Genetics Test Review - Science with Ms. Wang
advertisement

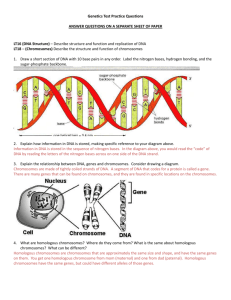
Genetics Test Practice Questions ANSWER QUESTIONS ON A SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER LT16 (DNA Structure) – Describe structure and function and replication of DNA LT18 – (Chromosomes) Describe the structure and function of chromosomes 1. Draw a short section of DNA with 10 base pairs in any order. Label the nitrogen bases, hydrogen bonding, and the sugar-phosphate backbone. 2. Explain how information in DNA is stored, making specific reference to your diagram above. 3. Explain the relationship between DNA, genes and chromosomes. Consider drawing a diagram. 4. What are homologous chromosomes? Where do they come from? What is the same about homologous chromosomes? What can be different? LT17 – (Protein Synthesis) Explain the process of protein synthesis. 5. What information is stored in a gene? How is this information stored? 6. Using the sequence of bases in a gene in DNA, determine the sequence of bases in mRNA. Using the sequence of bases in mRNA, determine the sequence of amino acids Gene/DNA: T A C G T A A T A A T C A G C T A A mRNA: amino acids: 7. Describe the steps of protein synthesis beginning with an order of bases in a gene and ending with an order of amino acids in a protein. (the gene, mRNA and amino acids above as an example) Include in your answer the following vocabulary and how mRNA and tRNA function in this process: (You can also draw and label a diagram instead) transcription translation amino acid mRNA codon tRNA anticodon nucleus cytoplasm ribosome LT15 (Protein and Traits) - Proteins express inherited traits and carry out most cell functions. 8. What is a trait? Provide several examples. 9. Explain how traits are controlled by proteins. Provide an example. 10. Explain how genes on homologous chromosomes control our traits. 11. Diagram and explain the difference between the proteins and traits of someone with sickle cell anemia, and someone with normal blood. LT19 – (Meiosis) Explain the possible allele combinations in an egg or sperm through meiosis LT21 – (Variation) Explain that mutation and recombination increases variation 12. Describe the overall process of meiosis. In your description, address: a. Why meiosis occurs b. Where meiosis occurs (in what types of cells) c. What happens in meiosis I and meiosis II d. The relationship between chromosome numbers for parent and daughter cells. 13. Using words or a diagram, demonstrate that you understand how crossing-over can also increase genetic variability. 14. Pretend that a fruit fly has two pairs of chromosomes: one long, and one short - each with the following genes and genotype: On the long chromosome is the gene for eye color (R/r) and this organism is heterozygous for eye color. On the short is the gene for hairiness (H/h) and the fly is also heterozygous for hair. a. Diagram two different options for how the homologous chromosomes could line up in metaphase I. For each different option, determine the genotypes of the four gametes. 15. Identify different types of mutation that can occur on a DNA strand, and describe how those mutations could affect traits. Punnett Squares LT20 – (Punnett Squares) Explain the outcomes of monohybrid (one trait) and dihybrid (two trait) crosses. 15. Woodrats are medium sized rodents with lots of interesting behaviors. You may know of them as packrats. Let's assume that the trait of bringing home shiny objects (H) is controlled by a single gene and is dominant to the trait of carrying home only dull objects (h). Suppose two heterozygous individuals are crossed. What are the chances that their offspring will bring home shiny objects? dull objects? 16. Travis is heterozygous for Polycystic kidney disease (a dominant allele disease) and homozygous recessive for Sickle Cell Anemia. He and his partner Pei-Yee, are considering having children. Pei-Yee is homozygous recessive for Polycystic kidney disease and heterozygous for Sickle Cell Anemia. Using the following allele key, create the di-hybrid cross for this couple. H – Polycystic kidney h – normal kidney A – normal hemoglobin a – hemoglobin that sickles What are the chances their offspring will have their father’s phenotype (traits)? What are the chances their offspring will have their mother’s phenotype? 17. There are three possible genotypes and phenotypes for wing color in a species of moth: RR = red wings; RY = orange wings; YY = yellow wings. a. What is the pattern of inheritance in this example: complete dominance, incomplete dominance, or codominance? b. An orange-winged moth mates with a red-winged moth. What are the genotypes of the parents? c. What fraction of the offspring will have red wings? Yellow wings? Orange wings? d. If this trait in moths exhibited co-dominance, what color of wings might the RY moths have?