Ch 8 & 9 Study Guide
advertisement

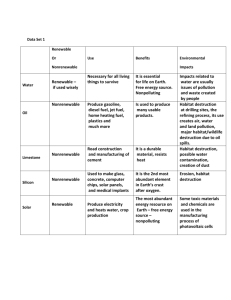
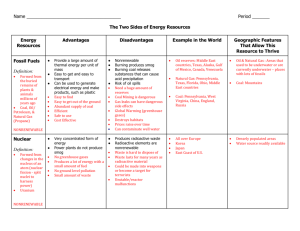
Ch 8 & 9 Study Guide pH - is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution/liquid Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline. Pure water has a pH very close to 7. renewable resource - – Sunlight, wind, water – resource that can be replaced through natural processes of the Earth. environmental science - The study of natural processes in the environment and how humans can affect them fishery - An area with a large population of valuable ocean organisms selective cutting - Cutting down only some trees in a forest, leaving a mix of tree sizes and species standing biodiversity - The number of different species in an area invasive species – A non-native(not indigenous) that has invaded or been introduced to an ecosystem and has changed the ecosystem in some way. Examples – Pacu, Burmese Python, Asian (Silver) carp exotic species – Species that are introduced into an area that can outcompete and damage native species. Examples – Pacu, Burmese Python, Asian (Silver) carp extinct - If all members of a species disappear from Earth captive breeding - The mating of California condors in zoos habitat destruction - The loss of a natural habitat ecological footprint – The amount of land and water Exponential growth - When a population grows at an ever-increasing rate. population growth – Advances in medicine and technology have improved human health and allowed for exponential human population growth. Certified wood- Certified wood comes from trees grown in sustainable forests. nonrenewable resource - Metals and minerals, as well as fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are resources that cannot be replaced once they have been used up. land reclamation - The process of restoring an area of land to a more natural, productive state agriculture - Using land to grow food crops sanitary landfill - A type of landfill designed to hold municipal solid waste safely radioactive waste – a type of hazardous waste that gives off radiation nutrient depletion - Farmers may leave fields unplanted or plant alternate crops to reduce this. carbon monoxide - An indoor air pollutant is a colorless, odorless gas that forms when wood, coal, oil, or gas are incompletely burned CFCs - One group of gases that is responsible for destroying ozone in the ozone layer % of earth’s water salt and fresh - Most of Earth's water (about 97 percent) is salt water in the oceans. 3% of that water is fresh water and most is stored in ice and as groundwater. sulfur oxides (sulfur dioxide) One of the acids in acid rain forms when water combines with sulfur oxides strip mining - A type of land use called mining involves the removal of nonrenewable resources from the land. Removing a strip of land to obtain minerals is strip mining. Leachate - Rainwater falling on a dump or landfill dissolves chemicals from wastes and forms a polluted liquid Sewage - The water and human wastes that are washed down sinks, toilets, and showers soil layers – See chart on page 358 Short Answer 1. Explain how renewable resources and nonrenewable resources are different. Give two examples of each. Renewable resources are either always available or are naturally replaced in a relatively short time; whereas, nonrenewable resources are not replaced in a useful time frame. Examples of renewable resources include sunlight and trees. Examples of nonrenewable resources include coal and oil. 2. Describe how setting fishing limits can help protect fish species. Laws that limit the number or size of fish that can be caught can ensure that young fish live long enough to reproduce and that all of the adult fish in a species aren’t caught 3. All environmental decisions require weighing the costs and benefits of different solutions to environmental problems. Choose one environmental issue that we have read about or learned about in class and give examples of some costs and benefits of finding a solution to that problem or issue.