LAB Properties of Acids and Bases (2D)
advertisement
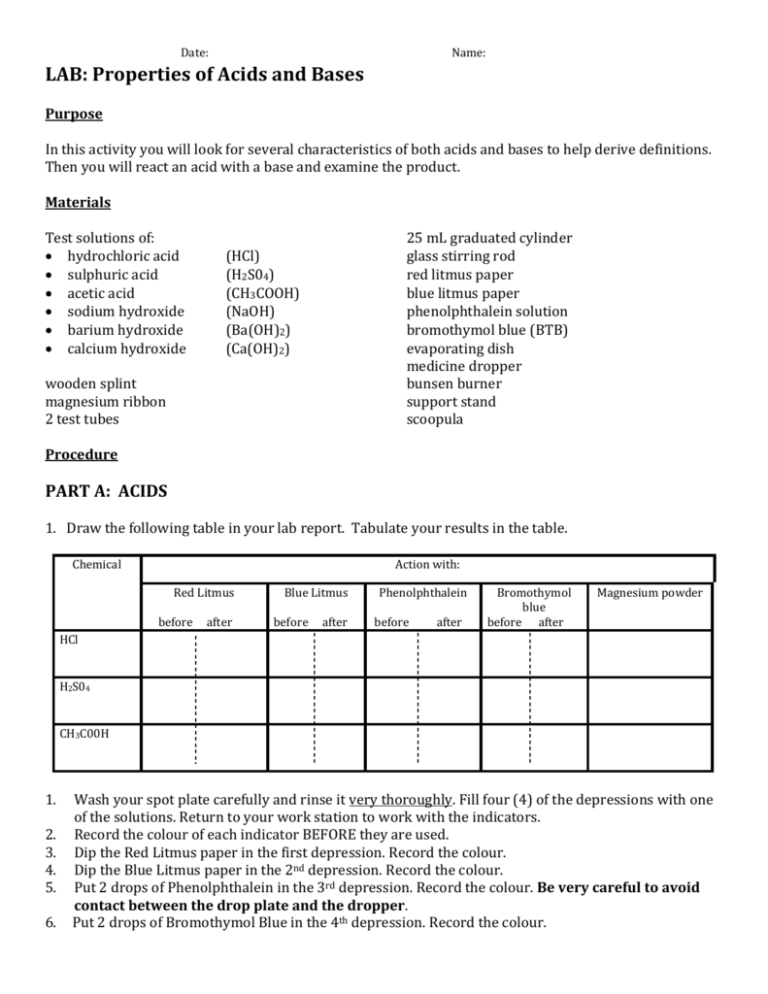
Date: Name: LAB: Properties of Acids and Bases Purpose In this activity you will look for several characteristics of both acids and bases to help derive definitions. Then you will react an acid with a base and examine the product. Materials Test solutions of: hydrochloric acid sulphuric acid acetic acid sodium hydroxide barium hydroxide calcium hydroxide 25 mL graduated cylinder glass stirring rod red litmus paper blue litmus paper phenolphthalein solution bromothymol blue (BTB) evaporating dish medicine dropper bunsen burner support stand scoopula (HCl) (H2S04) (CH3COOH) (NaOH) (Ba(OH)2) (Ca(OH)2) wooden splint magnesium ribbon 2 test tubes Procedure PART A: ACIDS 1. Draw the following table in your lab report. Tabulate your results in the table. Chemical Action with: Red Litmus before after Blue Litmus before after Phenolphthalein before after Bromothymol blue before after Magnesium powder HCl H2S04 CH3C00H 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Wash your spot plate carefully and rinse it very thoroughly. Fill four (4) of the depressions with one of the solutions. Return to your work station to work with the indicators. Record the colour of each indicator BEFORE they are used. Dip the Red Litmus paper in the first depression. Record the colour. Dip the Blue Litmus paper in the 2nd depression. Record the colour. Put 2 drops of Phenolphthalein in the 3rd depression. Record the colour. Be very careful to avoid contact between the drop plate and the dropper. Put 2 drops of Bromothymol Blue in the 4th depression. Record the colour. 7. 8. 9. Obtain a test tube and fill it with 5 mL of the solution used in steps 1 to 6. Place the test tube in a test tube rack. Add a small amount of magnesium ribbon to the acid in the test tube standing in the test tube rack. After 20 seconds, insert a blazing splint down into the test tube. Record your observations in the chart. Completely wash out the test tube and spot plate. Repeat steps 1 to 9 with each of the other two acids. Complete your table. PART B: BASES 1. Draw the following table in your lab report. Tabulate your results in the table. Chemical Action with: Red Litmus before after Blue Litmus before after Phenolphthalein before after Bromothymol blue before after Magnesium powder NaOH Ba(OH)2 Ca(OH)2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Wash your spot plate carefully and rinse it very thoroughly. Fill four (4) of the depressions with one of the solutions. Return to your work station to work with the indicators. Record the colour of each indicator BEFORE they are used. Dip the Red Litmus paper in the first depression. Record the colour. Dip the Blue Litmus paper in the 2nd depression. Record the colour. Put 2 drops of Phenolphthalein in the 3rd depression. Record the colour. Be very careful to avoid contact between the drop plate and the dropper. Put 2 drops of Bromothymol Blue in the 4th depression. Record the colour. Obtain a test tube and fill it with 5 mL of the solution used in steps 1 to 6. Place the test tube in a test tube rack. Add a small amount of magnesium powder to the base in the test tube standing in the test tube rack. After 20 seconds, insert a blazing splint down into the test tube. Record your observations in the chart. Completely wash out the test tubes and spot plate. Repeat steps 1 to 8 with each of the other two bases. Complete your table. PART C: REACTING AND ACID WITH A BASE 1. Pour 5 mL of sodium hydroxide solution into a clean evaporating dish. Use a stirring rod to add two drops of phenolphthalein solution, stir, and note any observable change. As you stir the mixture, use a medicine dropper to slowly add hydrochloric acid solution, drop by drop, to the dish. When the pink colour just disappears stop adding acid. 2. Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure on the right and be sure you are wearing your safety goggles. Evaporate the solution to dry- ness. Allow the dish to cool. 3. Examine the solid substance that forms in the evaporating dish. DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Look at the formulas for the acids you used. (See the table Part A.) What do they have in common? 2. Look at the formulas for the bases you used. (See the table Part B.) What do they have in common? 3. How do acids and bases differ in their effect on red and blue litmus paper? 4. How do acids and bases differ in their effect on phenolphthalein? 5. a) What happens when a metal such as magnesium is placed in an acid? b) What happens when such a metal is placed in a base? c) Name any gases produced in a) or b). 6. a) What happens when sodium hydrogen carbonate is placed in an acid? b) What gas is produced? 7. a) What product was formed when hydrochloric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide? b) The reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralization. Water and a salt are formed in every neutralization reaction. Write a word and chemical equation for the neutralization reaction that occurred in Part C. 8. a) List all properties common to acids and bases. b) List all properties possessed only by acids. c) List all properties possessed only by bases. 9. Suppose you are given five beakers, each containing an unknown liquid. One is distilled water, one is a strong acid, one is a weak acid, one is a base and one is a salt solution. Describe how you would find out which was which.










