Ch 15 Notes - OCPS TeacherPress
advertisement
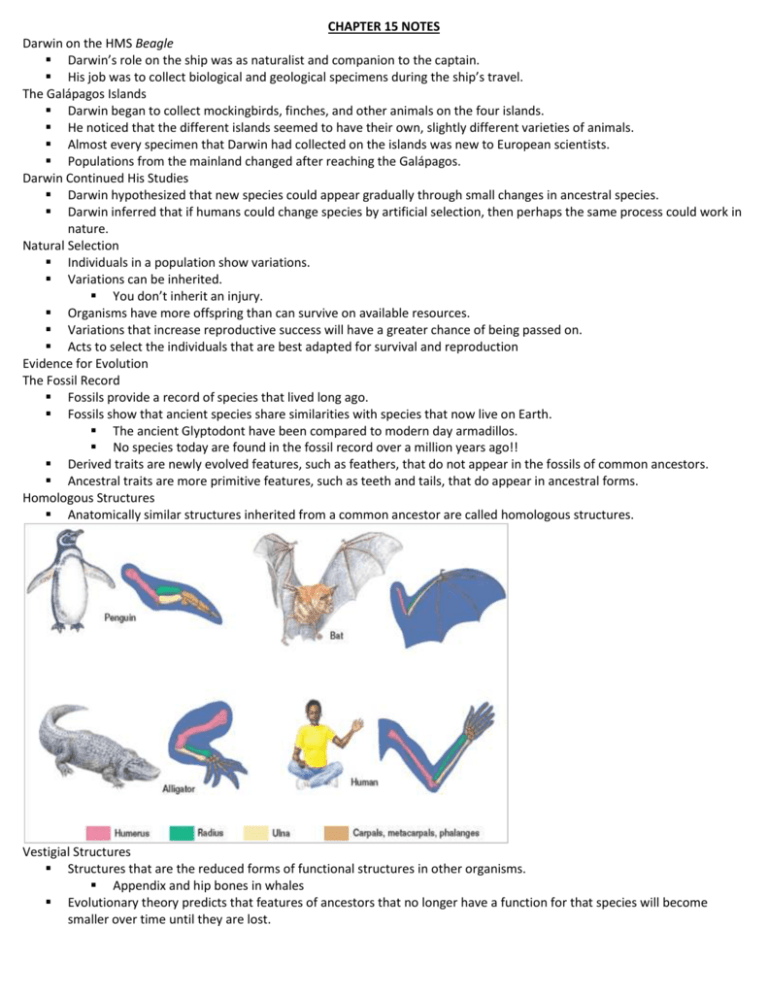
CHAPTER 15 NOTES Darwin on the HMS Beagle Darwin’s role on the ship was as naturalist and companion to the captain. His job was to collect biological and geological specimens during the ship’s travel. The Galápagos Islands Darwin began to collect mockingbirds, finches, and other animals on the four islands. He noticed that the different islands seemed to have their own, slightly different varieties of animals. Almost every specimen that Darwin had collected on the islands was new to European scientists. Populations from the mainland changed after reaching the Galápagos. Darwin Continued His Studies Darwin hypothesized that new species could appear gradually through small changes in ancestral species. Darwin inferred that if humans could change species by artificial selection, then perhaps the same process could work in nature. Natural Selection Individuals in a population show variations. Variations can be inherited. You don’t inherit an injury. Organisms have more offspring than can survive on available resources. Variations that increase reproductive success will have a greater chance of being passed on. Acts to select the individuals that are best adapted for survival and reproduction Evidence for Evolution The Fossil Record Fossils provide a record of species that lived long ago. Fossils show that ancient species share similarities with species that now live on Earth. The ancient Glyptodont have been compared to modern day armadillos. No species today are found in the fossil record over a million years ago!! Derived traits are newly evolved features, such as feathers, that do not appear in the fossils of common ancestors. Ancestral traits are more primitive features, such as teeth and tails, that do appear in ancestral forms. Homologous Structures Anatomically similar structures inherited from a common ancestor are called homologous structures. Vestigial Structures Structures that are the reduced forms of functional structures in other organisms. Appendix and hip bones in whales Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are lost. Analogous Structures Analogous structures can be used for the same purpose and can be superficially similar in construction, but are not inherited from a common ancestor. Show that functionally similar features can evolve independently in similar environments Examples include dorsal fins of dolphins vs. sharks or wings of birds vs. insects Comparative Embryology Vertebrate embryos exhibit homologous structures during certain phases of development but become totally different structures in the adult forms. All vertebrates have a: post anal tail dorsal nerve cord (becomes the spinal cord) pharyngeal slits (gills) notochord (becomes the spine) Comparative Biochemistry Common ancestry can be seen in the complex metabolic molecules that many different organisms share As species evolved, one change after another should have become part of their genetic instructions. Therefore, more and more changes in a gene’s nucleotide sequence should build up over time. Geographic Distribution Evolution is intimately linked with climate and geological forces. If environments never changed, then the traits best suited to survive would continue and mutations would not be beneficial Examples are alligators, swamps haven’t changed in many years. As climates change, new mutations may now be beneficial. Types of Adaptation An adaptation is a trait shaped by natural selection that increases an organism’s reproductive success. Organisms cannot change “adapt” to their environment. Either they have the genetic traits to survive or they do not. Fitness is a measure of the relative contribution an individual trait makes to the next generation. Camouflage Allows organisms to become almost invisible to predators Mimicry One species evolves to resemble another species. Mechanisms of Evolution Hardy-Weinberg principle states that when allelic frequencies remain constant, a population is in genetic equilibrium. In order for populations to remain constants, the five components of Hardy-Weinberg must occur: 1. No natural selection 2. Mating is random 3. No mutations 4. Large population 5. No gene flow - migration Genetic Drift A change in the allelic frequencies in a population that is due to chance In larger populations, the alleles tend to remain more stable In smaller populations, the effects of genetic drift become more pronounced, and the chance of losing an allele becomes greater. Genetic drift reduces genetic variation!!! Genetic Drift - Founder Effect Occurs when a small sample of a population settles in a location separated from the rest of the population. Alleles that were uncommon in the original population might be common in the new population. For example, one of the founding members of a small group Germans that began an Amish community in Pennsylvania had an allele for polydactylism (more than 5 fingers or toes) After 200 years of isolation, the 8000 Amish have a much higher % of polydactylism than the rest of the world Genetic Drift - Bottleneck Occurs when a population declines to a very low number and then rebounds. Certain traits may become more prevalent while others may die out because of the traits that survived. Caused by disasters such as floods or hurricanes Gene Flow Increases genetic variation within a population and reduces differences between populations Caused by migrations Nonrandom Mating Promotes inbreeding and could lead to a change in allelic proportions favoring individuals that are homozygous for particular traits Sexual Selection Sexual selection operates in populations where males and females differ significantly in appearance. Qualities of sexual attractiveness appear to be the opposite of qualities that might enhance survival. Sexual selection will effect natural selection by increasing certain traits in a population such as big pretty feathers on peacocks