The student will describe and identify properties of quadrilaterals. Tuesday 6.16 The student will a) describe mean as balance point; and b) decide which measure of center is appropriate for a given purpose. Grade Level or Course:06 Mathematics Wednesday 6.11 The student will a) identify the coordinates of a point in a coordinate plane; and b) graph ordered pairs in a coordinate plane. New skills: (Monday only) 6.12 The student will determine congruence of segments, angles, and polygons. 6.19 The student will investigate and recognize a) the identity properties for addition and multiplication; b) the multiplicative property of zero; and c) the inverse property for multiplication. STAGE 1: Desired Results ~ What will students be learning? Geometry Remediation: SOL 6.13 The student will use problem solving, mathematical communication, mathematical reasoning, connections, and representations to • Sort and classify polygons as quadrilaterals, parallelograms, rectangles, trapezoids, kites, SOL/Learning Objective rhombi, and squares based on their properties. Specify the behaviors, conditions, and criteria. Indicate Properties include number of parallel sides, angle the verbs used in the Curriculum measures and number of congruent sides. • Identify the sum of the measures of the angles of a Framework. quadrilateral as 360°. 6 Create 5 Evaluate New skills: (Monday)SOL 6.12 The student will use problem solving, 4 Analyze mathematical 3 Apply communication, mathematical reasoning, 2 Understand connections, and representations to 1 Remember • Characterize polygons as congruent and noncongruent according to the measures of their sides and angles. • Determine the congruence of segments, angles, and polygons given their attributes. • Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given 1 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version Lesson Plan Template (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply these techniques in the context of solving practical and mathematical problems.† Tuesday - Wednesday)New skills SOL 6.19 The student will use problem solving, mathematical communication, mathematical reasoning, connections, and representations to • Identify a real number equation that represents each property of operations with real numbers, when given several real number equations. • Test the validity of properties by using examples of the properties of operations on real numbers. • Identify the property of operations with real numbers that is illustrated by a real number equation. Essential Questions & Understandings/Big Ideas Look for Essential Questions that are overarching or topical and help guide the unit plan. These questions promote conceptual thinking and add coherence to a series of lessons. An idea is “big” if it helps make sense of seemingly isolated facts. Remediation (Monday)SOL 6.13 Can a figure belong to more than one subset of quadrilaterals? Any figure that has the attributes of more than one subset of quadrilaterals can belong to more than one subset. For example, rectangles have opposite sides of equal length. Squares have all 4 sides of equal length thereby meeting the attributes of both subsets. New skill- (Monday only) SOL 6.12 • Given two congruent figures, what inferences can be drawn about how the figures are related? The congruent figures will have exactly the same size and shape. • Given two congruent polygons, what inferences can be drawn about how the polygons are related? Corresponding angles of congruent polygons will have the same measure. Corresponding sides of congruent polygons will have the same measure. 6.13: quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, square, rhombus, bisect, trapeqoid, kite, parallel, 90 degrees, 360 degrees, congruent, sum attributes/characteristics 6.11 x-axis, y-axis, origin (0), negative, positive, ordered pairs, quadrants, counterclockwise, +, -, Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, Quadrant IV Key Vocabulary 6.12 congruent, noncongruent, congruent symbol, correponding angles, Look for in the Curriculum Framework and other adopted polygons, vertices, resources. 6.19 additive identify is zero, multiplicative identity is one, additive identity property, multiplicative identify property, inverse, multiplicative inverse property, reciprocal, multiplicative property of zero, division by zero is undefined. STAGE 2: Assessment Evidence ~ What is evidence of mastery? 2 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version Lesson Plan Template (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) Assessment Part 1 Start with the end in mind! Consider here a sample question or performance task students will need to do as evidence of mastery of this objective. Review Questions (handouts) 6.13 Students are able to identify the shapes but are unable to put them in groups according to attritutes. Also, they need additional practice in finding the missing angles when give three or two. Possible misconceptions or learning gaps Complete the above task yourself; think about what might be hardest for students to grasp? 6.12 Students know what “congruent” means but have problems finding congruent (corresponding) congruent angles. They have problems drawing polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices; use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. 6.19 Students might get the various properties confused. STAGE 3: Learning Plan ~ What are the strategies and activities you plan to use? Snapshot / Warm-up Activate prior knowledge and get students thinking about & motivated for today’s lesson. Instructional Strategies Think in term of high yield strategies, such as: ● Identifying similarities and differences ● Summarizing and note taking ● Reinforcing effort and providing recognition ● Homework and practice ● Nonlinguistic representations ● Cooperative learning ● Setting objectives and providing feedback ● Generating and testing hypothesis ● Questions, cues, and advance organizers (handout or written on the board or shown on the overhead) Provided by the team and Ms. Smith. Provided on request Teaching Format has changed due to remediation. 10 minutes - Snapshot 20 minutes - Remediation 25 minutes - New Skill 5 - 7 minutes - Exit ticket/Question 5 - 8 minutes - Give instructions for homework Monday: Remediate 6.13 Complete lesson on 6.12 Practice Questions Tuesday: Remediate 6.16 Probability New skill Properties 6.19 (Ms. Smith will demonstrate/teach) Vocabulary will be displayed Practice Questions Wednesday: Remediate 6.11 Cordinate Planes New skill Properties (groups) Hands-on-activities Practice Questions Thursday: SOL 06 Mock Math Assessment on Iinteractive Achievement (IA) 3 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version Lesson Plan Template (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) Friday: complete Mock Assessment if time allows review latest released and older released tests by VDOE. Teaching and Learning Activities Plan for modeling, small or whole group instruction, and work stations. Include your examples, guided practice, problems or questions to pose, independent activities. It may help to think in terms of: “I do …” “We do…” “Students do …” 6.19 (properties) New skill: Activity A: Identity Properties for Addition and Multiplication 1. Write the word identity on the board. Ask students to think about what it means to have an identity. Allow students time to talk this over with partners, and have students share their responses. 