UNIT 1 REVIEW- answers
advertisement

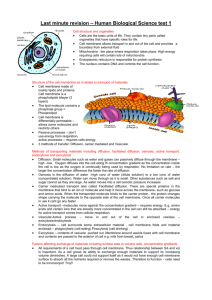
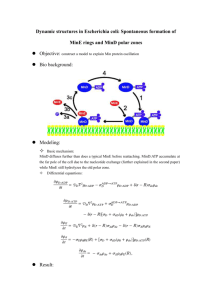
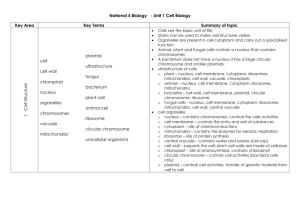
UNIT 1 REVIEW – PAGE 88 to 91 # 1-4, 6, 9, 11, 12, 14, 16, 17, 22, 24, 26-30, 32, 33, 36, 39 b),c) CELL THEORY: (from your notes) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms. All cells come from previously existing cells. The activity of an entire organism depends on the total activity of the independent cells. #1. a) All cells come from previously existing cells. b) All cells come from previously existing cells. c) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. #2. Type of microscope Scanning electron microscope Compound light transmission electron microscope Magnifying energy source electrons Max. magnification Max. resolution 300 000x 10 nm light electrons 2000x 5 000 000x 200 nm 0.2 nm b) total magnification = ocular lens mag. X objective lens mag. = 15 x 100 = 1 500 #3. Cell component Diagram of cell Plant/animal/both Main function Nucleolus both Cell membrane Cell wall both Plant only Thought to be involved in making proteins in the cell Regulates what goes in and what leaves the cell Cell rigidity #4. . #6. Chloroplast structure Contains chlorophyll Contains stroma (a protein-rich fluid) Builds up glucose using photosynthesis Contains 2 membranes (an inner membrane and an outer membrane) Mitochondria structure Does not contain chlorophyll Does not contain stroma, but a fluid called matrix Breaks down glucose using cellular respiration Contains 2 membranes (an inner membrane and an outer membrane) Free-floating organelle found in Free-floating organelle found in the cytoplasm the cytoplasm #9. Chlorophyll molecules are found embedded in the thylakoid membranes that are found in the chloroplast. #11. An oxygen atom is a lone atom that is not bonded to another atom; an oxygen molecules is made up of 2 oxygen atoms that are covalently bonded to each other (they share 2 pairs of electrons) #12. Hydrogen, covalent, ionic bond Weak strong #14. Water is a polar molecule and it is able to dissolve all solutes that are also polar. “like dissolves like” means that if a molecule is polar, it will be able to dissolve molecules that are also polar; if a molecule is nonpolar, it will be able to dissolve other molecules that are also polar. Water is polar, sugar is polar sugar is able to dissolve in water #16. Plant cells use cellulose to form their cell wall Humans are unable to digest cellulose, but use it as fibre – ensures regular bowel movements. #17. a) Solid at room temperature Usually derived from animals Carbon chain is saturated with hydrogen Straight fatty acid – packs well together liquid at room temperature Usually derived from plants Carbon chain is not saturated with hydrogen Kinked chain (caused by double bonds ) does not allow fatty acid to pack together b) Fatty acids in vegetable oil are hydrogenated (hydrogen is added to them) in order for the fatty acids to become solid at room temperature; this makes margarine. c) steroids fatty acids - made of carbon rings - made of carbon chains - too much of both of these macromolecules in your diet can lead to clogged arteries #22. a) the 3-D shape of a protein is important because the shape of the protein determines its function in the body. If the shape of the protein changes, it can no longer work. b) If a protein in the human body is heated above 40⁰C, the protein will denature (change shape) and no longer function. This is dangerous because there are many important proteins in our body that we depend on for survival. If these proteins stop working, we will die. c) When a steak is cooked, the proteins with the steak become denatured. #24. a) ATP is the energy source for all of the cell’s functions. b) If a cell does not produce an adequate amount of ATP, the cell will not have enough energy to complete all the necessary cellular functions and therefore die. #26. a) Process A is showing simple diffusion Process B is showing facilitated diffusion Process C is active transport (bulk transport) b) The “purple blob” through the membrane in process B represents a carrier protein. c) Process C requires energy (it’s active transport) and processes A and B do not require energy (they’re passive transport) #27. a) simple diffusion ends once dynamic equilibrium has been met. b) Simple diffusion ends because there is no longer a concentration gradient (there is no longer a difference in concentration on either side of the membrane) c) No. Since Active transport is moving molecules against the concentration gradient, dynamic equilibrium will never be reached while active transport is taking place. #28. The key difference between the transmembrane protein carriers in facilitated diffusion and the transmembrane protein carriers of active transport is the carrier involved in facilitated diffusion does not require energy to function and the carrier involved in active transport does require energy to function. #29. a) Cell A: hypotonic Cell B: isotonic Cell C: hypertonic b) Cells A will eventually burst before dynamic equilibrium is reached due to the movement of water into the cell. c) Cells C will eventually loose so much water before dynamic equilibrium is met that they will die, due to the continuous movement of water out of the cell #30. #32. a) The process of glycolysis is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. b) 2 molecules of ATP are formed by 1 glucose molecule during anaerobic cellular respiration; compared to 36 ATP formed during aerobic respiration. #33. Lactic acid fermentation occurs in the muscle cells in humans. It forms when there is not enough oxygen getting to the cells to break down glucose using aerobic respiration. The cell then resorts to anaerobic respiration, which results in the formation of 2 ATP molecules and lactic acid. #36. Field of view = 1mm number of cells that will fit in the field of view = 25 (approximately) estimated size of cell = estimated size of cell = size of field of view . number of cells in field of view 1mm = 0.04mm 25 #39. b) the optimal temperature of amylase is 35⁰C. c) Once the temperature is above 35⁰C, the shape of amylase begins to change (it denatures) and therefore stops breaking down amylose into maltose.