Quiz 4 - s3.amazonaws.com
advertisement
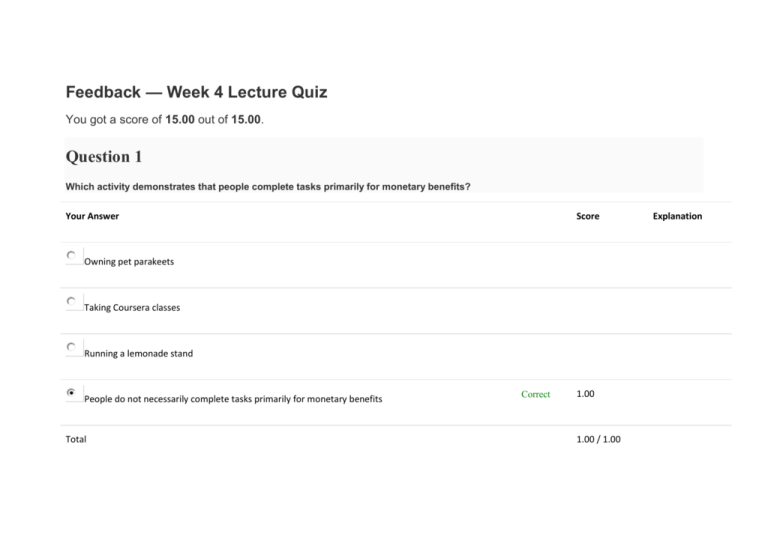
Feedback — Week 4 Lecture Quiz You got a score of 15.00 out of 15.00. Question 1 Which activity demonstrates that people complete tasks primarily for monetary benefits? Your Answer Score Owning pet parakeets Taking Coursera classes Running a lemonade stand People do not necessarily complete tasks primarily for monetary benefits Total Correct 1.00 1.00 / 1.00 Explanation Question 2 What did the experiment with Bionicles measure? Your Answer Score The effect of creation on a sense of camaraderie. How a sense of futility would affect participants’ willingness to work. Correct 1.00 How much the Sisyphean condition would make people love building Legos. How we should look to Greek mythology for hints about how to go about our lives. Total Question 3 Imagine you’re an employer. Some of your employees have done work that your company has decided to not use. Would acknowledging their unused work be important for their willingness to do future work? 1.00 / 1.00 Explanation Your Answer Yes, if the acknowledgement gave their work meaning. Score Correct Explanation 1.00 No, it would not be worthwhile, because morale has nothing to do with efficiency and productivity. Not unless you were trying to encourage your employees to go on strike. Yes, if you also gave them a bonus for their work under high-stakes conditions. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Question 4 Which of the following demonstrates the IKEA effect? Your Answer Score Explanation You think your painting ought to cost $3000, and other people also think it ought to cost $3000. You enjoy the cake you baked more than you enjoy the cake your aunt baked. Correct 1.00 You are your own worst critic. You hate the way your grandmother makes lasagna. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Question 5 What does the IKEA effect show? Your Answer Shopping should always be paired with Swedish meatballs and Lingonberry desserts. Score Explanation Labor leads to love. Correct 1.00 You think all furniture should have red slipcovers. We misremember the agony that goes along with assembling IKEA furniture and overvalue our creations. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Question 6 How could clothing retailers take advantage of the IKEA effect? Your Answer They could spell their product names with umlauts, creating an impression of authenticity. They could anticipate exactly what you will want and have it hanging in a dressing room that’s already playing your favorite music. Score Explanation They could give you only three options and make you choose one. They could make you put a bit of effort into customizing your clothes. Total Correct 1.00 1.00 / 1.00 Question 7 How does the Toothbrush Theory illustrate the IKEA effect? Your Answer We don’t all need a toothbrush; some people have dentures. Just like theories. We all need a toothbrush, but if you borrow someone else’s, it’s probably best not to tell him or her about it--just like when you borrow someone else’s theories. We undervalue things that belong to us and ideas we’ve come up with, just as we underestimate the importance of our Score Explanation toothbrushes. We all need a toothbrush, we all want a toothbrush, but nobody wants to use anybody else’s toothbrush. We want to create our own ideas and theories, but we don’t want to rely on the ideas of others. Correct Total 1.00 1.00 / 1.00 Question 8 Pick the statement that includes a benefit and a drawback of the IKEA effect. Your Answer Falling in love with your own project makes you work much harder, but it can also keep you working on a lost cause. Falling in love with your own project makes you open-minded, but it also makes you disparage your own ideas. Falling in love with your own project leads to a reasonable appraisal of your own work, but it makes you falsely Score Correct 1.00 Explanation modest. Falling in love with your own project can stymie your academic career, but also leads you to be more cooperative. