Radioactivity
advertisement
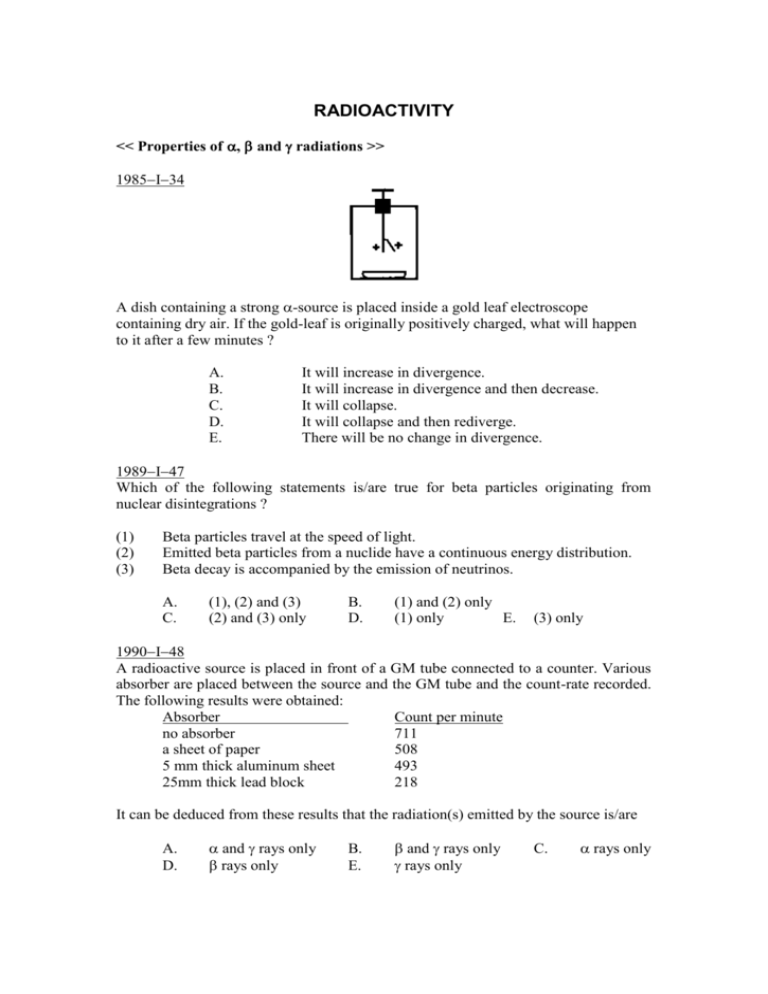
RADIOACTIVITY << Properties of , and radiations >> 1985I34 A dish containing a strong -source is placed inside a gold leaf electroscope containing dry air. If the gold-leaf is originally positively charged, what will happen to it after a few minutes ? A. B. C. D. E. It will increase in divergence. It will increase in divergence and then decrease. It will collapse. It will collapse and then rediverge. There will be no change in divergence. 1989I47 Which of the following statements is/are true for beta particles originating from nuclear disintegrations ? (1) (2) (3) Beta particles travel at the speed of light. Emitted beta particles from a nuclide have a continuous energy distribution. Beta decay is accompanied by the emission of neutrinos. A. C. (1), (2) and (3) (2) and (3) only B. D. (1) and (2) only (1) only E. (3) only 1990I48 A radioactive source is placed in front of a GM tube connected to a counter. Various absorber are placed between the source and the GM tube and the count-rate recorded. The following results were obtained: Absorber Count per minute no absorber 711 a sheet of paper 508 5 mm thick aluminum sheet 493 25mm thick lead block 218 It can be deduced from these results that the radiation(s) emitted by the source is/are A. D. and rays only rays only B. E. and rays only rays only C. rays only 1994II41(AL) When a radioactive atom emit a -rays, which of the following statements about the atom is/are correct ? (1) (2) (3) Its mass number remains unchanged. The energy of the atomic nucleus decreases. An electron falls from a higher energy level to a lower one. A. D. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only (3) only C. (1) and (2) only E. (1), (2) and (3) 1994II44(AL)/24(AS) A detector is used for monitoring an -source and a reading of 120 units is observed. After a time equal to the half-life of the -source, the reading has fallen to 64 units. If a 5 mm thick lead sheet is inserted between the -source and the detector, the reading would probably be A. D. 0 unit 16 units B. E. 4 units 32 units C. 8 units 1994II23(AS) When a radioactive atom emit a -rays, which of the following statements about the atom is/are correct ? (1) Its atomic number decreases. (2) Its mass number remains unchanged. (3) The energy of the atomic nucleus decreases. A. D. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only (3) only C. (1) and (2) only E. (1), (2) and (3) 1996II41(AL)/24(AS) A radioactive source is tested as follows : (1) (2) (3) Absorber placed between source and GM counter Thin aluminium foil (0.2 mm) Thin lead sheet (2 mm) Thick lead sheet (20 mm) Effect on count rate Falls appreciably No significant difference with (1) Falls below that in (1) What type(s) of radiation does the source emit ? A. D. only B. and only E. only C. and only only 1996II44(AL)/23(AS) A counter is placed nearly a very weak radioactive source which has a half-life of 1 hour. The counter registers 100 counts/min at noon and 80 counts/min at 1 p.m. The expected count rate, in counts/min, at 3 p.m. on the same day is A. C. E. 40 55 65 B. D. 50 60 1999II42(AL)/22(AS) For stable nuclides, the number of neutrons N when plotted against the number of protons Z would give points lying within the above shaded region. Which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) (2) (3) The heavy stable nuclides have more neutrons than protons Unstable nuclides decay to produce new nuclides closer to the shaded region. Unstable nuclides above the shaded region usually decay through -emission. A. D. