Grade-8-Unit-4-The-Pythagorean
advertisement
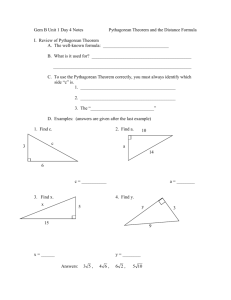
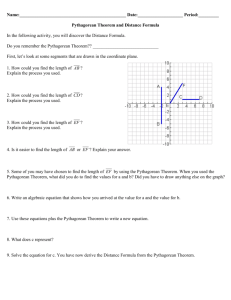
UNIT 4: THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Unit Description/ Topic Length: In this 8-week unit, students will explore the subgroups of the real number system, the Pythagorean Theorem, and the Distance Formula. Students will know that there are numbers that are not rational, and approximate them by rational numbers. They will explore how to simplify and approximate square roots and apply these skills when solving problems involving the Pythagorean Theorem. Class discussions and instructional tasks will provide a deeper understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse for students. They will apply the theorem to problems involving right triangles that model real world problems. They will also find distances and midpoints between two points. Students will recognize that the Pythagorean Theorem is widely used throughout mathematics and in practical applications. Essential Questions: How are real numbers classified? How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real-world and mathematical problems? Key Ideas: In the real number system, all numbers that can be made as a ratio of two integers are rational numbers. All real numbers are either rational or irrational. Any fraction whose denominator has only prime factors of 2s and/or 5s can be written as a terminating decimal. Any number that cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers is an irrational number. Irrational numbers are characterized by a nonterminating and nonrepeating decimal representation. The size of any irrational number can be compared using their rational approximations. In right triangles, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. We can find the distance between any two points in a plane using the Guiding Questions: 1. What is the difference between rational and irrational numbers? 2. How can you determine to which sets of numbers a particular number belongs? 3. How can you find or estimate the square and cubed root of non-negative numbers, including 0? 4. How do you interpret square and cubed roots as both points of a line segment and lengths on a number line? 5. How do you work with radical expressions and approximate them as rational numbers? 6. What is the relationship between the hypotenuse and legs of a right triangle? 7. How do you use deductive reasoning to prove the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse? 8. How can you use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems? 9. How can you utilize the Pythagorean Theorem to determine the distance between any two points? Pythagorean Theorem. NYS Common Core Standards for Mathematics Assessed: Mathematical Content 8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. 8.NS.2 Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., π2). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations. 8.G.6 Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. 8.G.7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 8.G.8 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to find the distance between two points in a coordinate system. Mathematical Practices 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Content The Real Number System Introducing the Real Number System Representing Rational Numbers on the Number Line Writing Rational Numbers as Decimals Skills Distinguish between rational and irrational numbers Convert a rational number to a decimal. Describe the difference between rational and irrational numbers. Convert a repeating decimal into a Introducing Irrational Numbers The Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem and Plane Figures The Pythagorean Theorem and Solids The Distance Formula The Pythagorean theorem on a coordinate plane Understanding the Distance Formula fraction. Plot the approximate location of an irrational number on a number line. Compare the size of two irrational numbers by using a number line. Estimate the value of an irrational number. Identify the legs and hypotenuse of a right triangle. Skills Explain a proof of Pythagorean Theorem. (If a triangle is a right triangle, then a2 + b2 = c2) Explain a proof of the converse of Pythagorean Theorem. (If a2 + b2 = c2, then a triangle is a right triangle) Solve multi-step equations. Calculate the length of a leg of a right triangle using Pythagorean Theorem. Calculate the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle using Pythagorean Theorem. Calculate the diagonal of a threedimensional figure using Pythagorean Theorem. Read and interpret a word problem involving Pythagorean Theorem. Solve word problems involving Pythagorean Theorem. Calculate the distance between two points in a coordinate plane using the Pythagorean Theorem. Vocabulary/ Key Terms integer, irrational numbers, nonterminating decimal, perfect squares, pi, radicals, ratio, rational numbers, real numbers, repeating decimal, square roots, terminating decimal, whole number converse, hypotenuse, leg, principal (or positive) square roots, Pythagorean Theorem, Pythagorean triples, right angle, right triangle, squares, square roots, theorem ordered pair, coordinate plane, coordinate plane ASSESSMENT EVIDENCE Diagnostic and Pre/Post Assessments: The Pre/Post