Ratios and Unit Rates
advertisement

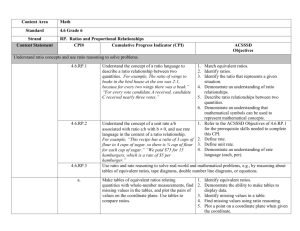
6th Grade Mathematics UNIT 2: RATIOS AND UNIT RATES Ratios and Unit Rates (8 weeks) Students develop an understanding of ratio concepts and using ratio reasoning to solve problems. By viewing equivalent ratios and rates as deriving from, and extending, pairs of rows (or columns) in the multiplication table, and by analyzing simple drawings that indicate the relative size of quantities, students connect their understanding of multiplication and division with ratios and rates. Students learn to use ratio and rate language to describe relationships; expand the scope of problems for which they can use multiplication and division; connect ratios and fractions; and solve a wide variety of problems involving ratios and rates. 1 6th Grade Mathematics Key Ideas: A ratio is a multiplicative comparison of two quantities. A ratio compares two related quantities. If one quantity in a ratio is multiplied or divided by a particular factor, then the other quantity must be multiplied by the same factor to maintain the proportional relationship. Ratios can be represented in a variety of formats including each, to, per, for each, %, 1/5, etc. Knowledge of equivalent fractions and equivalent ratios can be used to model ratio, rate and proportional reasoning. This knowledge can be generalized into algorithms for solving ratio, rate and proportion problems. A percent is a type of ratio that compares a quantity to 100. A unit rate is the ratio of two measurements in which the second term is 1. Determine when it is appropriate to use ratios/rates to solve mathematical or real life problems. Mathematical strategies for solving problems involving ratios and rates, including tables, tape diagrams, double line diagrams, equations, equivalent fractions, graphs, etc. Guiding/Focus Questions: How can reasoning with ratios and rates help solve real-world and mathematical problems? How are ratios and percents alike? How are they different? How do you determine a unit rate given a table of values? What are the differences between converting measurements in the metric and standard measurement systems? Given the quantity and price of two objects, how can you determine which one is the better buy? How are fractions,decimals andpercents related? How are common factors and multiples applied to solve real-world scenarios? How can I use multiplication and division to solve ratio and rate problems? What is the difference between a ratio and a rate? How can I use tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations to compare rates of change? How and where are ratios and rates used in the real world? 2 6th Grade Mathematics NYS Common Core Standards for Mathematics https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics] Focus Standards: Understand ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning to solve problems. 6.RP.1 Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities 6.RP.2 Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. 6.RP.3 Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. a. Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole-number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios. b. Solve unit rate problems including those involving unit pricing and constant speed. c. Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per; solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent. d. Use ratio reasoning to convert measurement units;manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. Foundational Standards(Prerequisites): Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems. 4.OA.2 Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem, distinguishing multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.3 Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions. 5.NF.3 Interpret a fraction as division of the numerator by the denominator (a/b = a ÷ b). Solve word problems involving division of whole numbers leading to answers in the form of fractions or mixed numbers. Convert like measurement units within a given measurement system. 5.MD.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world problems. Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems. 5.G.1 Define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the origin) arranged to coincide with the 0 on each line and a given point in the plane located by using coordinates. Understand that coordinates indicate how far to travel from the origin in the direction onboth axis 5.G.2 Represent real world and mathematical problems by graphing points in the first quadrant of the coordinate plane, and interpret coordinate values of points in the context of the situation. 