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only (3) only C. (1) and (2) only E. (1), (2) and (3) 1984I33 4 An alpha particle collides with a stationary helium nucleus (2 He) in a cloud chamber. Which of the following diagrams represents the most probable set of tracks ? << Natural nuclear transformations >> 1997II43(AL)/23(AS) 226 88 Ra is one of the nuclides in the uranium decay series. If the stable end-product of 226 this series is 206 82 Pb , the number of -particles emitted between the 88 Ra stage and the end of the series is A. D. 4 14 B. E. 6 20 C. 10 << Exponential law of decay >> 1982I35 A radioactive source with a half-life t1/2 initially contains N atoms of the radioactive element. The energy released in each disintegration is E What is the total energy released in time 2 t 1/ 2 ? 1 1 3 A. B. C. 4 NE 2 NE 4 NE 1 D. E. NE t 1/ 2 2 NE t 1/ 2 1983I28 A radioactive source of gamma rays has a half-life of 2 days. A Geiger counter placed 3 m from the source initially has a count-rate of 1440 per minute. After 6 days the counter is moved back to a distance of 9 m from the source, and its count-rate, in counts per minute, is then A. C. 20 180 B. D. 60 E. 320 360 1985I31 Protactinium extracted from a solution of uranyl nitrate decays with a half-life of 72 s. The value of the decay constant is A. D. 9.6 x 10-3 s 49.9 s B. E. 9.6 x 10-3 s-1 49.9 s-1 C. 0.014 s-1 1988I44 An -source originally consisted entirely of the element polonium. After the emission of a single -particle, each polonium atom becomes an atom of lead. At the end of two years, the source was found to contain 98% lead and 2% of polonium. At the end of one year, the sample would have had the approximate composition: A. C. E. 14% lead, 86% polonium. 50% lead, 50% polonium. 86% lead, 14% polonium. B. D. 25% lead, 75% polonium. 75% lead, 25% polonium. 1993I48 The number of radioactive nuclides in two different samples P and Q are initially 4N and N respectively. If the half-life of P is t and that of Q is 2t, the number of radioactive nuclides in P will be the same as the number of radioactive nuclides in Q after a time of A. t/2 B. t C. 2t D. 4t E. 8t 1995I44(AL)/1995II24(AS) 226 222 88Ra decays to 86 Rn with a half-life of 1600 years. Which of the following statements is/are correct ? (1) (2) (3) particle is produced in the decay All 226 88Ra has decayed after 3 200 years The half-life of 226 88Ra can be shortened by heating. A. D. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only E. (3) only C. (1), (2) and (3) (1) and (2) only 1998-IIA-41(AL) The activity of a simpe of radioactive isotopes decreases to 1/3 of its initial value in 12 s. How much more time would be required for the activity to decrease to 1/9 of its initial value? A. D. 4s 16 s B. E. 8s 24s C. 12 s 1998-IIA-43(AL) A radioactive sample, initially consists of only nuclide X, decays by the emission of an alpha particle to form a stable daughter nuclide Y. Which of the following quantities will decrease with time? (1) (2) (3) A. D. The rate of decay of nuclide X. The rate of growth of nuclide Y. The rate of emission of alpha particles. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only (3) only C. E. (1) and (2) only (1), (2) and (3) << Random nature of decay >> 1998-IIA-32(AL) Which of the following is/are random process(es) ? (1) The background radiation in radioactivity. (2) The Brownian motion of smoke particles in a smoke cell (3) The scattering of -particles by the nuclei in a piece of gold foil. A. D. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only (3) only C. (1) and (2) only E. (1), (2) and (3) 1998-IIA-43(AL) A radioactive sample, initially consists of only nuclide X, decays by the emission of an alpha particle to form a stable daughter nuclide Y. Which of the following quantities will decrease with time? (1) (2) (3) The rate of decay of nuclide X. The rate of growth of nuclide Y. The rate of emission of alpha particles. A. D. (1) only B. (2) and (3) only 1985I34 1989I47 1990I48 1994II41(AL) 1994II44(AL)/24(AS) 1994II23(AS) 1996II41(AL)/24(AS) C C A C C (3) only C. (1) and (2) only E. (1), (2) and (3) 1996II44(AL)/23(AS) 1999II42(AL)/22(AS) 1984I33 1997II43(AL)/23(AS) 1982I35 1983I28 D 1985I31 E C D A C A B 1988I44 1993I48 1995I44(AL)/1995II24(AS) 1998-IIA-41(AL) 1998-IIA-43(AL) 1998-IIA-32(AL) 1998-IIA-43(AL) E D A C E C E