Period 1/ Period 5 Period 3 Period 4 Period 6 B Topic/Objective
advertisement
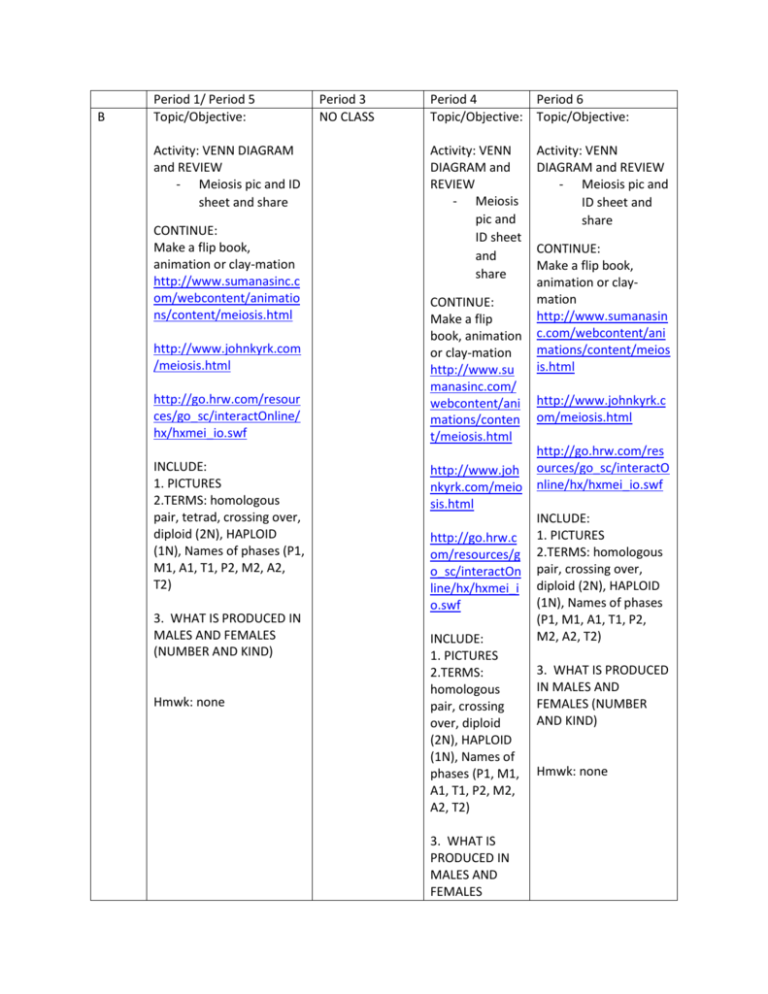
B Period 1/ Period 5 Topic/Objective: Activity: VENN DIAGRAM and REVIEW - Meiosis pic and ID sheet and share CONTINUE: Make a flip book, animation or clay-mation http://www.sumanasinc.c om/webcontent/animatio ns/content/meiosis.html http://www.johnkyrk.com /meiosis.html http://go.hrw.com/resour ces/go_sc/interactOnline/ hx/hxmei_io.swf INCLUDE: 1. PICTURES 2.TERMS: homologous pair, tetrad, crossing over, diploid (2N), HAPLOID (1N), Names of phases (P1, M1, A1, T1, P2, M2, A2, T2) 3. WHAT IS PRODUCED IN MALES AND FEMALES (NUMBER AND KIND) Hmwk: none Period 3 NO CLASS Period 4 Period 6 Topic/Objective: Topic/Objective: Activity: VENN DIAGRAM and REVIEW - Meiosis pic and ID sheet and share CONTINUE: Make a flip book, animation or clay-mation http://www.su manasinc.com/ webcontent/ani mations/conten t/meiosis.html http://www.joh nkyrk.com/meio sis.html http://go.hrw.c om/resources/g o_sc/interactOn line/hx/hxmei_i o.swf INCLUDE: 1. PICTURES 2.TERMS: homologous pair, crossing over, diploid (2N), HAPLOID (1N), Names of phases (P1, M1, A1, T1, P2, M2, A2, T2) 3. WHAT IS PRODUCED IN MALES AND FEMALES Activity: VENN DIAGRAM and REVIEW - Meiosis pic and ID sheet and share CONTINUE: Make a flip book, animation or claymation http://www.sumanasin c.com/webcontent/ani mations/content/meios is.html http://www.johnkyrk.c om/meiosis.html http://go.hrw.com/res ources/go_sc/interactO nline/hx/hxmei_io.swf INCLUDE: 1. PICTURES 2.TERMS: homologous pair, crossing over, diploid (2N), HAPLOID (1N), Names of phases (P1, M1, A1, T1, P2, M2, A2, T2) 3. WHAT IS PRODUCED IN MALES AND FEMALES (NUMBER AND KIND) Hmwk: none (NUMBER AND KIND) C Topic/Objective: meiosis Topic/Objective: Activity: Finish flipbook Activity: VENN DIAGRAM and REVIEW - Meiosis pic and ID sheet and share Hmwk: none CONTINUE: Make a flip book, animation or clay-mation http://www.sum anasinc.com/we bcontent/animat ions/content/me iosis.html http://www.john kyrk.com/meiosi s.html http://go.hrw.co m/resources/go_ sc/interactOnline /hx/hxmei_io.sw f INCLUDE: 1. PICTURES 2.TERMS: homologous pair, crossing over, diploid (2N), HAPLOID (1N), Names of phases (P1, M1, A1, T1, P2, M2, A2, T2) Hmwk: none Topic/Objective: NO CLASS meiosis Activity: Finish flipbook Hmwk: none 3. WHAT IS PRODUCED IN MALES AND FEMALES (NUMBER AND KIND) Hmwk: none PARCC P6: 12- 12:47 Topic/Objective: meiosis Activity: Finish flipbook PARCC Hmwk: none P5: 11:33-12:28 P6: 12:34- 1:30 Topic/Objective: meiosis Topic/Objective: meiosis Activity: Finish flipbook and Activity: Finish flipbook and IF TIME PERMITS START: IF TIME PERMITS START: How are these genes passed on and expressed? GENETICS! How are these genes passed on and expressed? GENETICS! 1. 2. When you are trying to determine what kind of genes you might pass on to your offspring it becomes a probability game… what are the chances of my child having???? There are different types of genetics and ways these genes can be expressed: - Dominance - Incomplete dominance - Sex linked - Multiple allele Heritable diseases can be shown in a family tree diagram. When you are trying to determine what kind of genes you might pass on to your offspring it becomes a probability game… what are the chances of my child having???? There are different types of genetics and ways these genes can be expressed: - Dominance - Incomplete dominance - Sex linked - Multiple allele Heritable diseases can be shown in a family tree diagram. Hmwk: none Hmwk: none B Topic/Objective: terminology NO CLASS Topic/Objective: Topic/Objective: terminology terminology Activity: Pair define and find Activity: Pair define and find Activity: Pair define and find GENETICS TERMINOLOGY: HybridHomozygousHeterozygousGenotypePhenotypeP, F1, F2, F3…. Generations Probability of genetic crosses Linked genesSex- linkedPedigree- GENETICS TERMINOLOGY: HybridHomozygousHeterozygousGenotypePhenotypeP, F1, F2, F3…. Generations Probability of genetic crosses Linked genesSex- linkedPedigree- GENETICS TERMINOLOGY: HybridHomozygousHeterozygousGenotypePhenotypeP, F1, F2, F3…. Generations Probability of genetic crosses Linked genesSex- linkedPedigree- MENDELIAN GENETICS LAWS: Law of Dominance- a dominant characteristic will override a recessive one. Recessive will only be seen when dominant isn’t around. Law of SegregationSeparation of alleles during gamete formation (you only get one from each parent) Law of Independent assortmentjust because you have