Study Guide - Integers
advertisement

Grade 7 Math
Study Guide
Chapter 2 ~ Integers
Vocabulary to Know:
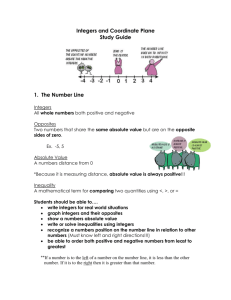
absolute value: the distance a number is from zero on a
number line
additive inverse: two integers that are opposites; the sum of
an additive inverse and its opposite is zero
coordinate plane: a plane in which a horizontal number line
and a vertical number line intersect at their zero points;
also called a coordinate grid
graph: locating the position of a point on the coordinate
plane, and drawing a dot at that location based on the
ordered pair
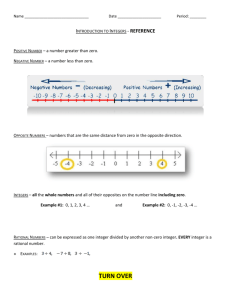
integer: any number from the set {…, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,…}
negative integer: an integer that is less than zero; negative
numbers are written with a – sign
opposites: two integers are opposites if they are
represented on the number line by points that are the same
distance from zero, but on opposite sides of zero; the sum
of two opposites is zero
ordered pair: a pair of numbers used to locate a point in the
coordinate plane; an ordered pair is written in the form (xcoordinate, y-coordinate)
origin: the point at which the x-axis and the y-axis intersect
in a coordinate plane; the origin is at (0,0)
positive integer: an integer that is greater than zero; these
numbers are written either with or without a + sign
quadrant: one of the four (4) regions into which the two
perpendicular lines of the coordinate plane separate the
plane
x-axis: the horizontal axis in a coordinate plane
x-coordinate: the first number in an ordered pair; it
corresponds to a number on the x-axis
y-axis: the vertical number in a coordinate plane
y-coordinate: the second number in an ordered pair; it
corresponds to a number on the y-axis
Rules to Remember:
Integers and Absolute Value
Integers less than zero are negative numbers.
Integers greater than zero are positive numbers.
When writing the absolute value of a positive or negative
number, two vertical bars are used. The symbol for absolute
value of the integer 3 is l3l.
The Coordinate Plane
The coordinate plane is used to locate points; the
horizontal number line is the x-axis; the vertical line is the yaxis; their intersection is called the origin.
Points are located using ordered pairs. The first number in
an ordered pair is the x-coordinate; the second number is
the y-coordinate.
The coordinate plane is separated into four regions called
quadrants. The quadrants are labeled using Roman
Numerals.
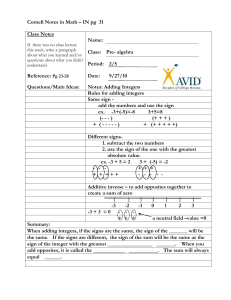
Adding & Subtracting Integers
To add integers with the same sign, add their absolute
values. The sum is:
o positive (+) if both integers are positive (+)
o negative (-) if both integers are negative (-)
To add integers with different signs, subtract their
absolute values. The sum is:
o Positive (+) if the positive (+) integer’s absolute value is
greater
o Negative (-) if the negative (-) integer’s absolute value is
greater
To add integers, sometimes it is helpful to use a number
line.
To subtract an integer, add its opposite
Multiply Integers
The product of two integers with the same sign is positive
(+).
The product of two integers with different signs is negative
(-).
Divide Integers
The quotient of two integers with the same sign is positive
(+).
The quotient of two integers with different signs is
negative (-).