Geology Study Guide What do geologists study? The Earth
advertisement

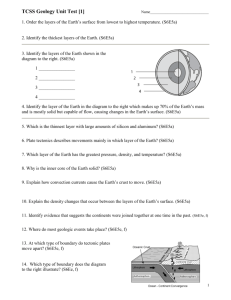
Geology Study Guide 1. What do geologists study? The Earth 2. Compare constructive and destructive forces. Give an example of each. Constructive forces build (volcano) destructive forces wear down (weathering) 3. Are scientists able to study the layers of the Earth directly? If no, explain how they determine the make up of the layers. No, they study them indirectly by using seismic waves. 4. What happens to the temperature and pressure as you travel deeper into the Earth’s layers? Both increase 5. Which type of crust is more dense, continental or oceanic? oceanic 6. The rigid layer that includes the crust and the upper most part of the mantle is referred to as the… lithosphere 7. The hotter, upper mantle that is below the lithosphere is referred to as the… asthenosphere 8. Heat from the core creates convection currents in the mantle. 9. Who was the scientist who developed the theory of continental drift? Alfred Wegener 10. What were the three pieces of evidence he used to support his theory? Fossils, Climate change, Landforms, and jig-saw fit of continents 11. Why was his theory rejected? He couldn’t explain how they moved. 12. What device was used to map the ocean floor? sonar 13. The theory that states that new land is continually being added to the ocean basin is known as… seafloor spreading 14. A deep ocean trench is created when… one plate subducts another 15. If new land is being created, why is the Earth not getting bigger? Old land is being recycled at subduction zones 16. Discovery of the mid-atlantic ridge, magnetic variations on the ocean floor, and the development of new ocean crust were all pieces of evidence that helped support the theory of… seafloor spreading 17. The Earth’s “shell” is broken up into (asthenospheric, lithospheric, or biospheric) plates. 18. Name the three main types of boundaries. Divergent, Convergent, Transform 19. At which boundary is crust neither created or destroyed? transform 20. The circle of intense volcanic and earthquake activity around the Pacific is known as… The Ring of Fire 21. Volcanoes are mostly found on convergent boundaries. 22. The Andes Mountains are volcanic. They must lie along a convergent boundary. 23. The sudden release of energy within the Earth’s crust causes an… earthquake 24. Faults, earthquakes, and volcanoes usually occur along… plate boundaries 25. Are volcanoes constructive or destructive forces? both 26. At which boundary are volcanoes NOT likely to occur? transform 27. Series of volcanic islands, such as the Hawaiian Islands, are the result of … Hot spot volcanoes 28. Volcanic eruptions can release magma, dissolved gasses, and ash/soot. 29. What is viscosity? The amount of resistance a fluid has 30. A volcano that is sleeping is… dormant 31. In order to be considered “volcanic activity” there must be an eruption of lava, water, and gas. 32. What’s the difference between a geyser and a hot spring? Geysers erupt and hot springs are calm 33. Convection currents cause plates to move towards each other or apart? 34. Glacial deposits in Massachusetts show evidence of change over time. 35. Describe the age of the seafloor at mid-ocean ridges compared to against the continents. Youngest at mid-ocean ridges (new seafloor is being created), oldest against the continents) 36. Fossils are least likely to occur in igneous intrusions or sedimentary rocks? 37. What does the principle of crosscutting relations state? Faults and igneous intrusions are younger than the rocks they cut through. 38. Faults are younger than the rocks they cut through. 39. If identical index fossils are found in two different rock layers, what can you conclude about those rock layers? They are the same age. 40. The figure below shows rock layers from 2 continents that were once apart of a super continent. When did the continents break apart? 125 million years ago 41. What is an unconformity? Between what 2 layers is there an unconformity? A disturbance or change in the rock layers. Between layers 1 and 3. 42. Define uniformitarianism. The geological processes that occur today are the same geological processes that occurred in the past. “The present is the key to the past” Open Response Topics 1. Convection Currents: What is happening and how they are the cause for movement of lithospheric plates. Diagrams would be helpful. How the earth continues to make new crust but the size of the earth does not increase. 2. Relative Age Dating: Ordering rock layers (relative age), evidence to back up ordering (geologic principles, fossils, etc.). How environments have changed over time using fossil evidence (ex. Marine environment turning to land or vise versa and what might have caused this (volcano creating new land).