Assessments focus on the two essential questions to gauge students’ understanding of the unit content. Formative Assessments: Short- and Extended-Response questions used throughout the unit. Quizzes Formative Assessment Lesson 1: Repeating Decimals http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?taskid=421&subpage=concept This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to: Translate between decimal and fraction notation, particularly when the decimals are repeating. Create and solve simple linear equations to find the fractional equivalent of a repeating decimal. Understand the effect of multiplying a decimal by a power of 10. Formative Assessment Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem (Square Areas) http://map.mathshell.org/materials/lessons.php?taskid=408&subpage=concept This lesson unit is intended to help you assess how well students are able to: Use the area of right triangles to deduce the areas of other shapes. Use dissection methods for finding areas. Organize an investigation systematically and collect data. Deduce a generalizable method for finding lengths and areas (The Pythagorean Theorem.) Summative Assessments: Unit Test Fourth Quarter Summative Test Performance Tasks o #1: The Real Number System o #2: Proving the Pythagorean Theorem o #3: Applying the Pythagorean Theorem TEACHING PLAN Teaching and Learning Activities: 1. Administer the Preassessment. 2. Discuss the real number system. Students engage in learning activities that build capacity for rigor in the following concepts and skills: rational and irrational numbers, determining to which sets of numbers a particular belongs, square root and cubed root, approximating irrational numbers as rational numbers, converting repeating decimals to fractions 3. Administer Formative Assessment Lesson #1 titled Repeating Decimals. a. Before the lesson, students work individually on a task designed to reveal their current levels of understanding and difficulties. b. Review their solutions and write questions to help students improve their work. c. During the lesson, the students first work in pairs or threes on the same task. Then working in the same small groups, they analyze work produced by other students on the task. d. In a whole-class discussion, students compare and evaluate the methods they have seen and used. e. In the final part of the lesson, students review their initial, individual solutions and use their learning to complete a new task. 4. Have students work on Performance Task #1: The Real Number System. 5. Review the properties of right triangles. 6. Discuss at least one theorem proof of the Pythagorean Theorem (e.g. Pythagoras, Garfield) and have students explain why this proof is mathematically sound. 7. Students investigate the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem: If a, b, and c are lengths of the sides of a triangle and a2 + b2 = c2, then the triangle is a right triangle. 8. Administer Formative Assessment Lesson #2 titled The Pythagorean Theorem (Square Areas). 9. Have students work on Performance Task #2: The Pythagorean Theorem. 10. Develop the distance formula with the class using the Pythagorean Theorem. Teach the distance formula incrementally, beginning with what students already know and progressing from more concrete representations to more abstract ones. 11. Have students work on Performance Task #3: Applying the Pythagorean Theorem. 12. Assess students on the unit by administering the unit test. Time should be provided for students to investigate and discuss a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. There needs to be strong emphasis on mathematical discourse in the classroom. Students need to be held accountable for the use of precise vocabulary and meanings of numbers, terms, and variables and the quantities they represent. Students should be asked to explain their understanding in a written form on a regular basis. This includes but is not limited to short answer responses, explanations of concepts/new ideas (e.g., a letter to an absent classmate), or full page journals where they explain different ideas within the unit. Materials Needed: Connected Math Project 3 (CMP3) Unit: Looking for Pythagoras NYS Common Core Math Module 1: Integer Exponents and Scientific Notation Impact Mathematics Course 3 Integrated Algebra Textbook MathXL (Pearson’s online homework, tutorial, and assessment system) Scientific Calculators Graph Papers Web Resources: Mathematics Assessments Resource Service (MARS) BOCES Deep Curriculum Alignment Project for Mathematics Illustrative Mathematics State of Nevada Department of Education Math Resources New Jersey Center for Teaching & Learning Teching the CCCS CALENDAR Time Spent on Standard 3 weeks Standards 8.NS.1 8.NS.2 Topics To Cover The Real Number System Introducing the Real Number System Representing Rational Numbers on the Number Line Writing Rational Numbers as Decimals Introducing Irrational Numbers Resources Connected Math Project 3 (CMP3) Unit – Looking for Pythagoras: The Pythagorean Theorem [8.NS.1, 8.EE.2, 8.G.6, 8.G.7, 8.G.8] 5 weeks 8.G.6 8.G.7 8.G.8 The Pythagorean Theorem The Pythagorean Theorem and Plane Figures The Pythagorean Theorem and Solids The Distance Formula The Pythagorean theorem on a coordinate plane Understanding the Distance Formula