NITROGEN - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

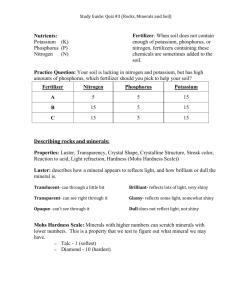
NITROGEN---Can purchased in 4 FORMS 1. Nitrate of soda NaNO3 *a highly soluble & quickly available *tends to reduce soil acidity *It has 16% Nitrogen 2. Ammonium Nitrate NH4NO3 * Not a soluble *Available over a longer period of time *Contains 33% Nitrogen 3. Ammonium Sulfate NH4SO4 *Available slowly *Leaves soil acidic *Good for plants that grow well in very acidic soil *21% Nitrogen 4. Urea formaldehyde *Original form of Nitrogen *More slowly available than the inorganic *contains 38% Nitrogen NITROGEN—is the Major Plant food that is most noticeable effects on plants sooner A. B. C. D. Encourages above ground vegetation -=gives dark green leaves Tends to produce soft tender growth—Great for Lettuce Tender Growth makes plants taste better Nitrogen helps to regulate the use of other major elements TOO MUCH NITROGEN: 1. 2. 3. 4. Lowers plants resistance to diseases Weakens the stem because of long soft growth Lowers the quality of the fruit-causing them to be too soft to ship Delays maturity or hardiness of tissues, thus increase winter damage to plant NOT ENOUGH NITROGEN: 1. Yellow or light Green 2. Stunted in roots and top growth Nitrogen : is lost through soil easily *It is water soluble & is not held by the soil particles because of the charges of the Particles involved. *Soil Particles –Have a Negative Charge *Ammonium Form of Nitrogen has a Positive charge & is held by negatively Charged soil particles *Nitrate Nitrogen is leached quickly because of the Negative charge—However Organic Matter does tend to hold insoluble that is released slowly into the soil. Nitrogen --Should Not be used in EXCESS for 2 Reasons 1. It is quickly Lost from soil through leaching –especially in Sandy soil 2. It can DAMAGE plants if applied in too great of amounts—Some plants such as Legumes ( beans & peas) manufacture their own Nitrogen. PHOSPHORUS: Purchased in the following forms: Superphosphate 20% Phosphate Treble superphosphate 46% Phosphate Rock Phosphate -25-35% Phosphate Ammonium Phosphate 48% Phosphate PHOSPHOROUS: *Is Present in some extent in All Soils *Phosphorus is held tightly to soil particles *therefore not easily Leached from soil PHOSPHORUS AFFECTS ON PLANTS: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. It encourages plant cell division Flowers & seed do not form without phosphorus It Speeds up Maturity thereby offsets the quick growth caused by Nitrogen It encourages Root Growth & development of strong root system It make Potash (Potassium) more easily available It increases the Plants Resistance to Disease Improves quality of Grain , Root & Fruit Crop Phosphorous is held very Tightly ty SOIL PATICLE IT DOESNOT CAUSE DAMAGE TO FIELD GROWN PANTS –if in EXCESSIVE AMOUNT HOWEVER: CONTAINER GROWN PLANTS- can be Damaged by excessive Phosphorous.. It can dehydrate (dry out) plant roots by pulling water from the roots LOW PHOSPHORUS: in sufficient results in: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Purple color on under surface of leaves Reduced flower, fruit & seed production Susceptibility to cold injury Susceptible to plant disease Poor quality fruits & Seeds POTASSIUM: common sources 1. Muriate of potash 60% Potash 2. Sulfate of Potash 49% Potash 3. Nitrate of Potash 44% of Potash POTASSIUM *Is rarely in soil in sufficient amounts to harm plants *Potassium modify both fast, soft growth of Nitrogen & the Early Maturity of Phosphorus PRESENT OF POTASSIUM IS ESSENTIAL FOR: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. INCREASE PLANTS RESISTANCE TO DISEASES IT ENCOURAGES A STRONG, HEALTHY ROOT SYSTEM IT IS ESSENTIAL FOR STARCH FORMATION IT IS NEEDED FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF CHLOROPHYLL IT IS ESSENTIAL FOR TUBER DEVELOPMENT Because it is a major element is generally added to soil SOIL TEST IS RECOMMENDED POTASSIUM DEFFIENCY APPEARS: 1. As a marginal yellowing 2. Scorching on edges of leaves on the lower portion of the plants LIME: CaCO3 *Lime acts as a plant food & as a material that affects soil acidity *In turn it affects the availability of other plant food elements\ LIME furnishes : Calcium ---Which is one of the most important of the secondary food Elements CALCIUM is IMPORTANT IN THE FORMATION OF PLANT CELL WALLS AMONG OTHER – Just like bones. SOIL ACIDITY (PH) Most plants grow best in 5.6-7.0 ph 7.0 ph is Neutral –Not ACID or ALKALINE 1-14 Lower than 7 indicate ACID SOIL Higher than 7 indicates ALKALINE SOIL