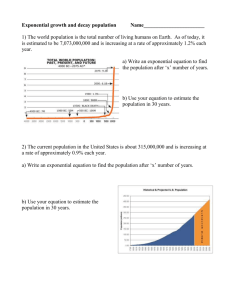
Data Task 1---Describing a Level Using a Point to Point Models
advertisement

Data Task 1: Constructing Point to Point Models 1.1 Use a geometric point to point model to calculate the average annual growth rate for real GDP over the period beginning with 1948 and ending with the most recent year for which you can obtain data. Similarly, calculate the growth rate for 1990 to present. Use your two results to draw a conclusion about whether or not the U.S. economy is slowing down. 1.2 Use an exponential point to point model to calculate the average annual growth rate for real GDP over the period beginning with 1948 and ending with the most recent year for which you can obtain data. Compare this growth rate to that which you obtained using the geometric model, and explain why this growth rate is lower. 1.3 Create a model data series using the geometric model for the 1948 to present period. Do the same using the exponential model. (You should see that the two models yield the same path, even though the two average growth rates for the two models are different.) Plot the actual data along with the model path (for one of the two models) in a diagram. (If you do this correctly, you should see that the model begins and ends at the same points where the actual series begins and ends.) 1.4 Explain why the exponential model follows the same path as the geometric model, even though the exponential growth rate is lower. 1.5 The “rule of 72” is a useful rule of thumb. There are many whole numbers that one divide 72 by and obtain another whole number as the result. The rule of 72 provides the number of time periods it will take a quantity to double when quantity is growing at a constant rate. For example, 72/8=9 indicates a quantity growing at 8 percent per year will double in 9 years. Use the exponential formula y t y 0 e rt to derive the rule of 72. (You should be able to show that the rule of 72 would more accurately be presented as the rule of 69.3. But, of course, such a rule is not nearly so convenient, so the rule of 72 is more valuable as an approximation tool.) 1.6 Approximately, how fast does the U.S. economy grow? At that rate, approximately how long will it take for the U.S. economy to double in size?