Chapter 9 Fundametals of Genetics outline
advertisement

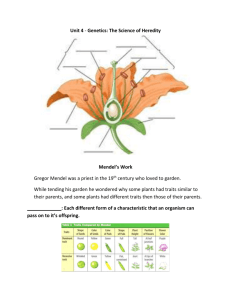
FG 1 Fundamentals of Genetics Enduring Understanding Chromosomes contain genes in which heredity information is stored. Genetic variation is essential to biodiversity and the stability of a population. Genetic variation is the result of the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment. One or more genes can determine an inherited trait of an individual and a single gene can influence more than one trait. Random mutations in DNA may be caused by the environment and are another source of genetic variation. Essential Questions What causes different traits throughout different generations of an organism? What causes variation within a population? I. Mendel’s Legacy *Genetics branch of biology that studies how characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring *Gregor Mendel Austrian monk father of genetics experimented w/ garden peas A. GREGOR MENDEL * Heredity the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspringused garden peas *Used math (statistics) and science 1) Mendel’s Garden Peas a) Traits(characteristics)mendel(7)plant height, seed color……. b)Found Variations tall plant seedsgive tall and short plants B. MENDEL’S EXPERIMENTS FG 2 1) Pure(for a trait) then plant always produces that trait 2) Strain plants that are pure for a specific trait C. MENDEL’S RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS 1) Recessive and Dominate Traits a) Dominate allele masks or dominates other alleles b) Recessive allele trait that does not appear (masked)(is not seen in phenotype) 2) The Law of Segregation a) Paired alleles separate during meiosis b) Gametes only have 1 allele from each pair c) Gamete + Gamete = fertilized egg(zygote) (Offspring)2 alleles controlling a specific trait d) The Law of Segregationa pair of alleles is segregated (separated) during the formation of gametes 3) The Law of Independent Assortment a) Law of Independent Assortment Alleles for different traits are distributed to gametes independently (the distribution of one trait does not influence the distribution of another) Mendel’s Principles Unit Characters (Factors) Every characteristic is controlled by at least two factors, or genes (alleles), one coming from each parent. Dominance and Recessiveness One allele masks the other allele of the pair, preventing it from being expressed. Segregation The two alleles for a trait separate during sperm and egg formation (meiosis). FG 3 Independent Assortment Alleles for different traits are independently distributed to reproductive cells. Explanations should include: Characteristics are caused by genes, which occur in pairs. First generation (F1) organisms are all dominant, the recessive trait shows up in second generation (F2). In the formation of a sex cell or gamete, the gene separates or segregates out independently so that each daughter cell will contain only one gene from the parent: e.g., in the pea plant gene for tallness (T) or shortness (t), Tt will be segregated out during meiosis as T or t. Differentiate between probability and independent assortment. In independent assortment. Chance and Probability The probability of two or more independent events occurring together is the product of the individual probabilities of such an event occurring alone. This Product Rule is shown for two events in the equation 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4. The principle may be visualized by use of a Punnett Square in a test cross or known cross. According to Mendelian genetics, what is the probability of having any one child be a boy or a girl? (1 in 2) According to the Product Rule, what is the probability of a family having five boys or five girls in a row? (½ x ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ = 1/32) D. CHROMOSOMES AND GENES *Molecular genetics study of the structure and function of chromosomes and genes *Chromosomes occur in pairsgenes occur in pairsalleles (Tt)(TT)(tt)…T is an allele…t is an allelealternative forms of a gene FG 4 II. Genetic Crosses A. GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE 1) Genotype the genetic makeup of an organism consists of the alleles the organism inherits(PP) or (Pp) are 2 different genotypes…but both give a purple flower 2) Phenotype the appearance of an organism as a result of its genotype 3) Homozygous both alleles are alike(TT) or (tt) 4) Heterozygous both alleles are different (Tt) B. PREDICTING RESULTS OF MONOHYBRID CROSSES *Monohybrid crossa cross between 2 individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits (TT) x (Tt) *Punnett Square diagram to assist in predicting The probability that certain traits will be inherited by offspring *Punnett Square diagram to assist in predicting The probability that certain traits will be inherited by Offspring FG 5 *Genotypic ratio 1BB:2Bb:1bb *Phenotypic ratio 3black:1brown *Complete dominanceP totally dominates p… *Incomplete dominance2 or more alleles influence Phenotype…EX, FOUR O’CLOCKS (flower) *CodominanceBoth alleles are expressed in heterozygous Offspring no allele is dominate or recessive