Chapter 2 Review Sheet Answers
Name ___________________________Per ______
Chapter 2 Review Sheet
2.1 – Atoms, Ions & Molecules
1.
The three parts of an atom?
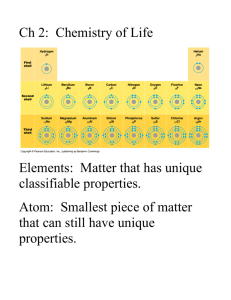
2. All matter is composed of these?
3. Where protons and neutrons are found in an atom?
4. Where electrons are found in an atom?
Format:
27 M/C
11 Completion
4 Short Answer
50 PTS TOTAL
What to Study:
Ch 2 Notepacket
Ch 2 SG
Macromolecule Review Sheet
Quizzes
This Sheet
Answers
PROTON, NEUTRON, ELECTRON
ATOMS
NUCLEUS
SURROUNDING THE NUCLEUS,
ORBITAL, ELECTRON CLOUD
COVALENT BOND
IONIC BOND
5. When atoms share electrons?
6. When electrons are exchanged between atoms (one takes and one accepts)?
7. How does an ionic bond form?
8. A substance containing only one type of atom?
2.2 Properties of Water
9. Water is a ________ molecule because the oxygen atom carries a slight _______ charge, while the hydrogen atoms carry a slight ________ charge.
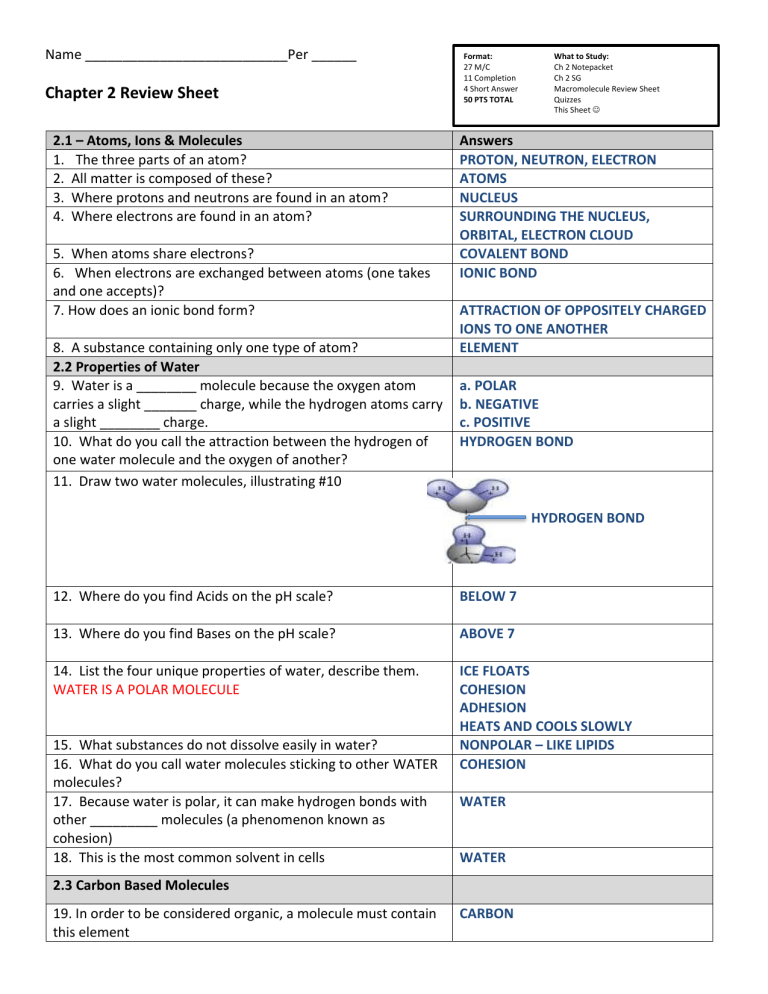
10. What do you call the attraction between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen of another?
11. Draw two water molecules, illustrating #10
ATTRACTION OF OPPOSITELY CHARGED
IONS TO ONE ANOTHER
ELEMENT a. POLAR b. NEGATIVE c. POSITIVE
HYDROGEN BOND
H BOND HYDROGEN BOND
12. Where do you find Acids on the pH scale?
13. Where do you find Bases on the pH scale?
14. List the four unique properties of water, describe them.
WATER IS A POLAR MOLECULE
15. What substances do not dissolve easily in water?
16. What do you call water molecules sticking to other WATER molecules?
17. Because water is polar, it can make hydrogen bonds with other _________ molecules (a phenomenon known as cohesion)
18. This is the most common solvent in cells
2.3 Carbon Based Molecules
19. In order to be considered organic, a molecule must contain this element
BELOW 7
ABOVE 7
ICE FLOATS
COHESION
ADHESION
HEATS AND COOLS SLOWLY
NONPOLAR – LIKE LIPIDS
COHESION
WATER
WATER
CARBON
20. How many electrons does carbon have in its outermost energy level?
21. Molecules that are long chains and large rings can be made in cells because carbon loves to bond with what?
22. What kind of covalent bonds can carbon make with other atoms?
23. The formation of polymers from monomers occurs as a result of this type of reaction
24. The breakdown of polymers into smaller monomers occurs as a result of this type of reaction
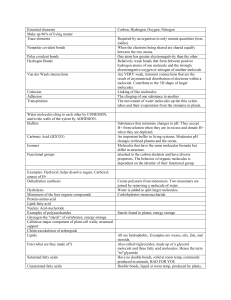
25. What are the four families of macromolecules
26. Give examples of carbohydrates
27. How do plants store glucose? (a molecule)
4
OTHER CARBON ATOMS
Non-polar covalent bonds
SINGLE, DOUBLE, OR TRIPLE
DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS (REMOVING
WATER TO MAKE)
HYDROLYSIS (ADDING WATER TO
BREAK)
CARBOHYDRATES
LIPIDS
PROTEINS
NUCLEIC ACIDS
SUGARS AND STARCHES
STARCH
28. How do you store glucose? (a molecule)
29. Give examples of lipids
GLYCOGEN
FATS. OILS, WAXES AND
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
PROTEINS 30. Where would you find long chains of amino acids, linked by peptide bonds?
31. What piece of an amino acid makes it unique from other amino acids?
32. Give examples of nucleic acids
33. What is the function of DNA?
2.4 Chemical Reactions
R GROUP/VARIABLE GROUP
(20 different)
DNA AND RNA
STORE AND TRANSMIT GENETIC INFO
34. In a chemical reaction, these are the substances that get changed (the “ingredients”)
35. In a chemical reaction, these are the new substances formed
REACTANTS
PRODUCTS
36. The amount of energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction ACTIVATION ENERGY
37. These reactions absorb energy overall. Draw a picture of the energy of this reaction.
ENDOTHERMIC RXN
38. These reactions release energy overall. Draw a picture of the energy of this reaction.
EXOTHERMIC RXN
2.5 Enzymes
39. Without these, the chemical reactions in your cells would occur too slowly to support life’s processes.
40. Reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are called:
41. What is the name of the place on an enzyme where the substrate binds?
ENZYMES
SUBSTRATES
ACTIVE SITE
42. List two factors that can impact the activity of an enzyme TEMP pH
43. If any of your answers to # 42 above changes too drastically, what happens to the enzyme?
DENATURE; CHANGE SHAPE AND
THEREFORE ALTER THE FUNCTION
44. Draw a graph comparing the energy pathways of a reaction without an enzyme and one with an enzyme.