3 6th Grade Mathematics Focus Standards for Mathematical Practice: MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Students make sense of and solve real world and mathematical ratio, rate, and percent problems using representations, such as tape diagrams, ratio tables, the coordinate plane, and/or double number line diagrams. Problems include ratio problems involving the comparison of three quantities, multistep changing ratio problems, using a given ratio to find associated ratios, and constant rate problems including two or more people or machines working together. MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students solve problems by analyzing and comparing ratios and unit rates given in tables, equations, and graphs. Students decontextualize a given constant speed situation, representing symbolically the quantities involved with the formula. MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. Students become proficient in selcecting and using a variety of representations that are useful in reasoning with rate and ratio problems such as tape diagrams, double line diagrams, ratio tables, a coordinate plane and equations. MP.6 Attend to precision. Students define and distinguish between ratio, the value of a ratio, a unit rate, a rate unit, and a rate. Students use precise language and symbols to describe ratios and rates. Students learn and apply the precise definition of percent. MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. Students recognize the structure of equivalent ratios in solving word problems using tape diagrams. Students identifying the structure of a ratio table and use it to find missing values in the table. Content/Skills 6.RP1 Explain the concept of a ratio as a comparison of two quantities Describe in written form (words and symbols) the relationship between two quantities. Express ratios in simplest form and understand how the reduced value relates to the original ratio. Create and label a visual model of a given ratio. 6.RP2 Convert a rate to a unit rate. Explain the concept of a unit rate as part-to-one. Unit rate is related to a ratio. Apply unit rates in real world situations. 6.RP3 Apply ratio and rate relationships and reasoning to solve real-world situations using tables, tape diagrams, number lines and equations. Make and interpret tables of equivalent ratios. Plot pairs of values of the quantities being compared on the coordinate plane. Use multiple representations such as tape diagrams, double number line diagrams or equations to solve rate and ratio problems. Solve unit rate problems (including unit pricing and constant speed). Solve percent problems, including finding a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 and finding the whole, given the part and the percent. 4 6th Grade Mathematics Vocabulary/ Key Terms Ratio Equivalent ratio Rate Unit Rate Constant speed Equivalent Ratios Percent Proportion Double Number Line Ratio Table Convert Tape Diagram Coordinate Plane Ordered pair Axis Origin Equation For ELLs, have them create a mini-glossary; instruct them to list each term, its meaning, and an illustration for each. When students have finished their glossaries, have them share them with the class. Allow them to use the glossaries as they work the exercises in the lesson and remind them to use them when they do their homework. ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE Initial Assessment: Unit Readiness Test Formative Assessments: Quizzes Exit Slips Checks for Understanding Short and Extended-Response questions used throughout the unit. Mathematical Reflections Formative Assessments Tasks Performance Task 1 (Ratios and Equivalency) Performance Task 2 (Ratio and Unit Rates) Performance Task 3 (Percent) Summative Assessment/s: Unit Test 5 6th Grade Mathematics TEACHING PLAN Teaching and Learning Activities: I. Administer the Unit Readiness Test. II. Use the guiding questions to focus each lesson. Lesson 1: Introduction to ratios Lesson 2: Writing ratios Lesson 3: Equivalent ratios Lesson 4: Equivalent ratios Lesson 5: Comparing ratios using ratio tables Lesson 6: Ratio tables to double number line diagrams Lesson 7: Equations using the value of ratios Lesson 8: Plotting ratios on the coordinate plane Lesson 9: Ratio problem solving Lesson 10: Ratios: Review and Assess Lesson 11: Understanding rates Lesson 12: Unit rates Lesson 13: Rate problem solving Lesson 14: Consumer math using rates Lesson 15: What is a percent? Lesson 16: Percents and tape diagrams Lesson 17: Percent problems – missing part Lesson 18: Percent problems – missing percent Lesson 19: Percent problems – missing whole III. Assess students on the unit. Final Performance Assessment Unit Test Resources Needed: Connected Math Project 3 (CMP3): Comparing Bits and Pieces NYS Common Core Math Module 1: Ratio and Unit Rates https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6-mathematics-module-1 Impact Mathematics Course 1 Math Handbook MathXL (Pearson’s online homework, tutorial, and assessment system) Glencoe New York State Review Series Ready New York CCLS (6th Grade) njctl.org http://www.algebrahelp.com/ https://grade6commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org 6 6th Grade Mathematics CALENDAR Time Spent 3 weeks Standards 6.RP.1 Topics To Cover Ratio and Equivalency Resources 3 weeks 6.RP.2 6.RP.3 Rates and Unit Rates 2 weeks 6.RP.3 Percents Connected Math Project 3 (CMP3):Comparing Bits and Pieces NYS Common Core Math Module 1: Ratio and Unit Rates https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-6mathematics-module-1 Impact Mathematics Course 1 Math Handbook MathXL (Pearson’s online homework, tutorial, and assessment system) Glencoe New York State Review Series Ready New York CCLS (6th Grade) njctl.org http://www.algebrahelp.com/ https://grade6commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcp ss.org 7