Modelling Gas Separation in Metal
advertisement
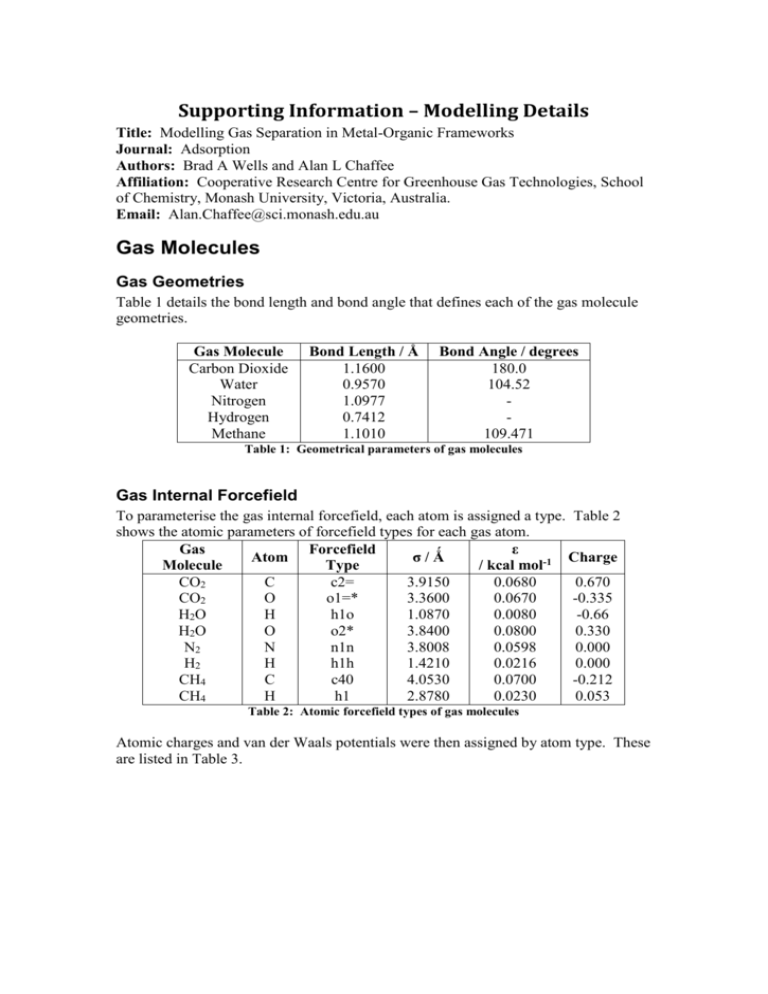
Supporting Information – Modelling Details Title: Modelling Gas Separation in Metal-Organic Frameworks Journal: Adsorption Authors: Brad A Wells and Alan L Chaffee Affiliation: Cooperative Research Centre for Greenhouse Gas Technologies, School of Chemistry, Monash University, Victoria, Australia. Email: Alan.Chaffee@sci.monash.edu.au Gas Molecules Gas Geometries Table 1 details the bond length and bond angle that defines each of the gas molecule geometries. Gas Molecule Carbon Dioxide Water Nitrogen Hydrogen Methane Bond Length / Ǻ 1.1600 0.9570 1.0977 0.7412 1.1010 Bond Angle / degrees 180.0 104.52 109.471 Table 1: Geometrical parameters of gas molecules Gas Internal Forcefield To parameterise the gas internal forcefield, each atom is assigned a type. Table 2 shows the atomic parameters of forcefield types for each gas atom. Gas Forcefield ε Atom σ/Ǻ Charge Molecule Type / kcal mol-1 CO2 C c2= 3.9150 0.0680 0.670 CO2 O o1=* 3.3600 0.0670 -0.335 H2O H h1o 1.0870 0.0080 -0.66 H2O O o2* 3.8400 0.0800 0.330 N2 N n1n 3.8008 0.0598 0.000 H2 H h1h 1.4210 0.0216 0.000 CH4 C c40 4.0530 0.0700 -0.212 CH4 H h1 2.8780 0.0230 0.053 Table 2: Atomic forcefield types of gas molecules Atomic charges and van der Waals potentials were then assigned by atom type. These are listed in Table 3. σ/Ǻ 3.9150 3.3600 1.0870 3.8400 3.8008 1.4210 4.0530 2.8780 Forcefield Type c2= o1=* h1o o2* n1n h1h c40 h1 ε / kcal mol-1 0.0680 0.0670 0.0080 0.0800 0.0598 0.0216 0.0700 0.0230 Charge 0.670 -0.335 -0.66 0.330 0.000 0.000 -0.212 0.053 Table 3: Gas nonbonding potential parameters Bond length energies were modelled with a quartic function of the form 𝑉 = 𝑘2 (𝑟 − 𝑟0 )2 + 𝑘3 (𝑟 − 𝑟0 )3 + 𝑘4 (𝑟 − 𝑟0 )4 (1) The parameters, in angstroms and kcal/mol for each bond are given in Table 4. Type I o1=* h1o n1n h1h c40 Type J c2= o2* n1n h1h h1 r0 1.1600 0.9570 1.0977 0.7412 1.1010 k2 1161.3421 553.2800 1651.3730 414.2185 345.0000 k3 -2564.5706 -1278.9600 -4069.3178 -805.6549 -691.8900 k4 3932.8735 1788.6820 5984.9629 914.1296 844.6000 Table 4: Gas bond potential parameters Bond angle energies were modelled with a quartic function of the form 𝑉 = 𝑘2 (𝜃 − 𝜃0 )2 + 𝑘3 (𝜃 − 𝜃0 )3 + 𝑘4 (𝜃 − 𝜃0 )4 (2) The