Word
advertisement

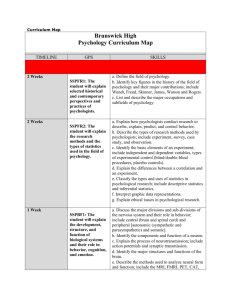
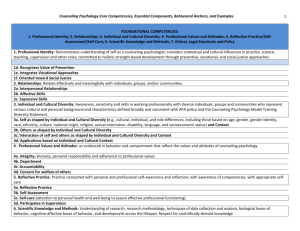
Study Guide Written Comprehensive Exams (Updated Fall 2012) GOAL 1: BROAD AND GENERAL UNDERSTANDING OF THEORETICAL AND CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF PSYCHOLOGY Theories and research related to biological psychology Practical applications of biological psychology Terminology of biological psychology Relationship between biological functioning and typical and atypical behavior Familiarity with the role of psychopharmacology Key concepts in social psychology Social bases of individual and group behavior (self-concept, identity) Key concepts in community psychology Impact of community on family and neighborhood dynamics Social pressures that shape human behavior and experience Major historical developments in psychology Theoretical concepts of cognition Theories of development across the lifespan (Piaget, Kohlberg, Erikson, Vygotsky) Developmentally appropriate practice Personality development from several theoretical perspectives Concepts of vulnerability and resiliency Characteristics and etiology of the major categories of disorders Knowledge of DSM-IV-TR and ECEA rules as related to disorder/disability Prevention and treatment of psychopathology Physical and behavioral characteristics of a variety of severe and low-incidence disabilities Early childhood development related to developmental disabilities GOAL 2: SYSTEMIC AND CONSULTATIVE INTERVENTIONS Various models of consultation (i.e., medical model, behavioral model, ecological model, reciprocal determination model, problem-solving model, mental health consultation, instructional consultation model, ecobehavioral model, Caplan’s mental health model) Rationale for consultation service delivery model Special issues in using consultation in educational/clinical settings (cultural/normative issues in such settings and how to address them) Instructional and curricular modifications for students experiencing academic difficulty Problem-solving process Best practices in providing psychological services to infant/toddlers and their families (consultation services and family-centered services) Consultation to agencies that serve infants/toddlers Basic components of effective and efficient instructional design Teaching practices related to student outcomes Levels of intervention (prevention, secondary, and tertiary models) Empirically supported prevention and intervention across different levels of service Major theories and current approaches to crisis prevention, preparedness, and response, and recovery Essential components of school-based crisis intervention plans Difference between normal reactions to crisis and the symptoms of post-traumatic stress Signs of suicide and how to assess the degree of suicide risk Signs of school-based violence Grief process and grief complications in children GOAL 3: COMPREHENSIVE ASSESSMENT, BOTH FORMAL AND INFORMAL Theories of intelligence Psychometrics as related to test use and interpretation (i.e., reliability, validity, measures of central tendency, indices of variability, correlations) Principles of test construction Test selection (know a variety of intelligence, academic, and other targeted assessments) Curriculum-based approaches for assessing skill level Progress monitoring as related to academic and behavioral skills Assessment of social and emotional development Assessment of adaptive skills Different methods for assessing behavior Use task analysis for basic skills in reading, math, and written language Alternative assessment techniques (including: criterion-referenced assessment, environmental assessment, performance assessment, interviews, behavioral observations, record review, etc.) Curriculum and intervention evaluation in academics Intervention programs for reading, math, and written language Formative and summative evaluation of academic skills Local norms Major models used to evaluate programs in mental health, health, and education Program evaluation design and implementation including: the development of measures, data collection, and analyzing data (qualitative and quantitative) GOAL 4: DIRECT PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES Behavioral theories and their application Behavioral assessment strategies Various interventions, especially as relevant to schools Knowledge of the effect of instruction, curriculum, environment, and the child in developing academic interventions Counseling theories and models Evidence-based practices and treatments Strategies for evaluating counseling outcomes Theoretical perspectives in personality and counseling Supervision models, practices, and processes GOAL 5: CULTURALLY COMPETENT LEGAL, ETHICAL AND PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE History of professional school psychology, including current issues Role and functions of a school psychologist Different models of preparing school psychologists (i.e. scientist-practitioner model) Different methods of service delivery (i.e., Problem Solving/ RTI vs. traditional psychological service) State and federal laws impacting school psychologists NASP and APA Ethical Principles and application to school psychologists Ethical and legal considerations in assessment Legal foundations for service delivery to young children and their families Multicultural issues related to school psychologists Minimizing cultural, linguistic, and socioeconomic bias in assessment Cross-cultural variables that impact the assessment of psychopathology Acculturation Theories of multicultural counseling, theories of identity development, and multicultural competencies Understanding of the terms: cultural self-awareness, cultural social justice, advocacy, and conflict resolution Strategies for eliminating biases, prejudices, and processes of intentional and unintentional oppression and discrimination Effects of racism (including institutional), discrimination, sexism, power, privilege, and oppression Advocacy and public policy as related to multicultural issues Historical and current political climate regarding immigration, poverty, and welfare Biases of commonly used diagnostic tools with multicultural populations Cultural, ethical, economic, legal, and political issues surrounding diversity, equity, and excellence in terms of student learning Societal trends and treatment issues related to working with multicultural and diverse family systems (e.g., families in transition, dual-career couples, blended families, same-sex couples) Age, gender, sexual orientation, ethnicity, language, disability, culture, spirituality, and other factors related to the assessment and evaluation of individuals, groups, and specific populations Note that we assess Goal 6 (Understanding, Using, and Conducting Research) during your Oral Comprehensive Exams.