Meiosis Notes
advertisement

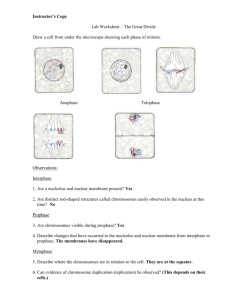
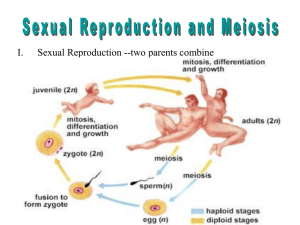
Meiosis Notes Go to the following website: http://goo.gl/OiN0m Introduction ______________ reproduction requires meiosis. _____________ is a process in which a _________ cell divides to produce cells with _____ the genetic material of the parent. NOTE (This is not on the website. This is extra information provided by the teacher): Haploid cells contain only half of the number of chromosomes needed to make an organism. The most common type of haploid cell is a gamete or sex cell (sperm or egg). A diploid cell has a whole set of chromosomes. A diploid cell is created when a sperm fertilizes an egg creating a zygote (diploid cell). In humans, a diploid cell (zygote) contains 46 chromosomes. If a haploid cell contains only half the number of chromosomes, how many will it have? ______ A diploid _________ cell divides to make _____ haploid cells. In sexual reproduction, ___________ gametes from two individuals then combine to produce a diploid ____________. Offspring resulting from _________ reproduction is genetically ____________ from both parents. Interphase DNA ______________ takes place during interphase. Chromosomes are not __________ during this phase. _____________ consists of two cell divisions – meiosis I and ___. Prophase I ___________ condenses into discrete chromosomes. Two centrosomes form the __________ spindle and migrate to opposites poles. The diploid cell contains _______________ chromosomes which pair up later. One set of chromosomes is ___________ (female) derived while the other is _________ (male) derived. The pairing of maternal and paternal chromosomes is called ____________. During this phase, the _________ envelope breaks down. Late in prophase I, the _____________ chromosomes exchange genetic material, as indicated by __________________. The chromosomes cross over at points called ________________. ______________ chromosomes consist of both maternally and paternally-derived _____. ________________ attach to the chromosomes, directing them to the _________ plate. Draw a representation of crossing over: Metaphase I _____________ chromosomes have lined up on the ______________ plate in a pair-wise fashion, with one ____________ on either side of the plate. Note that the chromosomes assort _______________. For example, the maternal chromosomes align randomly, not necessarily on the same side of the plate. Anaphase I Chromosomes from each pair move to _________ poles of the cell. The ___________ of the chromosomes do not divide, so each chromosomes still consists of two sister ____________, which now may not be genetically identical due to ________________. Telophase I Chromosomes ___________, nuclear membranes _________, and the _________ divides in a process called _______________. A short interphase period occurs called ___________. Note that DNA replication does not occur during this period. Prophase II ______________ again condenses into discrete chromosomes. There are now only a _________ number of chromosomes per cell. Each chromosome consists of two _________ joined together by a _____________. Metaphase II Chromosomes have lined up at the ___________ plate. ___________________ from opposite poles attach to each sister ___________ of a chromosome. Anaphase II The centromeres ___________, and both chromatids become ______________ chromosomes and move to the opposite poles of the cell. Telophase II Chromosomes again ____________ and nuclear ___________ reform. Depending on the species, _______________ may occur. Conclusion Meiosis and sexual reproduction produce genetic ____________. When a ________ cell divides by meiosis to produce gametes, each of the four daughter cells is genetically _________. The uniqueness arises in part from the _____________ assortment of chromosomes in meiosis. Through independent assortment each ____________ cell randomly receives either a _________ derived homolog or the ____________ derived homolog from each chromosome pair. In addition, the process of ___________ over produces chromosomes that have unique combinations of paternally and maternally derived regions. This shuffling of the __________ material produces genetically unique __________, each of which can fuse with another unique gamete during _____________ to produce a unique _______________ of the next generation.