8th - CPR Notes
advertisement
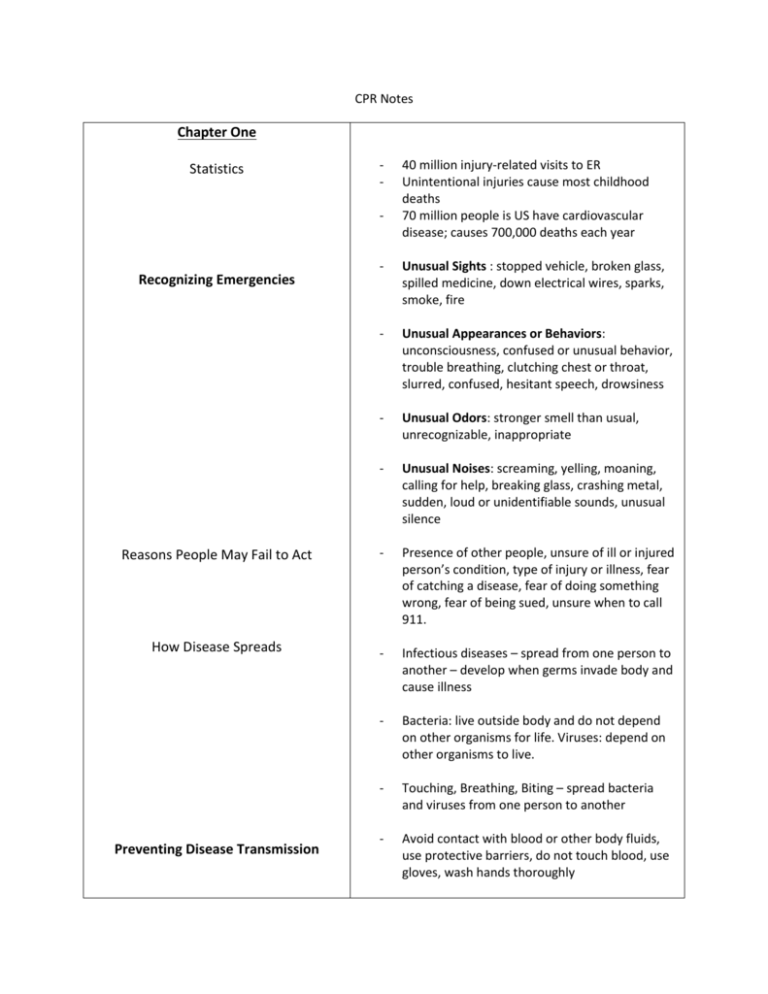
CPR Notes Chapter One Statistics - 40 million injury-related visits to ER Unintentional injuries cause most childhood deaths 70 million people is US have cardiovascular disease; causes 700,000 deaths each year - Unusual Sights : stopped vehicle, broken glass, spilled medicine, down electrical wires, sparks, smoke, fire - Unusual Appearances or Behaviors: unconsciousness, confused or unusual behavior, trouble breathing, clutching chest or throat, slurred, confused, hesitant speech, drowsiness - Unusual Odors: stronger smell than usual, unrecognizable, inappropriate - Unusual Noises: screaming, yelling, moaning, calling for help, breaking glass, crashing metal, sudden, loud or unidentifiable sounds, unusual silence Reasons People May Fail to Act - Presence of other people, unsure of ill or injured person’s condition, type of injury or illness, fear of catching a disease, fear of doing something wrong, fear of being sued, unsure when to call 911. How Disease Spreads - Infectious diseases – spread from one person to another – develop when germs invade body and cause illness - Bacteria: live outside body and do not depend on other organisms for life. Viruses: depend on other organisms to live. - Touching, Breathing, Biting – spread bacteria and viruses from one person to another - Avoid contact with blood or other body fluids, use protective barriers, do not touch blood, use gloves, wash hands thoroughly Recognizing Emergencies Preventing Disease Transmission Good Samaritan Law Activate the EMS System Getting Permission to Give Care - Protects citizens who act the same way that a “reasonable and prudent person” would if that person were in the same situation - Protect you against lawsuits - Calling 911 is the most important step you can take in an emergency - Permission is referred to as “consent” Tell person who you are, how much training you have, what you think is wrong and what you plan to do DO NOT GIVE CARE TO A CONSCIOUS PERSON WHO REFUSES IT, but call 911 Child or infant, get consent from guardian Life-threatening condition – permission is implied (especially if unconscious) - Chapter Two Three Basic Emergency Action Steps - CHECK, CALL, CARE - Check: scene safe? What happened? How many people involved? Immediate danger? - Call: Most important action. Call first or care first? Up to you, usually call first. - Care: provide as much help as possible until trained personnel arrive Identifying Life-Threatening Emergencies - Pg. 18. Review Only Move Injured Person on these 3 conditions - When faced with immediate danger, when you have to get to another person who may have a more serious problem, when it is necessary to give proper care When to Call 9-1-1 - Pg. 20 Review, Person has trouble Breathing Emergency Moves - Walking assist, pack-strap carry, 2-person seat carry, clothes drag, blanket drag, foot drag Chapter 3 - Interview the person, Get Consent to give Care - Check the person from head to toe - A –Airway: open the airway - B – Breathing: Check for movement or breathing - C – Circulation: Check for signs of life(pulse) and severe bleeding - AIRWAY: head tilt/chin lift - BREATHING: Look, Listen, and Feel for breathing signals. Position self so you can hear and feel air as it escapes from the nose and mouth, while at the same time, look to see if the victims chest, clearly rises and falls. - Look, Listen, and Feel for NO MORE than 10 SECONDS. - Person not breathing – give 2 rescue breaths with each breath lasting 1 SECOND - CIRCULATION: not breathing and no pulse. No signs of life, will need to begin CPR. (learn next chapter) Shock - Condition in which the circulatory system fails to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues and vital organs. Caring for Shock - Call 911, have person lie down, control external bleeding, DO NOT GIVE ANYTHING TO EAT OR DRINK - Trouble breathing, slow or rapid breathing, deep or shallow breathing, gasping, wheezing, moist or cool skin, flushed, pale skin, dizziness or lightheadedness Checking a Conscious Person Checking an Unconscious Person CHAPTER FOUR Signals of Breathing Emergencies Choking - Common breathing emergency Conscious Person: encourage them to keep coughing Conscious Adult: combination of 5 back blows followed by 5 abdominal thrusts (pg.60) Chapter 5 Signals of A Heart Attack - CPR for Adults - Follow Emergency Action Steps CHECK – scene and injured person CALL 911 CHECK breathing for no more than 10 seconds, give 2 rescue breaths CARE – when no signs of life - Pg 74 -75 how to do it - 30 compressions/2 rescue breaths; complete 5 cycles in 2 minutes; check for signs of life again - Chest compressions, look for foreign object (finger sweep), 2 rescue breaths. Continue process - Too exhausted to continue Trained personnel has arrived Scene becomes unsafe Person starts to breathe on their own Best way to Check an Unconscious Person - Tap person and shout, “Are you OKAY?” Early CPR is important link in Cardiac Chain of Survival - Helps circulate blood that contains oxygen to vital organs until AED is ready to use - CPR should not be interrupted or stopped until AED is ready to use, another trained responder takes over or you see an obvious sign of life Unconscious Choking Person Continue CPR UNTIL - Chest discomfort lasting more than 3 to 5 minutes Dizziness, lightheadedness, trouble breathing, nausea, sweating