Pre-Calculus Polynomial Zeros Guided Notes
advertisement

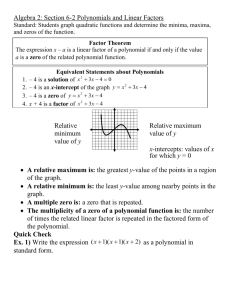
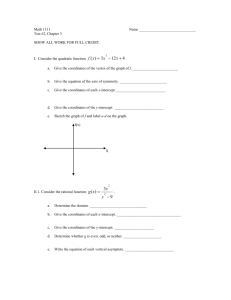
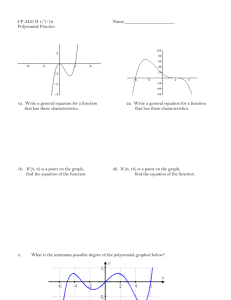
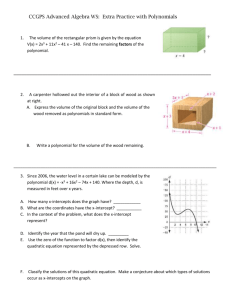
Name_________________________________________ Guided Notes 2.1 Pre-Calculus Honors Objective 2.1: Polynomial Zeros Do Now: 1. Find f(-5) if f(x) = a(x + 5) 2. Does the value of ‘a’ matter? Why? Power Functions and Polynomials: power functions: polynomials: f(x) = f(x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + … + a2x2 + a1x + a0 f(x) = an(x – zn)(x – zn-1)…(x – z2)(x – z1) where a and b are any number ex: where n is a non-negative integer (not a fraction, decimal, or _______________________ number) and the a and z values are any numbers ex: What do they look like? Make at least three observations about each group. You might want to sketch the general shape of each group as well. Non-Polynomial Power Functions: Polynomial Power Functions: Non-Power Polynomial Functions: Polynomial Intercepts: x-intercept: the point where the function intersects the ______-axis y-intercept: the point where the function intersects the ______-axis X-intercepts: 1. What is the y-value of the x-intercept? Is this always the case? Why or why not? 2. What happens when you substitute the x-value of the x-intercept into the function? Try this with both a polynomial in standard form and a polynomial in factored form. 3. The x-value of the x-intercept is sometimes called a zero of a function f(x) because when you substitute it in, it makes the function, f(x), equal _______________. The zero is also sometimes called the solution or root of the equation f(x) = 0. 4. What do you notice about the x-values of the x-intercepts and how they relate to the polynomial? 5. Is it easier to find the zeros from the factored form or standard form of the polynomial? 6. Find the zeros of the function. Why are these the zeros? f(x) = 4(x + 2)(x – 7) 7. Name_________________________________________ Find the roots of the equation f(x) = 0. Why are these the roots? f(x) = x2(x – z)(2x + 4) 8. Find the zeros of the function. Why are these the zeros? g(x) = -3(x – k)(x + z)? 9. How far apart are the x-intercepts of the function f(x) = 3(x – 3)(2x + 2)? 10. Find the x-intercept(s) of the function: f(x) = x2 - 11x + 30 11. Find the zeros of the function: f(x) = x3 – 2x2 – 63x Sum it up: Y-intercepts: 12. What is the x-value of the y-intercept? Is this always the case? Why or why not? 13. What happens when you substitute 0 in for x in the function? Try this with both a polynomial in standard form and a polynomial in factored form. 14. Find the y-intercept: f(x) = -2(x – 2)(x + a) 15. Find the y-intercept: f(x) = 3x4 – 2x2 + b 16. Is it easier to find the y-intercepts from the factored form or standard form of the polynomial? Why? 17. What do you notice about the y-values of the y-intercepts and how they relate to the polynomial? 18. Challenge: Let’s say x = (y – 3)(y – 2). Find the x-intercept (think about what y has to be). Find the y-intercepts (think about what x has to be!) Sum it up: For the x-intercept, the y-value is _______ For the y-intercept, the x-value is _______ Homework: 1. Find the zeros without graphing: f(x) = (x – 3)(x +2) 2. Find the x-intercepts and y-intercept of the function: f(x) = 3(x – 2)(3x + a) 3. Do these functions have different zeros: f(x) = (x – d)(x + w) and f(x) = 2(x – d)(x + w) 4. How far apart are the x-intercepts of the function (without graphing!) f(x) = x2 – 2x - 15