Reading Strategies for ESL/EFL Students
advertisement

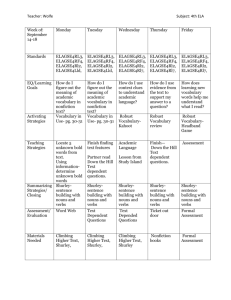
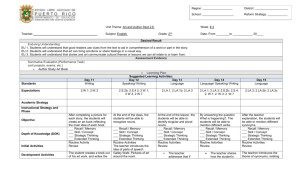
Reading Strategies for ESL/EFL Students Learning to read a new language is very difficult. It takes time and effort. English as a Second Language (ESL) students can improve reading comprehension by utilizing these tips: English-Foreign Language Dictionaries One of the easiest ways to learn new vocabulary words is to use a dictionary. However, new words are best understood within the context of sentences, and it takes a lot of time to look up new words. Create a list of new words and look them up when you're not reading paragraphs. Context Clues New vocabulary can be learned by identifying contextual clues. Look for these clues while reading: Type of Word: Verbs, nouns, adverbs, and adjectives can be identified through these clues: 1. Articles (the, an, or a) are typically placed before nouns 2. Adjectives (words that describe nouns), such as large, yellow, and angry, are placed immediately before nouns 3. Sentences usually begin with nouns, and nouns follow prepositions (at, to, before, during, in, etc.) 4. Verbs typically end with ing or ed suffixes 5. Adjectives frequently end with est, er, ous, and able suffixes 6. Adverbs describe verbs and typically end with ly suffixes Surrounding Words: Words surrounding unfamiliar terms provide indications about meaning. 1. Nouns typically provide insights into verbs. For example: The coach used a whiteboard to teach his players. 2. Verbs typically offer clues about a noun's meaning. For example: The students ran around the track. 3. Verbs and nouns also provide insights into other words within the sentence. For example: John documented the company's meeting minutes in his notebook. Verb Tense: Indicates whether an event: 1. Is currently taking place 2. Occurred in the past 3. Will take place in the future Singular and Plural: Indicates whether a noun refers to single or multiple entities Paired Storytelling Strategy Word-for-word translation is an ineffective way to learn foreign languages. Many ESL students have benefitted greatly by using the paired storytelling strategy, a method where writing and reading skills are developed by working in groups. The Paired Storytelling Strategy is comprised of these 5 learning strategies: o o o o o Cultural background is incorporated into reading comprehension exercises ESL students are taught in similar ways as native English speakers Reading and writing skills are learned simultaneously Teachers avoid using discouraging teaching methods ESL students are encouraged to communicate in English This method offers numerous advantages. ESL students enjoy the opportunity to practice English individually with other students in non-threatening settings, and since students work in groups, they encourage their peers. Additionally, confidence increases since students are not placed in intimidating situations. Likewise, since students are required to practice speaking, they simultaneously improve writing and readings skills. Students learning through the Paired Storytelling Strategy also learn new vocabulary within the context of paragraphs. This is one of the best advantages of using this method. ESL teachers use the Paired Storytelling Strategy as follows: 1. Organize Groups o Separate the class into groups 2. Introduce Concepts o Introduce reading assignments by writing new concepts to learn on the whiteboard 3. Brainstorm Ideas o o o Assist students while they brainstorm ideas. Teachers typically get students to think about how personal experiences related to concepts Teachers help students feel at ease during this phase by making it clear that wrong answers do not exist. Rather, they encourage students to apply what they've already learned to new concepts Teachers require students to brainstorm to assess whether they're sufficiently prepared to learn new concepts. When appropriate, teachers provide additional instruction. 4. Pass out the Assignment o Teachers separate assignments into two sections. Students work in pairs, and each one is provided with a section 5. Read and Summarize Main Points o Students are required to jot down the main points from their assigned sections. Teachers typically provide readings with just a few points to avoid confusion 6. Switch Lists o Teachers require students to switch sections and their lists of key concepts with other students. Students are then instructed to review the list compiled by their partners. When students are unfamiliar with concepts on an exchanged list, the teacher creates a sentence with the concept. 7. Write a Short Story o Students are required to write a short story using concepts from both lists. The students who reviewed the first list predicts what occurs during the beginning of the story, while the second predicts what occurs during the end of the second story. 8. Read Both Stories o Each student is then required to read aloud what they predicted. Teachers also call on students to read their stories to the class. Teachers remind students not to ridicule other students. 9. Compare Each Students' Story o Students now compare their stories to the stories of their classmates. 10. Discussion o In pairs and with the class, students discuss what they learned. This enables them to familiarize new concepts and learn from the insights of other class members. Teachers typically take a few minutes to observe the conversations of both students. 11. Assessment o Teachers typically test what their students learned during this phase. Each student is evaluated separately.