2. Explain that the identity properties are numbers that when combined with other numbers do not change the other numbers. Ask students to think about how this idea relates to what they just discussed. Display the chart papers with the two identity properties labeled. Point out that there is an identity property for addition and an identity property for multiplication. 3. Ask students what number could be used for the identity property for addition—that is, what number, when added to any other number, does not change the value of the original number. Have students test different numbers to find which number fits the identity property for addition. Have a discussion of student responses. If they do not identify zero as the number, tell them that when zero is added to any number, the number remains the same. Have them revisit their work and test using zero to see whether they agree. Write a description of the identity property for addition on the chart paper along with some examples: “The sum of any real number and zero is equal to the given real number (e.g., 5 + 0 = 5).” 4. Ask students what number could be used for the identity property for multiplication—that is, what number, when multiplied by any other number, does not change the value of the original number. Have students test different numbers to find which number fits the identity property for multiplication. Have a discussion of student responses. If they do not identify 1 as the number, tell them that when 1 is multiplied by any number, the number remains the same. Have them revisit their work and test using 1 to see whether they agree. Write a description of the identity 4 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version Lesson Plan Template Differentiation Some ideas include: ● Flexible grouping ● Tiered instruction ● Interest-based activities ● Varied products ● Task cards ● Personal agendas ● Graphic Organizers (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) property for multiplication on the chart paper along with some examples: “The product of any real number and one is equal to the given real number (e.g., 8 ∙ 1 = 8).” As you write examples, use the symbol (∙) for multiplication throughout the lesson. Activity B: Inverse Property for Multiplication 1. Write the word inverse on the board. Talk to students about the meaning of this word, reviewing the meaning of inverse operations from the “Balanced” lesson. Tell students that inverses are numbers that combine with other numbers and result in identity elements. 2. Display the chart paper with the inverse property labeled. Point out that students will be exploring the inverse property for multiplication. 3. Have students brainstorm what numbers could be used as factors with other numbers to have a product of 1. Provide students with a few examples, such as 4 ∙ = 1 and 1 3 ∙ = 1. Have students generate ideas as to how to find the multiplicative inverse of a number. Have a discussion of student responses. Explain that the multiplicative inverse of a number is also referred to as the reciprocal of the number. Note that zero has no multiplicative inverse. Write a description of the inverse property for multiplication on the chart paper along with some examples: “The product of a number and its multiplicative inverse (or reciprocal) always equals one (e.g., 4 1 4 = 1).” Activity C: Multiplicative Property of Zero 1. Display the chart paper with the multiplicative property of zero labeled. Ask students to make predictions about what the multiplicative property of zero might be. Discuss student responses. 2. Explain that any real number multiplied by zero is equal to zero. Have students come up with examples to support this property. Write a description of the multiplicative property of zero on the chart paper along with some examples: “The product of any real number and zero is zero (e.g., 4 ∙ 0 = 0).” Higher Level Technology Use Connections to other subject How will you be Thinking areas and/or authentic incorporating Plan for a applications challenging cognitive level, such as apply, analyze, evaluate, or create technology Practice SOL test online including CAT training test online Account / Bookkeeper / Cafetria manager . Powerpoints 5 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version Lesson Plan Template (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) The teacher will walk around the room to ensure students are engaged and understanding. Questions will be asked of ALL students. No student will be allowed to pass. (additional assistance we be given if needed) The discovery approach will be used. Checking for Understanding Check throughout the lesson using: ● Question and Answer ● Class discussions ● Group Response ● Demonstrations ● Practice sheets ● Quick Quizzes • How are the identity properties for multiplication and addition the same? Different? For each operation the identity elements are numbers that combine with other numbers without changing the value of the other numbers. The additive identity is zero (0). The multiplicative identity is one (1). • What is the result of multiplying any real number by zero? The product is always zero. • Do all real numbers have a multiplicative inverse? No. Zero has no multiplicative inverse because there is no real number that can be multiplied by zero resulting in a product of one. *Additional activities will be available: AAA math activities, practice sheets, hands-on-activities, etc. STAGE 4: Closure ~ What did the students master & what are they missing? Lesson Closure & Student Summarizing of their Learning Exit questions provided by team and Mrs. Smith. Review what students learned or should have learned. Recognize gaps and allow them to help you plan for the next lesson(s). Assessment Part 2 Revisit Assessment Part 1. Plan a formative assessment which shows concretely what students mastered today. This might be: ● Exit card ● Short Quiz ● Seatwork/Practice Sheet collected ● Written response to a prompt ● Oral responses/participation ● Exit card ● Short Quiz ● Seatwork/Practice Sheet collected ● Written response to a prompt ● Oral responses/participation Teacher Reflection / Effectiveness of Learning The students are learning new skills and being remediated on weak skills (based on data). It is taking them a longer length of time to complete the mock assessments therefore, there is limited time to teach new skills and 6 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version Lesson Plan Template (Stages adapted from the UBD model by McTighe and Wiggins) remediate. Ms. Smith is very helpful in providing hands-on-activities to assist with instruction and remediation. Kudos to Ms. Smith for being a team player. KN and LB have been sick and absent. Subsequently, they are behind on remediation and instruction. They are both staying after school for remediation. This will help. 7 Richmond Public Schools 2014-15 Explanations version