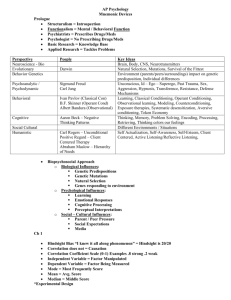
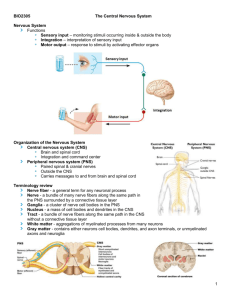
AP Exam Terms to Know
advertisement
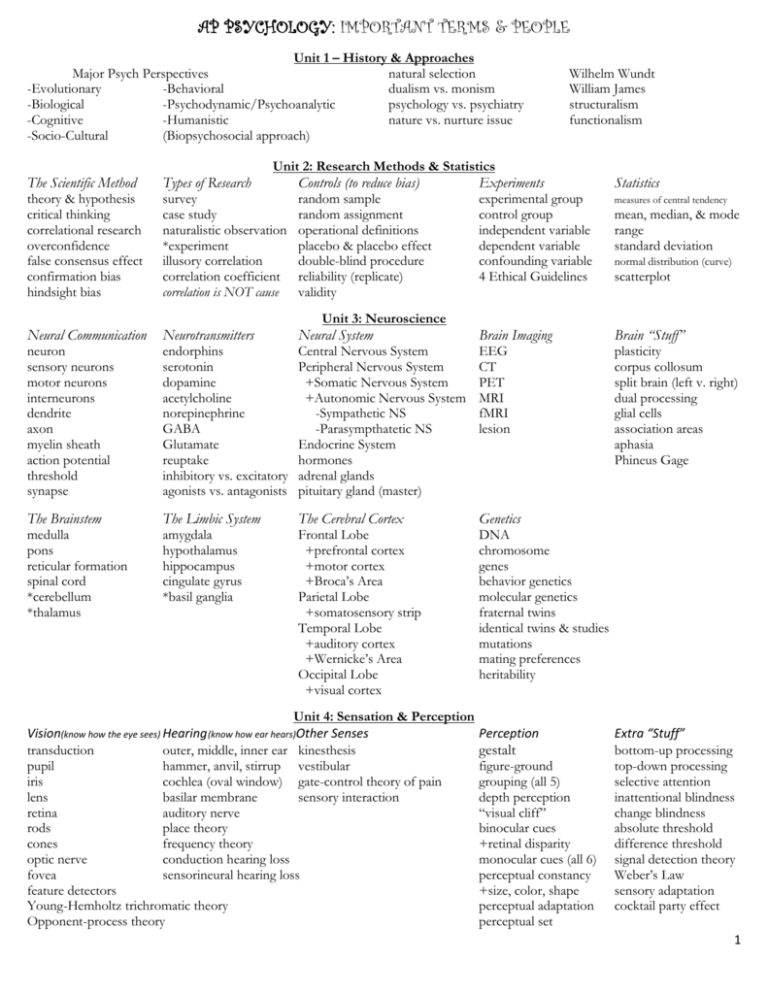
AP PSYCHOLOGY: IMPORTANT TERMS & PEOPLE Unit 1 – History & Approaches Major Psych Perspectives natural selection -Evolutionary -Behavioral dualism vs. monism -Biological -Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic psychology vs. psychiatry -Cognitive -Humanistic nature vs. nurture issue -Socio-Cultural (Biopsychosocial approach) The Scientific Method theory & hypothesis critical thinking correlational research overconfidence false consensus effect confirmation bias hindsight bias Types of Research Wilhelm Wundt William James structuralism functionalism Unit 2: Research Methods & Statistics Controls (to reduce bias) Experiments random sample random assignment operational definitions placebo & placebo effect double-blind procedure reliability (replicate) validity Neural Communication Neurotransmitters Neural System Brain Imaging Brain “Stuff” neuron sensory neurons motor neurons interneurons dendrite axon myelin sheath action potential threshold synapse endorphins serotonin dopamine acetylcholine norepinephrine GABA Glutamate reuptake inhibitory vs. excitatory agonists vs. antagonists Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System +Somatic Nervous System +Autonomic Nervous System -Sympathetic NS -Parasympthatetic NS Endocrine System hormones adrenal glands pituitary gland (master) EEG CT PET MRI fMRI lesion plasticity corpus collosum split brain (left v. right) dual processing glial cells association areas aphasia Phineus Gage The Brainstem The Limbic System The Cerebral Cortex Genetics medulla pons reticular formation spinal cord *cerebellum *thalamus amygdala hypothalamus hippocampus cingulate gyrus *basil ganglia Frontal Lobe +prefrontal cortex +motor cortex +Broca’s Area Parietal Lobe +somatosensory strip Temporal Lobe +auditory cortex +Wernicke’s Area Occipital Lobe +visual cortex DNA chromosome genes behavior genetics molecular genetics fraternal twins identical twins & studies mutations mating preferences heritability Unit 3: Neuroscience Unit 4: Sensation & Perception Vision(know how the eye sees) Hearing (know how ear hears)Other Senses transduction outer, middle, inner ear kinesthesis pupil hammer, anvil, stirrup vestibular iris cochlea (oval window) gate-control theory of pain lens basilar membrane sensory interaction retina auditory nerve rods place theory cones frequency theory optic nerve conduction hearing loss fovea sensorineural hearing loss feature detectors Young-Hemholtz trichromatic theory Opponent-process theory experimental group control group independent variable dependent variable confounding variable 4 Ethical Guidelines Statistics survey case study naturalistic observation *experiment illusory correlation correlation coefficient correlation is NOT cause Perception gestalt figure-ground grouping (all 5) depth perception “visual cliff” binocular cues +retinal disparity monocular cues (all 6) perceptual constancy +size, color, shape perceptual adaptation perceptual set measures of central tendency mean, median, & mode range standard deviation normal distribution (curve) scatterplot Extra “Stuff” bottom-up processing top-down processing selective attention inattentional blindness change blindness absolute threshold difference threshold signal detection theory Weber’s Law sensory adaptation cocktail party effect 1 drive-reduction theory homeostasis optimum arousal instinct incentives hierarchy of needs intrinsic motivation extrinsic motivation set point basal metabolic rate anorexia nervosa bulimia nervosa binge-eating Unit 5: Motivation & Emotion sexual response cycle +4 stages estrogen testosterone Unit 6: Learning Behaviorism Operant Conditioning associative learning law of effect (Thorndike) Classical Conditioning shaping unconditioned response (UCR) reinforcer unconditioned stimulus (US) positive reinforcement conditioned response (CR) negative reinforcement conditioned stimulus (CS) punishment (pos & neg) acquisition primary v. secondary reinforcers extinction B.F. Skinner spontaneous recovery generalization discrimination Pavlov’s experiments Watson & Little Albert Storage Cognition Thinking Language concepts prototypes algorithms availability heuristics representative heuristics functional fixedness mental set belief perseverance framing Reinforcement Schedules Other Types of Learning Fixed-Ratio Variable-Ratio Fixed-Interval Variable-Interval learned helplessness (Seligman) taste aversion (Garcia) latent learning cognitive map insight learning observational learning (Bandura) modeling mirror neurons Unit 7: