GeoGebra Tutorial 4 Graphs and Sliders
advertisement

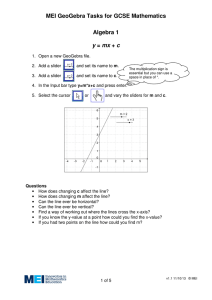
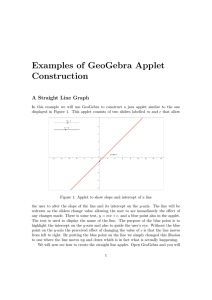
GeoGebra Tutorial 4 – Graphs and Sliders GeoGebra is capable of graphing a variety of functions as well as computing for areas under a curve. The screen shot below is an example of several graphs plotted in GeoGebra. Figure 1 - Graphs created with GeoGebra In this tutorial, we are going to use GeoGebra to investigate the effects of parameters of functions to its graph. Unlike in our previous activities, this time we are going to use the Algebra window and the coordinate axes. First, we are going to investigate the graph of by typing equations in the input field, then later, we are going to use a slider. Graphing Functions Open GeoGebra. We WILL need the Algebra window and the Coordinate axes so we will NOT hide them. To un-hide the Coordinate axes, click the View menu on the menu bar, and then click Axes. To un-hide the Algebra window, click View then click Algebra window. 1. To graph , type y = 2x in the input field. (The input field is the text box with the label Input located at the bottom of your GeoGebra window.) Press the ENTER key on your keyboard. 2. Type the following equations: each equation. 3. Type more equations of the form 4. How does the value of , and, and press the enter key after where m is any real number. affect the appearance of the graph of the function ? Using Sliders To avoid typing over and over again for varying values of parameters , we will use the slider control. A slider is a visual representation of a number. This time, we will also add the parameter b. This means that we will explore the graph of the function of where and are real numbers. START New 1.) Open the Geogebra window. We WILL need the Algebra window and the Coordinate axes so we will NOT hide them. To un-hide the Coordinate axes, click the View menu on the menu bar, and then click Axes. To un-hide the Algebra window, click View then click Algebra window. 2.) Select the Slider control and click anywhere on the drawing pad do display the Slider dialog box. 3.) In the Slider dialog box, change the slider’s name to m, change the interval to shown below. to as Figure 2 - The Slider Dialog Box Leave the other values as is and click the Apply button to finish. 4.) Adjust the position of your slider if necessary. Move the small black circle on your slider. What do you observe? 5.) To graph the function , type y = m*x in the Input box. 6.) Now, move the small circle on your slider. What do you observe? 7.) Now, create a new slider and name it . Set the interval to is. 8.) To change the function to menu, and type y = m*x + b. 9.) Now, move your leaving the other values as , right click the graph, click Redefine from the context slider. What do you observe? 10. ) How does the value of 11.) Graph the function the function. affect the appearance of the graph of the function ? . Explain the effects of the parameters a and b to the graph of Notes: 1. The ^ symbol is used for exponentiation in GeoGebra. Hence, we write as a*x^2 + c. 2. Instead of using you can also use and in writing equations of functions, for the function .