Option D topic outline
advertisement

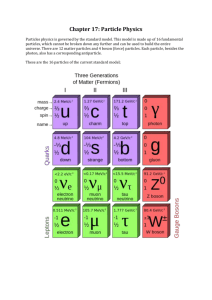
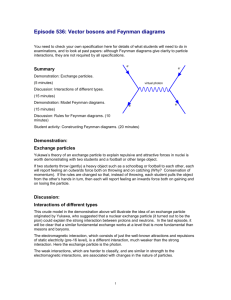
Topic Outline: Option D—Relativity and Particle Physics D1: Introduction to relativity Statement Assessment Statement Number Frames of Reference D.1.1 Describe what is meant by a frame of reference. D.1.2 Describe what is meant by a Galilean transformation Solve problems involving relative velocities using the Galilean transformation D.1.3 equations Obj 2 2 3 D2: concepts and postulates of special relativity Statement Number D.2.1 D.2.2 D.2.3 Assessment Statement Describe what is meant by an inertial frame of reference State the two postulates of the special theory of relativity Discuss the concept of simultaneity Obj 2 1 3 D3: Relativistic kinematics Statement Assessment Statement Number Time Dilation D.3.1 Describe the concept of a light clock D.3.2 Define proper time interval D.3.3 Derive the time dilation formula Sketch and annotate a graph showing the variation with relative velocity of the D.3.4 Lorentz factor D.3.5 Solve problems involving time dilation Length Contraction D.3.6 Define proper length D.3.7 Describe the phenomenon of length contraction D.3.8 Solve problems involving length contraction Obj 2 1 3 3 1 2 3 D4: Particles and interactions Statement Assessment Statement Number Description and classification of particles D.4.1 State what is meant by an elementary particle D.4.2 Identify elementary particles D.4.3 Describe particles in terms of mass and various quantum numbers D.4.4 Classify particles according to spin D.4.5 State what is meant by an antiparticle D.4.6 State the Pauli exclusion principle Fundamental interactions D.4.7 List the fundamental interactions D.4.8 Describe the fundamental interactions in terms of exchange particles Discuss the uncertainty principle for time and energy in the context of particle D.4.9 creation Obj 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 3 Feynman diagrams D.4.10 Describe what is meant by a Feynman diagram Discuss how a Feynman diagram may be used to calculate probabilities for D.4.11 fundamental processes D.4.12 Describe what is meant by virtual particles Apply the formula for the range R for interactions involving the exchange of a D.4.13 particle D.4.14 Describe pair annihilation and pair production through Feynman diagrams D.4.15 Predict particle processes using Feynman diagrams 2 3 2 2 2 3 D5: Quarks Statement Number D.5.1 D.5.2 D.5.3 D.5.4 D.5.5 D.5.6 D.5.7 D.5.8 D.5.9 D.5.10 Assessment Statement Obj List the six types of quark State the content, in terms of quarks and antiquarks, of hadrons (that is, baryons and mesons) State the quark content of the proton and the neutron Define baryon number and apply the law of conservation of baryon number Deduce the spin structure of hadrons (that is, baryons and mesons) Explain the need for color in forming bound states of quarks State the color of quarks and gluons Outline the concept of strangeness Discuss quark confinement Discuss the interaction that binds nucleons in terms of the color force between quarks. 1 1 1 2 3 3 1 2 3 3


![Midterm Exam Part I: Short Answer [50 points] Name: ____________________](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/014712924_1-7154945e04adb3086d9cd10402277a11-300x300.png)