MENDELIAN GENETICS LAWS: Law of Dominance- a dominant characteristic will override a recessive one. Recessive will only be seen when dominant isn’t around. Law of SegregationSeparation of alleles during gamete formation (you only get one from each parent) Law of Independent assortment- just because you have blonde hair doesn’t mean you’ll have blue eyes. MENDELIAN GENETICS LAWS: Law of Dominance- a dominant characteristic will override a recessive one. Recessive will only be seen when dominant isn’t around. Law of SegregationSeparation of alleles during gamete formation (you only get one from each parent) Law of Independent assortment- just because you have blonde hair doesn’t mean you’ll have blue eyes. VIDEO: Amoeba sistersgenetics and handout Hmwk: TBD VIDEO: Amoeba sistersgenetics and handout Hmwk: TBD blonde hair doesn’t mean you’ll have blue eyes. VIDEO: Amoeba sisters- genetics and handout Hmwk: TBDopic/Objecti ve: Activity: Hmwk: TBD WEEKLY STANDARDS How are the characteristics from one generation related to the previous Students demonstrate understanding of the relationship of DNA and chromosomes in the processes of cellula the next. Students can determine why individuals of the same species vary in how they look, function, and be role of DNA in the unity of life on Earth and use statistical models to explain the importance of variation within species. Ethical issues related to genetic modification of organisms and the nature of science are described. St inheritance and describe the environmental and genetic causes of gene mutation and the alteration of gene e function, patterns, and cause and effect developed in this topic help students to generalize understanding of i science (p. 2, Life Science Topics Storyline). # 1 2 3 4 5 STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Use a model to illustrate the role of cellular division (mitosis) and differentiation in prod maintaining complex organisms. [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include spe mechanisms or rote memorization of the steps of mitosis.] Compare the products of meiosis and mitosis. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the separation of DNA and cellular material, changes in chromosome number, number of cell d number of cells produced in a complete cycle. Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not memorization of the steps of meiosis or mitosis.] Explain how the process of meiosis results in the passage of traits from parent to offspring results in increased genetic diversity necessary for evolution. Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding for characteristic traits passed from parents to offspring. [Assessment Boundary: Assessm include the phases of meiosis or the biochemical mechanism of specific steps in the process Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines th proteins which carry out the essential functions of life through systems of specialized ce Statement: Emphasis is on the cause and effect relationships between DNA, the proteins it resulting traits observed in an organism.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not incl of specific cell or tissue types, whole body systems, specific protein structures and function biochemistry of protein synthesis.] 6 Create a visual representation to illustrate how changes in a DNA nucleotide sequence can in the polypeptide produced. [Clarification Statement: Focus is on how a change in genoty expressed as a phenotype, provides a variation that can be subject to natural selection.] [A Boundary: Assessment does not include enzymes and factors involved or rote memorizatio transcription and translation.] 7 Make and defend a claim based on evidence that inheritable genetic variations may resu genetic combinations through meiosis, (2) viable errors occurring during replication, and caused by environmental factors. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using data to su for the way variation occurs.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the pha the biochemical mechanism of specific steps in the process.] 8 Apply concepts of statistics and probability to explain the variation and distribution of e a population. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the use of mathematics to describe traits as it relates to genetic and environmental factors in the expression of traits.] [Assess Assessment does not include Hardy-Weinberg calculations.] NEXT WEEK REBOBS and SGO http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/BL_26/BL_26.html