Exam 2c
advertisement

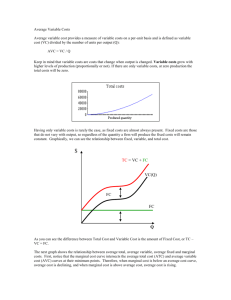
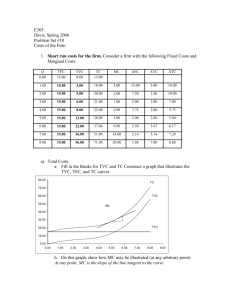
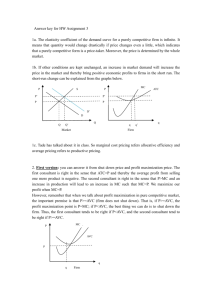
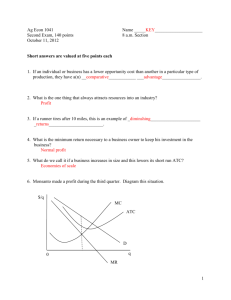
Ag Econ 1041 Second Exam, 140 points October 11, 2012 Name _________KEY_______________________ 11 a.m. Section True/False are valued at one point each T F 1. An action should always be taken if the total benefits exceed total costs. T F 2. Fixed costs in the short run do not vary with output. T F 3. If IBM decides to have Pam work on financial software instead of marketing software, the opportunity cost is her salary. T F 4. The decision to build an additional parking garage on campus should be based on average number of parking spaces occupied during a 24 hour period. T F 5. The sum of marginal costs equals variable costs when producing a good. T F 6. Demand for rice slopes downward because of income and substitution effects. T F 7. As the price of leather increases, the demand for leather belts will decrease. T F 8. Marginal costs rise with production due to diminishing returns. T F 9. Implicit costs refer to opportunity costs. T F 10. Without an increase in income, as the cost of consuming a good increases some of us will switch to consuming something else. T F 11. Short run decisions involve buying equipment, land or signing multi-year contracts. T F 12. Getting less output from using more of a variable input is called diseconomies of scale. T F 13. A positive cross-price elasticity indicates the goods are normal goods. T F 14. If water decreases in price, its demand will increase. T F 15. Opportunity costs are the value of all the other choices a person gives up by making a decision to do something. T F 16. Decision making, and its results, is what economics is all about. 1 T F 17. Demand for a normal good is always downward sloping. T F 18. Marginal utility is the utility derived from consuming additional increments of a good. T F 19. Management skill does not affect supply. T F 20. A person that likes something more than someone else will be willing to pay more, ceteris paribus. T F 21. An increase in demand means that consumers are willing to pay more for the same quantity. T F 22. Because we buy what we want there is no reason to worry about making choices. T F 23. Market demand for shoes shows the lowest price consumers are willing to pay for shoes. T F 24. Supply is a quantity. T F 25. Demand is always positively sloped. T F 26. It is best to use averages to make decisions. T F 27. The supply of celery is not related to opportunity cost. T F 28. Supply represents the highest opportunity cost facing a seller. T F 29. A decrease in the price of medicine will cause the supply of medicine to decrease. T F 30. Demand would decrease in the current period, if suppliers expected input costs to go up in the future. 2 Multiple choice are valued at two points each __D___ 31. Due to diminishing returns producers will only acquire more variable inputs if a) The price of the output falls b) ATC declines c) Demand decreases d) The price of the input declines e) Nuclear war occurs __B___ 32. An increase in supply a) Causes an increase in demand b) Can be due to lower input costs c) Is a typical result from higher input costs d) Guarantees profitability e) (c) and (d) __C___ 33. The law of demand defines a relationship between the quantity demanded and a) Income b) The quantity supplied c) The price d) Preferences e) Utility __C___ 34. Opportunity cost is a measure of a) All of the things foregone b) The thing you choose c) The best valued alternative foregone d) The lowest valued alternative foregone e) Buying a good __D___ 35. All of the following change demand or shift the demand curve, except a) The prices of related goods b) Income in the market area c) Preferences d) The price of the good itself e) Expectations of income changes 3 Matching are valued on one point each L 36. MR = MC A. Replacement Q 37. Diminishing returns B. Net value to sellers N 38. Opportunity cost C. AFC + AVC K 39. Economies of scale D. Lowest opportunity cost to buyers J 40. Profit E. MP x Price of output D 41. Demand F. Change or edge M 42. Price G. Quantities willing and able to be sold H 43 Consumer surplus H. Area below demand and above price C 44. ATC I. Source of purchasing power B 45. Producer surplus J. Attracts resources O 46. Utility K. Cost reduction due to firm getting larger A 47. Substitute L. Quantity were profit is maximized S 48. Complement M. Measure of scarcity/relative value G 49. Supply N. Net value foregone I 50. Income O. Value to an individual F 51. Margin P. Relatively unresponsive to price change T 52. Economics Q. Declining marginal product P 53. Inelastic demand R. Price of inputs E 54. Marginal value product S. Consumed with another product R 55. Supply determinant T. Study of decision making 4 Short answers are valued at five points each 56. Draw the average variable, average total and marginal cost curves for a typical business. At a quantity level less than where MC intersects AVC, show the amount of VC and FC. MC $/q ATC AVC FC VC q q 57. The eventual decrease in the addition to output as more of an input is used is called what? Diminishing returns 58. Use a diagram to show economies of scale for a business. $/Q ATC1 ATC2 ATC3 economies is scale Q 59. What type of cost should not affect short run decisions? Fixed 5 60. a) AVC + AFC = ____ATC_____________ b) ∑ MC = ___VC________________ c) Average Revenue (AR) = __Demand__(accept Price)____________ d) Profit is maximized at the output where ____MR = MC_____________________ e) If MR is negative then demand is __inelastic_________________________ 61. Show on a graph consumers’ response from an increase in the price of prescription drugs. $/Q P1 P0 D 0 Q1 Q0 62. Diagram the change in the production possibility frontier of a farmer who grows only sod for lawns and soybeans if there is an increase in land that is suitable only for soybean production. What is likely to happen to the output of each good? _both increase__________ Sod PPC0 0 PPC1 Soybeans 6 63. What happens to demand in the following situations (↑, ↓ or ↔) a) Price of complement rises ____D ↓___________________ b) Own price of good increases __Qd ↓ (nothing)_________________ c) Wealth increases __D ↑_____________________ d) Utility increases __D ↑__________________ e) Input costs decline _nothing_________________ 64. Businesses want to __maximize profit___________________________________. 65. UPS and Union Pacific have had revenue growth without changing price. This suggests what? Demand increased 66. What causes the quantity supplied of fish oil to fall if the supply curve does not shift? Lower price 67. If marginal cost rises rapidly (is steep) then how is AVC likely to look? It will also have steeper sides or look more like a ‘V’ 68. Given the following information what happens: a) Income falls and income elasticity is +0.6 __demand falls___________________ b) Ep > 1 and price declines __revenue increases________________________ c) The price of a complement rises and the cross price elasticity is -0.2 __demand falls_______________________ d) The price of soap declines by 10% __Qd of soap increases______________________ e) MC is greater than AVC ___AVC increases______________________ 7 69. Diagram supply change if new improved production technology is implemented. $/Q S0 S1 0 Q The following question is valued at 10 points each 70. Draw a graph of MC, ATC, D and MR and show on the graph the firm maximizing profit and the amount of total revenue. $/Q MC ATC TR D 0 q q MR 8