Heart notes and Study Guide
advertisement

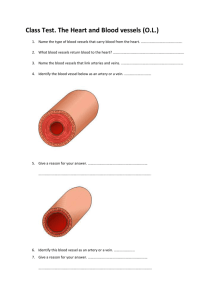
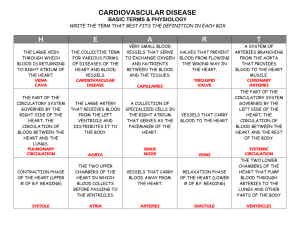
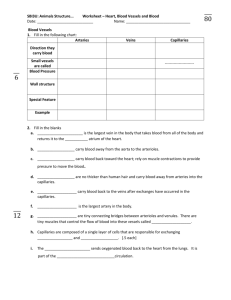
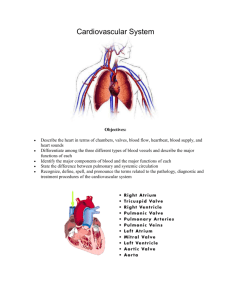
Name:________________________________________________________Date:_______________Block:____________ The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Page 408 Why the Blood Circulates: Your heart pumps blood to your body’s cells ____________ hours a day. Your heart accomplishes these important tasks: How Blood Circulation Works The cardiovascular system depends on the heart and its system of blood vessels to deliver ____________________________ throughout the body. You have over ___________________ miles of blood vessels in your body. Your circulatory system works with your respiratory system to supply necessary nutrients and oxygen to all parts of the body. The Heart: Your heart is the _________________________ that makes the cardiovascular system work. Inside the heart are ________________ chambers. The two top chambers are called the _______________________. The two lower chambers are called the ________________________________. A wall of tissue – _____________________________ – separates the four chambers of the heart. Valves between the atria and the ventricles allow blood flow through the chambers. At the top of the right atrium is an area of muscle that acts as a ________________________ for the heart. Electrical impulses stimulate the atria to contract forcing blood into the ventricles. These electrical impulses travel through the heart to an area between the two ventricles. There they stimulate the muscles of the ventricles to contract, pumping blood out of the heart. Pulmonary circulation is the process by which blood moves between the _______________________and __________________________________. Blood that has used up its oxygen and picked up carbon dioxide and wastes receives fresh ______________________________ in the lungs. That blood is _______________________________ through the body, and the process continues on and on. Blood: Blood is the fluid that delivers _________________________, _______________________________, and ______________________________ to the cells and carries away ________________________________. Blood is made up of the following components: 1) _________________________________– the fluid in which other parts of the blood are suspended. Makes up about __________________ percent of the total blood volume. Plasma is mainly water, but also contains ____________________________, ___________________, ____________________, and ____________________________________. 2) Red Blood Cells make up most of the blood. They contain __________________________ which is the oxygen-carrying part of blood. RBC’s job is to carry oxygen to all other parts of the body. 3) _________________________________________ – These cells protect the body against infection. Some white blood cells surround and ingest the organisms that cause disease. Others form _____________________________ that provide immunity against a second attack from that specific disease. Other types of _________________________________________ fight allergic reactions. WBC’s job is to fight diseases. 4) ______________________________________ – are the types of cells in the blood that cause blood clots to form. Platelets collect at a tear and release _______________________________ that when stimulated, they produce small threadlike fibers that trap nearby cells to help form a clot. Platelets job is to clot blood so we don’t bleed to death. All humans have one of the four types of blood: ___________, ___________, _________________, and ______________. Each blood type is determined by the presence of absence of certain substances called _______________________________. A person must receive blood from a person who has the same antigens. People with type O blood are __________________________________ donors because anyone can receive their blood. Blood Vessels: Blood vessels are hollow tubes that carry ___________________________ throughout the body. There are three main types of blood vessels ________________________ , ___________________________ and ____________________________. 1) Arteries – blood vessels that carry _________________________________________ blood away from the heart. Arteries branch into progressively smaller vessels called __________________________________________. Arteries are very elastic and strong to with stand the force of the blood being forced out of the heart 2) _____________________________ – the smallest vessels where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. Capillaries reach almost all body cells. Capillaries near the skin’s surface can also __________________________, allowing ____________________ to escape the body through the _________________________. They can also __________________________ to reduce _____________________ loss if the body temperature drops below normal. 3) ________________________________ – blood vessels that bring blood back to the heart. The walls of veins are ________________________________ and less _________________________ than arteries. Two types of specific veins are below: o ______________________________________ – the largest of veins, these bring deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body back to the right atrium of the heart so the blood can pick up oxygen again. o ______________________________________ - these veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart (specifically to the left atrium). How Lymph Circulation Works – Your Immune System The lymphatic system consists of a network of vessels and tissues that move and filter lymph. Lymph is the ________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________. Like __________________________, lymph contains water and proteins. It also contains fats and specialized ____________________ _____________________________________ called lymphocytes. Like white blood cells in the blood, these cells protect the body against pathogens. Pathogens are _______________________________ _____________________________________________. 1) B cells: B cells multiply when they come in contact with a pathogen. Some B cells produce ______________________________ to fight the pathogen; others create an ___________________________________________ by preventing a second attack of the same disease (this is related to how vaccines work) 2) T cells: There are two main types of T cells, Killer cells and Helper cells. a) ___________________________________ release toxins that prevent infections from spreading. b) __________________________________ activate both the B cells and Killer T cells. They also control the body’s immune system. Lymph is filtered by lymph nodes – _______________________________________________________________ ________________________________________. White blood cells within lymph nodes trap and destroy the pathogens. This is why you get “swollen glands” when you are sick. It indicates that you are infected and your immune system is fighting the microorganisms. Maintaining Your Circulatory Health You can reduce your risk by making the following behaviors a regular habit. Blood Pressure Pressure in the ____________________________ is created when the _____________________________ contract. As blood is forced into the ____________________________, arterial walls stretch under the increased pressure. When the __________________________ relax and refill with blood, arterial pressure ______________________. Blood pressure is ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________, particularly large arteries as it is pumped through the body. The first number (upper number) measures your _______________________________________ – the maximum pressure as your heart contracts to push blood into your arteries. The second number (bottom number) measures your ______________________________________ – the pressure at its lowest point when the ventricles relax. A healthy blood pressure is within a range of below _________________________. Blood pressure above ________________________ is considered high and places a strain on the heart. Disorders of the Heart or Blood Disorders of the cardiovascular system have wide-ranging effects and varying treatments. Congenital Heart Defects – are conditions of the heart that are ________________________________. A __________________________ defect is a hole in the septum that allows oxygenated blood to mix with oxygen-depleted blood. Medication and possibly surgery can sometimes repair the affected portion of the heart. ________________________________________ – is caused by a hole in the heart, or a leaking or malfunctioning valve which does not close properly. ________________________________________ – are enlarged veins formed as a result of the valves in veins not closing tightly enough to prevent backflow of blood. The blood pools in the legs causing pain and discomfort. Hemophilia – ___________________________________________________. Occurs when the blood does not ______________________________ properly. Hemophiliacs must be careful not to bleed to death. _______________________________– A cancer of the white blood cells. are produced excessively and abnormally. This causes the person to be susceptible to ______________________________, ___________________________________________, and possibly __________________________________________. Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation, and _______________________________________ transplants.