Notes: Laws of Thermodynamics Overview: (W) is a force acting over
advertisement
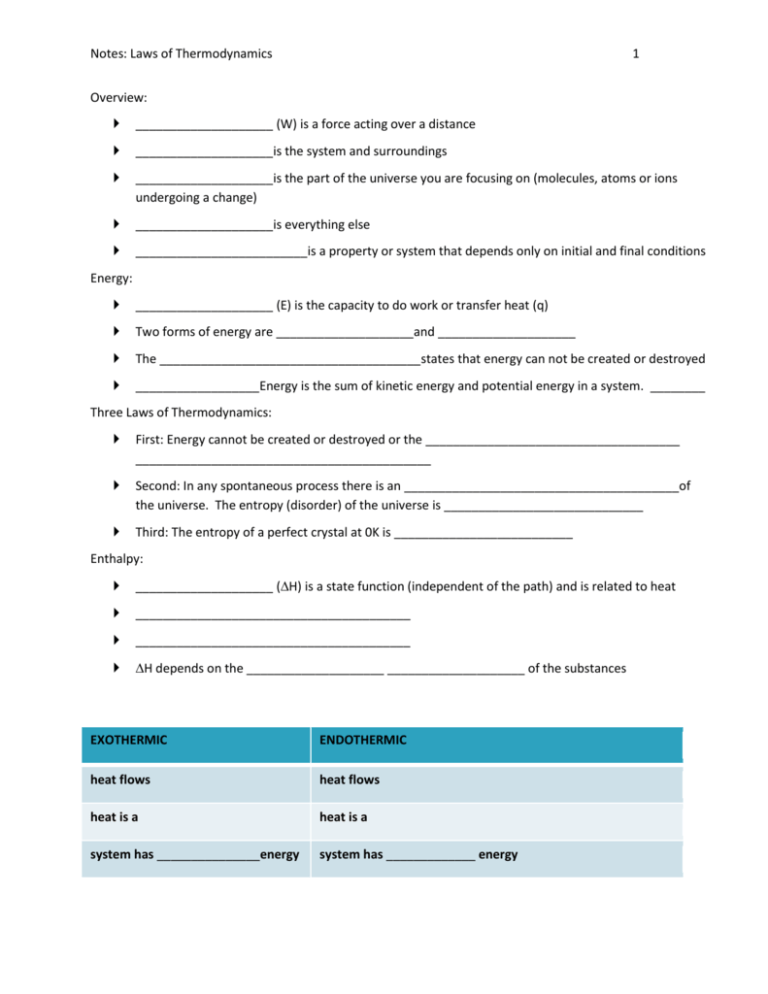
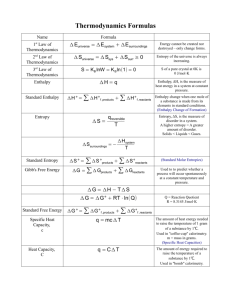
Notes: Laws of Thermodynamics 1 Overview: ____________________ (W) is a force acting over a distance ____________________is the system and surroundings ____________________is the part of the universe you are focusing on (molecules, atoms or ions undergoing a change) ____________________is everything else _________________________is a property or system that depends only on initial and final conditions Energy: ____________________ (E) is the capacity to do work or transfer heat (q) Two forms of energy are ____________________and ____________________ The ______________________________________states that energy can not be created or destroyed __________________Energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy in a system. ________ Three Laws of Thermodynamics: First: Energy cannot be created or destroyed or the _____________________________________ ___________________________________________ Second: In any spontaneous process there is an ________________________________________of the universe. The entropy (disorder) of the universe is _____________________________ Third: The entropy of a perfect crystal at 0K is __________________________ Enthalpy: ____________________ (H) is a state function (independent of the path) and is related to heat ________________________________________ ________________________________________ H depends on the ____________________ ____________________ of the substances EXOTHERMIC ENDOTHERMIC heat flows heat flows heat is a heat is a system has _______________energy system has _____________ energy Notes: Laws of Thermodynamics 2 ΔH is _______________to indicate direction of heat flow ΔH is _______________to indicate direction of heat flow energy released making bonds ____ than energy absorb to break bonds energy absorb to break bonds _____ than energy released making bonds product’s bond energy ____ reactant’s bond energy reactant’s bond energy ____ product’s bond energy H is an ____________________ property – it depends on the number of moles present Exothermic Reaction _______________ _______________ _______________ Endothermic Reaction _______________ _______________ _______________ Hess’s Law: The enthalpy of a reaction _______________ depend on the path, only initial and final conditions. It is a ______________________________ The enthalpy of a reaction is the _______________of the enthalpies of simpler reactions If a reaction is _______________, the sign of the enthalpy is _______________ Notes: Laws of Thermodynamics 3 If the coefficients in a balanced reaction are _______________by an integer, the enthalpy is _______________by the same integer Nitrogen and oxygen react to produce nitrogen dioxide N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2NO (g) H = 180 KJ 2NO (g) + O2 (g) NO2 (g) H = -112 kJ N2 (g) + O2 (g) 2NO2 (g) H = 68 kJ Notice that the compounds on both sides of the yield sign cancel out. The heat of the reaction is the sum of the two steps. Boron and hydrogen react to produce diboron hexahydride (diborane): Reaction H 2B (s) + 3/2O2 (g) B2O3 (s) -1273 kJ B2H6(g) + 3O2(g) B2O3(s) + 3 H2O(g) -2035 kJ H2 (g) + ½O2(g) H2O(l) -286 kJ H2O(l) + H2O (g) 44kJ 2B(s) + 3H2(g) B2H6(g) Label the reactions A, B, C … Determine how to add the reactions to obtain the desired overall reaction Multiply reactions by integers to make coefficients work (also multiply H) Flip reactions to make intermediate compounds cancel (change the sign of H) Notes: Laws of Thermodynamics 4 Heat of Formation: You can use the heat of formation to determine the heat of a reaction. This is a short cut which used the property of state functions (like Hess’s Law) Simply determine the heat of formation DHf for each substance from the provided charts Multiply the coefficient by the heat for each substance Determine the sum of the heat of formation for the reactants and then the products The heat of formation for an element in its standard state is 0kJ. Subtract the heat of formation for the reactants from the products H nH products nH reactants Calculate the change in enthalpy for the following using the ΔHof in the appendix 4NH3(g) + 7O2(g) 4NO2(g) + 6H2O(l)