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Question 9 How does Zappos use cognitive dissonance to make their staff more motivated? Your Answer Zappos pays people to accept their job offer so that their new employees will be anchored with high expectations for ROI (return on investment). Zappos coaches its staff on how to tolerate cognitive dissonance. First, they test them to make sure they only hire people who are prone to dissonance. Zappos creates cognitive dissonance by offering job applicants money to turn down the job. In this way, they sort out the Score Explanation greedy applicants from the non-materialistic ones. Zappos’ staff align their feelings with their behaviors. They become convinced that they prefer a job at Zappos to a significant sum of money. Correct Total 1.00 1.00 / 1.00 Question 10 Do big bonuses help white collar workers reach their potential? Your Answer Score Yes, but only if the bonus is paid in cash. No, only those in the financial sector benefit from big bonuses. Some incentives help, but very big bonuses can make people perform worse. Correct 1.00 Explanation Sometimes. They don’t work for everyone, but high bonuses do work for businessmen and professors. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Question 11 When would you want to motivate people with big bonuses? Your Answer Score When the stakes are high. When you are trying to cut costs and need each penny that you give to go a long way. When the problem-solving that you want them to do is particularly challenging. When the task is mechanical rather than mental. Correct 1.00 Explanation Total 1.00 / 1.00 Question 12 Why did Dan look at NBA “clutch players?” Your Answer Score To see whether a coach’s confidence in players could improve the team’s performance. He couldn’t convince bankers to participate in his experiments, so he looked for another example of a self-selecting club of professionals who perform under high pressure. Correct 1.00 Duke is thinking about starting an intramural basketball team, and Dan wants to be the clutch player. To see whether Duke’s Coach K was familiar with the best players in the NBA. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Explanation Question 13 Which of the following describes the results of the experiment with building Bionicles? Your Answer Score In both conditions, a greater love of Legos led to building more Bionicles. Participants with lower dexterity had trouble building Bionicles and were less likely to complete the experiment. Participants who predicted the results of the experiment realized the extent to which motivation would be dampened in the Sisyphean condition. People built more Bionicles in the Meaningful condition and fewer in the Sisyphean condition. Total Correct 1.00 1.00 / 1.00 Explanation Question 14 What happened in the experiment where participants were paid to find pairs of letters on sheets of paper? Your Answer Score In terms of motivating participants, ignoring their work was closer to acknowledging their work than to shredding their work. Participants stopped working at about 30 cents per page in the Shredder condition, at about 20 cents per page in the Acknowledged condition, and at about 15 cents per page in the Ignored condition. Performance suffered because participants were overwhelmed by the letter pairs. Acknowledging participants’ work was much more motivating than both ignoring and shredding their work. Total Correct 1.00 1.00 / 1.00 Explanation Question 15 How might social factors be similar to stress about big monetary stakes? Your Answer Score When solving anagrams for pay or when monetary stakes are high, increasing social stress increases both motivation and performance. When we are not included in social events, the effects are comparable to not getting a financial bonus. When solving anagrams for pay, increasing social stress increases motivation but not performance. This is similar to the pattern for increasing monetary stakes. Correct 1.00 Public pressure and high monetary stakes are both demotivating. Total 1.00 / 1.00 Explanation