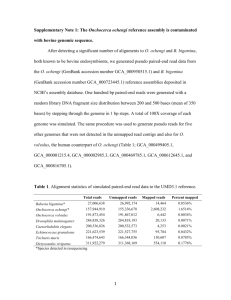
Table S1 Features of Erwinia genomes used in this study Species
advertisement

Table S1 Features of Erwinia genomes used in this study Species Strain Genbank accession no. Genome status amylovora ATCC 49946 CFBP 1430 IL-5 GCA_000027205.1 amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora amylovora billingiae piriflorinigrans pyrifoliae pyrifoliae pyrifoliae tasmaniensis tracheiphila mailotivora toletana UPN527 NBRC 12687 MR1 LA637 LA636 LA635 01SFR-BO ACW56400 Ea644 Ea356 Ea266 CFBP 2585 CFBP 1232 Eb661 CFBP 5888 Ep1/96 Ejp617 DSM12163 Et1/99 PSU-1 BTMARDI DAPP-PG 735 Complete Genome size (Mb) 3.9 No. of CDSs 3565 No. of contigs Contig N50 (Kb) Source or Reference GCA_000091565.1 FR719181FR719212 GCA_000367645.1 GCA_000696075.1 Complete Draft 3.8 3.8 3735 3857 32 345.9 Draft Draft 3.8 3.8 3729 3396 18 46 602.7 235.4 GCA_000367685.2 GCA_000513355.1 GCA_000513395.1 GCA_000513415.1 GCA_000367605.2 GCA_000240705.2 GCA_000367665.2 GCA_000367545.2 GCA_000367565.2 GCA_000367585.2 GCA_000367625.2 GCA_000196615.1 CAHS00000000.1 GCA_000027265.1 GCA_000165815.1 GCA_000026985.1 GCA_000026185.1 GCA_000404125.1 Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Draft Complete Draft Complete Complete Complete Complete Draft 3.8 3.9 3.8 3.8 3.8 3.9 3.8 3.8 3.8 3.8 3.8 5.3 4.0 4.1 4.0 4.1 4.1 4.7 4047 3505 3411 3413 3756 3830 3940 3773 3804 3784 3762 4917 3841 3697 3672 4038 3622 4401 31 8 8 8 12 24 41 15 39 14 43 182.4 1883.5 1883.7 1883.7 640.5 339.7 345.5 558.5 232.0 558.4 177.1 26 359.9 332 23.3 GCA_000590885.1 Draft 4.6 3991 75 107.4 (Jock et al. 2002) National Institute of Technology and Evaluation (Japan) (McManus and Jones 1995) (Smits et al. 2014) (Smits et al. 2014) (Smits et al. 2014) (Jock et al. 2002) (Rezzonico et al. 2011) (Rezzonico et al. 2011) (NORELLI et al. 1984) (NORELLI et al. 1984) (Lecomte et al. 1997) (Jock et al. 2002) (Kube et al. 2010) (Smits et al. 2013) (Kube et al. 2010) (Park et al. 2011) (Smits et al., 2010b) (Kube et al. 2010) U.S. Department of Agriculture (France) (Redzuan et al. 2014) GCA_000336255.1 Draft 5.3 4737 94 104.2 (Passos da Silva et al., 2013) (Smits et al. 2010) (Smits et al. 2010) (Powney et al. 2011) References Jock S, Donat V, Lopez MM, et al (2002) Following spread of fire blight in Western, Central and Southern Europe by molecular differentiation of Erwinia amylovora strains with PFGE analysis. Environ Microbiol 4:106–114. Kube M, Migdoll AM, Gehring I, et al (2010) Genome comparison of the epiphytic bacteria Erwinia billingiae and E. tasmaniensis with the pear pathogen E. pyrifoliae. BMC Genomics 11:393. Lecomte P, Manceau C, Paulin JP, Keck M (1997) Identification by PCR analysis on plasmid pEA29 of isolates of Erwinia amylovora responsible of an outbreak in Central Europe. European Journal of Plant Pathology 103:91–98. McManus PS, Jones AL (1995) Genetic fingerprinting of Erwinia amylovora strains isolated from tree-fruit crops and Rubus spp. Phytopathology 85:1547–1553. NORELLI JL, ALDWINCKLE HS, BEER SV (1984) Differential Host X Pathogen Interactions Among Cultivars of Apple and Strains of Erwinia amylovora. 74:136–139. Park DH, Thapa SP, Choi B-S, et al (2011) Complete genome sequence of Japanese erwinia strain ejp617, a bacterial shoot blight pathogen of pear. Journal of Bacteriology 193:586–587. Powney R, Smits THM, Sawbridge T, et al (2011) Genome sequence of an Erwinia amylovora strain with pathogenicity restricted to Rubus plants. Journal of Bacteriology 193:785–786. Redzuan RA, Abu Bakar N, Rozano L, et al (2014) Draft Genome Sequence of Erwinia mallotivora BT-MARDI, Causative Agent of Papaya Dieback Disease. Genome Announc 2:e00375–14. Rezzonico F, Smits THM, Duffy B (2011) Diversity, evolution, and functionality of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) regions in the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3819–3829. Smits THM, Guerrero-Prieto VM, Hernández-Escarcega G, et al (2014) Whole-Genome Sequencing of Erwinia amylovora Strains from Mexico Detects Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in rpsL Conferring Streptomycin Resistance and in the avrRpt2 Effector Altering Host Interactions. Genome Announc 2:e01229–13. Smits THM, Rezzonico F, Kamber T, et al (2010) Complete genome sequence of the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora CFBP 1430 and comparison to other Erwinia spp. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:384–393. Smits THM, Rezzonico F, López MM, et al (2013) Phylogenetic position and virulence apparatus of the pear flower necrosis pathogen Erwinia piriflorinigrans CFBP 5888T as assessed by comparative genomics. Syst Appl Microbiol 36:449–456.