biomes physical region
advertisement

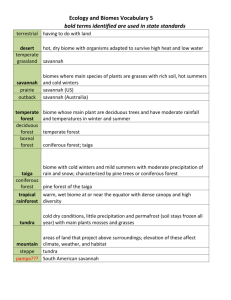
Landscape highlighted in green Physical regions The arctic region contains subarctic along with a tundra biome with its characteristics being plains lowlands and mountains. this region was formed by the pressure from the northeastern edge of the Canadian shield pushing up sedimentary rock to form a range of fold mountains, these mountain’s which called an innuitian a extend more than 1000 kilometres cordillera region includes parkland, grassland, mixed, coastal, inferior and coniferous forest with its characteristics being made up of parallel mountain ranges separated by plateaus, trenches, and valleys, dormant, volcanoes, glaciers, and ice fields these are the characteristics which occupy the majority of in the province of British Columbia along with the territory Yukon the regions landforms such as the Rocky’s and costal mountain ranges were formed when a plate collision caused the earth’s crust to buckle, pushing and folding volcanic rock into the mountains we see today but this plate movement dint only cause the formation of mountain’s it also cased the formation of plateaus, valleys and tranches Interior plains region which is placed in-between the cordillera and that Canadian Shield includes the following biomes tundra, open woodlands, coniferous forest, parkland, and grassland, this region formed by soils carried out by river from the Canadian shield the soils were deposited at its edge and formed layers of sedimentary rock which later on became large areas of mostly flat land, rolling hills and river valleys The Canadian Shield which makes nearly half of Canada’s surface includes mixed forest, coniferous forest, open woodland, tundra, and subarctic biomes regions Was formed because the shield was once a volcanic mountain range but through millions of years weathering erosion and especially the action of glaciers worn out the land to a landscape of, bare rocks, lakes and wetlands st. Lawrence lowlands region made out of a region of mixed forest This region was mainly formed by the retreating ice sheet that covered most of Canada during the last ice age. The ice sheets pushed soils from the shield into the area where the lowlands are today and as the sheets of ice melted it formed giant lakes Appalachian region open woodland, mixed forest and coniferous forest regions have contributed to create a varied landscape of rolling hills valleys, small mountains, highlands and costal fjords This region was formed by worn-down glaciers and millions of years of erosion. Biomes Subarctic: The subarctic region of Canada covers the physical regions of the arctic along with the Canadian Shield .its vegetation consists from many swampy areas of scattered coniferous trees, mixed with tundra vegetation. Making it ideal for Arctic wildlife such as caribou, lemmings, and snowy owls. Tundra: the tundra’s vegetation has a treeless landscape, permafrost with mostly low shrubs, mosses and lichens. not all wild life can survive this harsh climate but Polar bears, seals, walruses, muskox, and Arctic foxes are built to survive these conditions survive in this harsh climate bylot island Nunavut this picture shows everything that was used to describe the tundra. in addition the mountain region. https://www.google.ca/url?sa=i&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=images&cd=&ved=0CAcQjRxqFQ oTCMXLk6ON_ccCFQYsiAodveAFDg&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.hww.ca%2Fen%2Fwildspaces%2Farctictundra.html&bvm=bv.102829193,d.cGU&psig=AFQjCNFhlmZomzfVXNQAuEpxh5Dbf0H4rw &ust=1442546115678768 the tundra has every low temperatures with the winter average temperature is -34°C,and in the summer the average is between 3°C and 12°C http://www.hww.ca/en/wild-spaces/arctic-tundra.html Open woodland is an area of scattered evergreen trees, shrubs, and grass. This vegetation makes it ideal for Animals such as caribou, martens, bears, geese, beaver, and lynx to live in this region thimmens riviere, Quebec coniferous forest in this region soils are not so fertile making the vegetation plentiful of Evergreens such as spruce, fir, pine, and aspen. This region also features wild life such as deer, moose, black bears, and many furbearing animals, as well as hawks, eagles, and various types of wild ducks. Coastal and interior forest this region is primarily a coniferous forest area. The higher slopes of mountains above the treeline have tundra and Arctic vegetation. Some southern interior valleys have short grass and plants. Unsettled areas are home to abundant wildlife such as cougars, mountain sheep, bears, moose, and birds. Mixed forest Made up of softwood trees, such as hemlock and cedar, as well as hardwood trees such as maple, birch, oak, and ash. This region has the same wildlife as the coniferous region. Soil is more fertile in mixed forests than in coniferous forests In Nova Scotia Parkland A transition zone between the dry southern prairies and the coniferous forest, this region has long grasses and clumps of aspen and cottonwood trees. Alberta Grassland soils are far more fertile than in the forest regions and unlike the forest region, this is an area where the vegetation is mostly made up of short grasses because there’s not enough moisture for trees. Wild life features Antelope, gophers, and wild fowl. Grasslands national park Fun facts Bison, until hunted to near extinction, were the largest group of animal in the grassland. The Rocky and Coastal mountain ranges, along with British Columbia’s Interior Plateau, are the youngest landforms in Canada. Shield formations are among the oldest areas in the world.