AP Psychology
advertisement
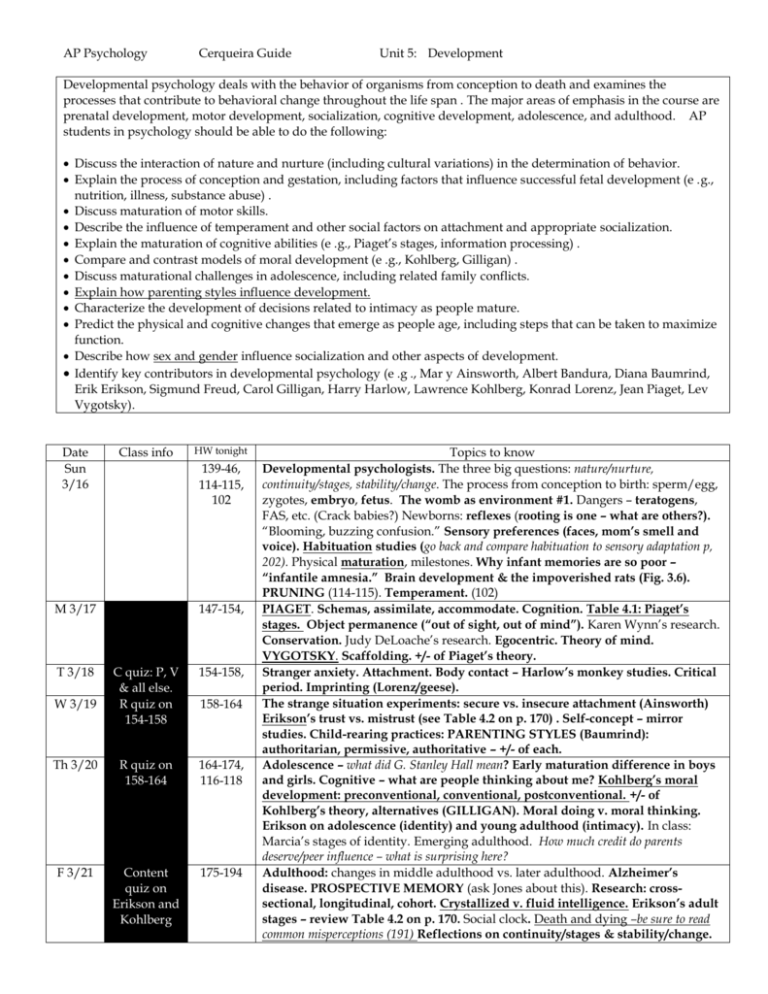
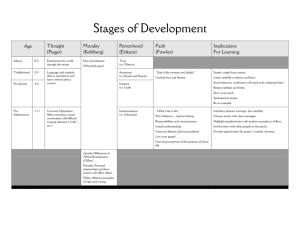
AP Psychology Cerqueira Guide Unit 5: Development Developmental psychology deals with the behavior of organisms from conception to death and examines the processes that contribute to behavioral change throughout the life span . The major areas of emphasis in the course are prenatal development, motor development, socialization, cognitive development, adolescence, and adulthood. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: Discuss the interaction of nature and nurture (including cultural variations) in the determination of behavior. Explain the process of conception and gestation, including factors that influence successful fetal development (e .g., nutrition, illness, substance abuse) . Discuss maturation of motor skills. Describe the influence of temperament and other social factors on attachment and appropriate socialization. Explain the maturation of cognitive abilities (e .g., Piaget’s stages, information processing) . Compare and contrast models of moral development (e .g., Kohlberg, Gilligan) . Discuss maturational challenges in adolescence, including related family conflicts. Explain how parenting styles influence development. Characterize the development of decisions related to intimacy as people mature. Predict the physical and cognitive changes that emerge as people age, including steps that can be taken to maximize function. Describe how sex and gender influence socialization and other aspects of development. Identify key contributors in developmental psychology (e .g ., Mar y Ainsworth, Albert Bandura, Diana Baumrind, Erik Erikson, Sigmund Freud, Carol Gilligan, Harry Harlow, Lawrence Kohlberg, Konrad Lorenz, Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky). Date Sun 3/16 Class info 139-46, 114-115, 102 M 3/17 T 3/18 HW tonight 147-154, C quiz: P, V & all else. R quiz on 154-158 154-158, Th 3/20 R quiz on 158-164 164-174, 116-118 F 3/21 Content quiz on Erikson and Kohlberg 175-194 W 3/19 158-164 Topics to know Developmental psychologists. The three big questions: nature/nurture, continuity/stages, stability/change. The process from conception to birth: sperm/egg, zygotes, embryo, fetus. The womb as environment #1. Dangers – teratogens, FAS, etc. (Crack babies?) Newborns: reflexes (rooting is one – what are others?). “Blooming, buzzing confusion.” Sensory preferences (faces, mom’s smell and voice). Habituation studies (go back and compare habituation to sensory adaptation p, 202). Physical maturation, milestones. Why infant memories are so poor – “infantile amnesia.” Brain development & the impoverished rats (Fig. 3.6). PRUNING (114-115). Temperament. (102) PIAGET. Schemas, assimilate, accommodate. Cognition. Table 4.1: Piaget’s stages. Object permanence (“out of sight, out of mind”). Karen Wynn’s research. Conservation. Judy DeLoache’s research. Egocentric. Theory of mind. VYGOTSKY. Scaffolding. +/- of Piaget’s theory. Stranger anxiety. Attachment. Body contact – Harlow’s monkey studies. Critical period. Imprinting (Lorenz/geese). The strange situation experiments: secure vs. insecure attachment (Ainsworth) Erikson’s trust vs. mistrust (see Table 4.2 on p. 170) . Self-concept – mirror studies. Child-rearing practices: PARENTING STYLES (Baumrind): authoritarian, permissive, authoritative – +/- of each. Adolescence – what did G. Stanley Hall mean? Early maturation difference in boys and girls. Cognitive – what are people thinking about me? Kohlberg’s moral development: preconventional, conventional, postconventional. +/- of Kohlberg’s theory, alternatives (GILLIGAN). Moral doing v. moral thinking. Erikson on adolescence (identity) and young adulthood (intimacy). In class: Marcia’s stages of identity. Emerging adulthood. How much credit do parents deserve/peer influence – what is surprising here? Adulthood: changes in middle adulthood vs. later adulthood. Alzheimer’s disease. PROSPECTIVE MEMORY (ask Jones about this). Research: crosssectional, longitudinal, cohort. Crystallized v. fluid intelligence. Erikson’s adult stages – review Table 4.2 on p. 170. Social clock. Death and dying –be sure to read common misperceptions (191) Reflections on continuity/stages & stability/change. M 3/24 T 3/25 Rev. Quiz Review! Test, Unit 5 with an FRQ