Cognition Memory Encoding effortful processing rehearsal spacing effect serial position effect semantic encoding visual encoding -imagery -mnemonic devices -chunking James-Lange theory Cannon-Bard theory Schacter-Singer two-factor theory catharsis feel good-do good phenomenon adaptation level phenomenon relative deprivation general adaptation syndrome Type A & B personality sensory memory iconic memory echoic memory long-term potentiation short-term memory working memory long-term memory flashbulb memories implicit memories explicit memories Retrieval recall recognition priming déjà vu mood-congruent Forgetting 7 sins of forgetting encoding failure storage decay proactive interference retroactive interference misinformation effect source amnesia Other Fun to Remember eyewitness testimony Elizabeth Loftus improving memory (7) phoneme morpheme grammar semantics syntax stages of language dev. linguistic determinism general intelligence (g) savant syndrome emotional intelligence mental age Unit 8: Testing & Individual Differences Stanford-Binet test standardization intelligence quotient (IQ-know how to determine) content validity achievement tests predictive validity aptitude tests intellectual disability WAIS Down Syndrome 2 Prenatal & Newborn zygote embryo fetus fetal alcohol syndrome teratogens placenta habituation maturation Piaget’s Cognitive Dev. Unit 9: Development Social Development Extra “Stuff” Know This!!! schema Erickson’s 8 Stages parenting styles Kohlberg’s Moral Dev. assimilation attachment +authoritarian +3 stages accommodation critical period +authoritative cross-sectional studies Sensorimotor Stage imprinting +permissive longitudinal studies +object permanence Ainsworth’s attachment studies puberty stages of grief +stranger anxiety Harlow’s monkeys primary sex characteristics Preoperational Stage secondary sex characteristics +egocentrism Concrete Operational Stage +conservation Formal Operational Stage Unit 10: Personality Sigmund Freud defense mechanisms Carl Jung terror-management theory psychoanalysis defense mechanisms collective unconscious self-actualization unconscious +repression projective tests Abraham Maslow id +regression Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) self-concept ego +reaction formation Roschach inkblot test Carl Rogers superego +projection personality inventory internal locus of control free association +rationalization +MMPI external locus of control psychosexual stages +displacement Big 5 Factors (CANOE) self-serving bias fixation +sublimation reciprocal determinism spotlight effect Oedipus complex +denial Unit 11: Abnormal Psychology DSM-IV Dissociative Disorders Schizophrenia Somatoform Disorders Anxiety Disorders +dissociative identity dis. Delusions +hypochondriasis +generalized anxiety dis. +dissociative amnesia hallucinations +conversion disorder +panic disorder +dissociative fugue disorganized thinking Personality Disorders +ocd Mood Disorders paranoid antisocial, narcissistic, borderline, histrionic +phobias +major depressive dis. catatonic schizoid, schizotypal, paranoid +ptsd +bipolar disorder avoidant, dependent, ocd -mania Unit 12: Treatment Dorothea Dix insight therapies Behavior Therapy Cognitive Therapy psychopharmacology eclectic approach client-centered therapy counterconditioning Aaron Beck biomedical therapy Psychotherapy active listening exposure therapy Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy antipsychotic drugs psychoanalysis rational-emotive therapy systematic desensitization group/family therapy antianxiety drugs resistance aversive conditioning EMDR antidepressants interpretation token economy light exposure therapy mood-stabilizers transference ECT Unit 13: Social Psychology fundamental attribution error conformity social facilitation prejudice central route persuasion Solomon Asch social loafing discrimination peripheral route persuasion normative social influence deindividuation stereotypes foot-in-the-door phenomenon informational social influence group polarization ingroup/outgroup door-in-the-face phenomenon obedience studies groupthink scapegoat theory cognitive dissonance theory Milgram experiment bystander effect just-world phenomenon mere-exposure effect Stanford Prison Experiment social exchange theory aggression self-fulfilling prophecy social responsibility norm frustration-aggression principle Unit 14: Consciousness Consciousness alpha waves dream hypnosis (& controversy) psychoactive drugs circadian rhythm delta waves hallucinations posthypnotic suggestions depressants REM sleep REM rebound narcolepsy night terrors stimulants NREM sleep sleep apnea manifest content hallucinogens latent content effects of drug use 3 4