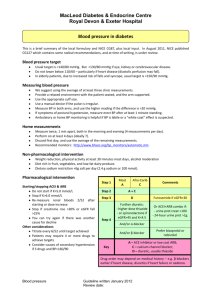
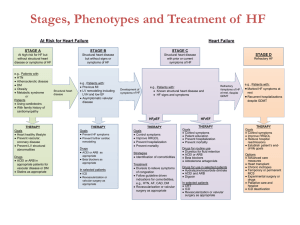
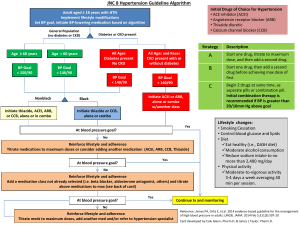
Blood Pressure Control Pharmacotherapy

Blood Pressure Control – Pharmacotherapy
Source DiGP/HSE/UCC Diabetes in Primary Care Conference 26
th
Sept 2012
Pharmacotherapy
Medication type/classifications Advantages of this medication
First line therapy -
ACE Inhibitors (ACEI)
Vasodilators
Effective blood pressure lowering agents
Reno-protective effect
Reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
Long term data available for its efficacy
Potential side effects and/or notes of caution when choosing this medication
Cough (switch to ARB)
Angioedema
Hyperkalaemia
If prescribing in patients with renal failure – check U&E 2 weeks after starting
Caution in patients with renal artery stenosis
Teratogenic – do not use in patients planning pregnancy
Hyperkalaemia
If prescribing in patients with renal failure – check U&E 2 weeks after starting
Caution in patients with renal artery stenosis
First line therapy - Angiotensin
Receptor Blockers (ARB)
Effective blood pressure lowering agents
Vasodilators Reno-protective effect
Reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
Long term data available for its efficacy
Second line therapy – Calcium
Channel Blocker
Vasodilators
Second line therapy –
Diuretic therapy (thiazide diuretic)
Diuretic
Natriuresis
Effective blood pressure lowering agents
Reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
Long term data available for its efficacy
Effective blood pressure lowering agents
Reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
Long term data available for its efficacy
Leg oedema
Constipation
Hyponatraemia
Dehydration
Gout
Hyperkalaemia
Avoid high dose thiazide diuretics such as bendrofluazide 5mg as this dose is associated with hyperglycaemia
Caution in elderly patients with low BMI
– increased risk of hyponatraemia
Medication type/classifications Advantages of this medication
Third Line Therapy* Effective blood pressure lowering agents
Beta- Blockers
Reduce heart rate
Reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality
Reduce myocardial contractility
Long term data available for its efficacy
*Cardio-selective beta blockers should be used
*Beta-blockers should be used as first line BP agents in patients with
co-existing angina
Lowers blood pressure Fourth Line Therapy
Aldosterone antagonist e.g. eplerenone or spironolactone
Diuretic
Block the action of aldosterone
Fourth Line Therapy – Alpha
Blocker e,g, doxazosin XL
Vasodilator
Lower Blood Pressure
Safe to prescribe in renal failure
Potential side effects and/or notes of caution when choosing this medication
Bradycardia
Fatigue
Cold peripheries
Dizziness
Hyperkalaemia
Dehydration
Hyponatraemia
Gynaecomastia with spironolactone only
Caution: high risk of hyperkalaemia if used in combination with ACEI or ARB
Dizziness
Postural hypotension
Increased urinary frequency
Source: National Diabetes Working Group
Notes re Treatment of Hypertension:
The renin antagonist (alsikerin) has recently been associated with a high risk of hyperkalaemia and increased risk of non-fatal stroke in patients with diabetes and so is currently not recommended as a routine blood pressure treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes.
Combination treatment of an ACEI and ARB is associated with a high risk of hyperkalaemia and increased risk of renal dysfunction and therefore combination therapy of an ACEI or ARB should be used with caution and under the supervision of a specialist.
In patients of Afro-Caribbean descent first line treatment for Blood Pressure is an ACEI in combination with a
Calcium Channel Blocker or a thiazide diuretic (do not use an ACEI on its own)
Patients with type 2 diabetes frequently have refractory or resistant hypertension despite the use of 3 or 4 blood pressure agents. If this is the case with a patient then seek expert advice from a consultant endocrinologist as per national model of care.
The following are treatment algorithms to help guide you in the medication management of Blood Pressure in Type 2 diabetes. All treatment should again be given in conjunction with advice on diet, reduced alcohol intake, exercise and weight loss where appropriate.
Treatment of Patients with High Blood Pressure and Type 2 Diabetes
See Options 1, 2 & 3. Choose Option 3 in patients with angina or following MI
Option 1
Add Calcium Channel Blocker
Add Thiazide Diuretic
(combination tablets with
ACEI & ARB available)
Add Beta Blocker
Start ACE Inhibitor
( If cough or other side effects on ACEI switch to Angiotensin
Receptor Blocker)
Blood Pressure remains above target then introduce extra BP lowering medications in a step-wise fashion.
Option 2
Add thiazide diuretic
(combination tablets with
ACEI & ARB available)
Add Calcium Channel Blocker
Add Beta Blocker
Option 3
Patients with angina or post-MI
Add beta blocker
Add Calcium Channel Blocker
Add thiazide diuretic
(combination tablets with
ACEI & ARB available)
Source: National Diabetes
Working Group
Ask for expert opinion
Consider addition of
1. Alpha-Blocker or
2. Aldosterone Anatagonist or
3. Use of combination ACEI or ARB