Chapter 10 Review The Senses General Senses (pp. 262
advertisement

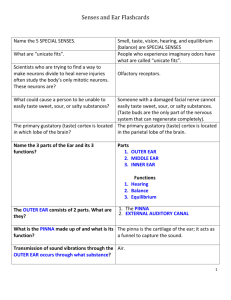
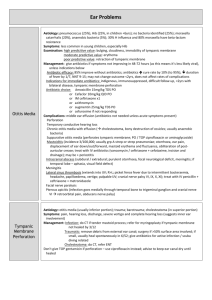
Chapter 10 Review The Senses I. General Senses (pp. 262-265) 1. Complete the table of GENERAL senses. (Mechano-)Receptor Sensation Free Nerve Ending (nociceptor) Meissner’s Corpuscle Pacinian Corpuscle Merkel Disk Ruffini’s Corpuscle Hair Root Plexus 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. II. Thermoreceptors are triggered by ________________________________________. Photoreceptors are triggered by __________________________________________. Chemoreceptors are triggered by _________________________________________. Mechanoreceptors are triggered by _______________________________________. What is the difference between referred pain and phantom pain? Special Senses (p. 265) Complete the table of SPECIAL senses. General Term Medical Term Smelling Seeing Hearing & Balance Tasting Organ Used III. Sense of Smell (pp. 266-267) 1. The sense of smell supplements the sense of _________________________________. 2. Odors in the air stimulate ________________ receptors which signal the ____________ nerve (I) which carries the message to the ___________________ lobe of the cerebrum. IV. Sense of Taste (pp. 267-268) 1. How is saliva used in the perception of taste? 2. Sketch the tongue and label the four primary regions with the taste sensation it triggers. 3. The sense of taste is interpreted by the _______________________ of the cerebrum. V. Sense of Hearing (pp. 269-273) 1. The external ear is called the _______________________ and functions to trap and funnel _____________________ waves. 2. The ear drum, or _________________________, is what separates the outer ear from the middle ear. 3. List the three ossicles of the middle ear. 4. The inner ear consists of the _______________________ for hearing and the ____________________ & ______________________ for equilibrium. 5. Sound is interpreted by the _______________________ of the brain. 6. ____________ is the unit for sound frequency (pitch) and _____________ is the unit for sound intensity (loudness). 7. Swimmer’s ear, or otitis ______________________ is an infection of the outer ear, whereas, otitis _____________________ is an infection of the middle ear. VI. Sense of Equilibrium (pp. 273-276) 1. Distinguish between static and dynamic equilibrium. 2. Hairs called ______________________ in the inner ear are responsible for balance. VII. Sense of Sight (pp. 276-284) 1. The medical doctor (M.D.) of the eye is called an ___________________________. 2. The clear, protective coating on the surface of the eye that covers the cornea and lines the eyelids is called the ________________________________. 3. What is the difference between rods and cones? 4. The sense of sight is interpreted by the _______________________ of the cerebrum. 5. Near-sightedness is called ____________________, whereas, far-sightedness is called _________________. 6. _____________________ is “old-sightedness” that is far-sightedness that occurs with natural aging of the eye. 7. Label the following structures on the illustration below: iris, cornea, ciliary body, vitreous humor (posterior chamber), aqueous humor (anterior chamber), sclera, optic disk, optic nerve, retina, pupil, lens VIII. Clinical focus questions 1. What is glaucoma and how is it treated? 2. What are cataracts and how are they treated? 3. What is astigmatism and how is it treated?