Volcano Lab
advertisement

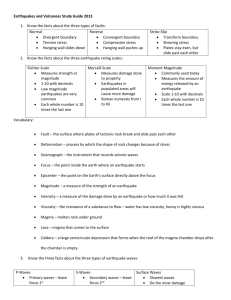
Volcano Identification Lab Name__________________________________________________________________Date____________________Period____ Chemistry of Magma - Does It Tell Us Anything About How a Volcano Burps? Overview: Geochemists study the chemical composition of magma to predict patterns of volcanic eruptions as well as to understand the composition of the Earth's interior. You will use the chemical composition of the magma to distinguish between the different types of volcanic rocks. The chemical data will be used to locate on a world map the different types of volcanoes based on their rock type. You will then use this data to predict where the most violent eruptions will occur. The Data Sheet includes the latitude and longitude of selected active volcanoes around the world and the chemical composition of rocks from each. The chemical composition includes silicon dioxide (SiO2) , aluminum oxide (Al 2O3), and iron oxide (Fe2O3). Directions: 1. The Volcano Data Sheet shows that rocks from volcanoes are classified into three basic rock types – rhyolite, andesite, and basalt. The three rock types are partially based on the percentage of silicon dioxide (SiO 2). Silicon dioxide, commonly known as the mineral quartz, is light in color. Based on your knowledge about the amount of silica, match the rock type to the percent of silica in the chart below. Write below the rock type based on its percent range of SiO 2: Percentage (%) Range of SiO2 in Magma Rock Type Percent Range of Silicon dioxide (SiO2) > 66 52 - 66 < 52 2. Use the table above to identify the missing rock types of volcanoes for the Volcano Data Sheet found on page 3. Base your identifications on SiO2 composition of the volcano’s magma. 3. Using the latitude and longitude coordinates on the Volcano Data Sheet plot all the volcanoes using a small triangle () on the World Map found on page 4. Include a key on your map and use a different colored pencil for the rock type associated with each volcano as follows: Rhyolite Andesite Basalt red blue green 4. As the percentage of iron oxide (Fe2O3) in volcanic rocks increases, what happens to the percentage of silicon dioxide (SiO2)? Refer to the Data Sheet to determine the correlation. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ _____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Trace a line segment along the tectonic boundaries using the colors below to indicate the plate boundary type, label the plate name and indicate the plate movement with an arrow on the World Map found on page 4. Refer to the attached Tectonic Plates map on page 5 as a reference. Include a key on your map. Purple for Convergent Boundaries Orange for Divergent Boundaries Black for plate name and movement 1 Volcano Identification Lab 6. Look your World Map. Describe the general relationship between the location of volcanoes you plotted and the tectonic plates. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) in magma is one factor that controls the violence of volcanic eruptions. Magma from the most violent eruptions has a higher percentage of silica compared to quiet eruptions. Use the three magma types: rhyolitic, andesitic, and basaltic in order to complete the table below. Label the type of eruption as either violent, quiet to violent or quiet based on percent of SiO2. Type of Magma Relative % of SiO2 Most Type of Eruption Intermediate Least 8. Look your World Map. Describe the general location of the type of eruption (violent and non-violent) based on the type of plate boundaries and rock types. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Look your World Map. Describe the general location of the type of earthquakes (violent and non-violent) you would find based on the type of plate boundaries. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Look your World Map. Describe the general relationship between the location of earthquakes you would find and the tectonic plates. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2 Volcano Identification Lab 3 Volcano Identification Lab 4 Volcano Identification Lab 5