parameters, in degrees and kcal/mol for each gas angle is given in Table 5. Type I o1=* h1o h1 Type J c2= o2* c40 Type K o1=* h1o h1 θ0 180.00 104.5200 107.6600 k2 57.1000 46.6500 39.6410 k3 0.0000 -11.7046 -12.9210 k4 0.0000 -8.7911 -2.4318 Table 5: Gas angle potential Parameters To increase the accuracy of the forcefield bond-bond, bond-angle and angle-angle terms were also included for some gases. These are of the general form 𝑉𝑏𝑜𝑛𝑑−𝑏𝑜𝑛𝑑 = 𝑘𝑏𝑏 (𝑟1 − 𝑟0,1 )(𝑟2 − 𝑟0,2 ) (3) 𝑉𝑏𝑜𝑛𝑑−𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 = 𝑘𝑏𝑎 (𝑟 − 𝑟0 )(𝜃 − 𝜃0 ) (4) 𝑉𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒−𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 = 𝑘𝑎𝑎 (𝜃1 − 𝜃0,1 )(𝜃2 − 𝜃0,2 ) (5) The relevant parameters, in angstroms degrees and kcal/mol are listed in Table 6 Type I o1=* h1o h1 Type J c2= o2* c40 Type K o1=* h1o h1 kbb 275.435 -10.932 5.331 kba 23.8488 18.1030 kaa -0.3157 Table 6: Gas bond and angle cross-terms Frameworks Types were assigned to different atoms following the general type assigning rules in Compass. Types for boron and scandium were added in from the Dreiding and Universal forcefields. Table 7 lists the nonbonding types used, the types of atoms they were used to represent and the van der Waals parameters for that atom type. Forcefield Type b3 o2 c44 c3a h1 cu+2 o1c3- Atom Description B O C C H Cu O C o_v O v3o o_m zn2o sc+3 o12 V O Zn Sc O n3o N n2a cl1 zn+2 c4 N Cl Zn C n3 N Boron in COF-102 Oxygen in COF-102 sp3 carbon with 4 heavy atoms Aromatic carbon Generic hydrogen Copper 2+ ion Carboxylate oxygen Carboxylate carbon Oxygen interacting with vanadium in MIL-47 Vanadium oxide in MIL-47 Oxygen in Zn4O clusters Zinc in Zn4O clusters Scandium in Sc-MOF Oxygen in nitro group in ZIF-69 Nitrogen in nitro group in ZIF69 Aromatic nitrogen Chlorine in ZIF-69 Zinc ion sp3 carbon in Zn2(BDC)2(TED) Tertiary amine in Zn2(BDC)2(TED) σ/Ǻ ε / kcal mol-1 4.0200 3.3000 3.8540 3.9150 2.8780 2.6500 3.3000 3.9000 0.0950 0.08000 0.02000 0.06800 0.02300 0.04500 0.05000 0.07000 3.6270 0.38280 3.5000 3.6270 3.9800 3.2950 3.4000 0.41278 0.07841 0.54423 0.01900 0.04800 3.7600 0.04800 3.5290 3.8230 2.7000 3.8540 0.09600 0.28600 0.04700 0.06200 3.7200 0.07500 Table 7: Atom types and nonbonding potentials for framework atoms










