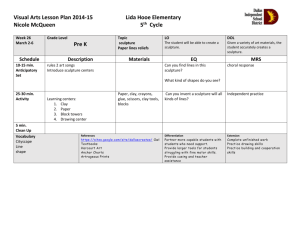
Sculpture Review for Final Types of Sculpture: Representational: Art
advertisement
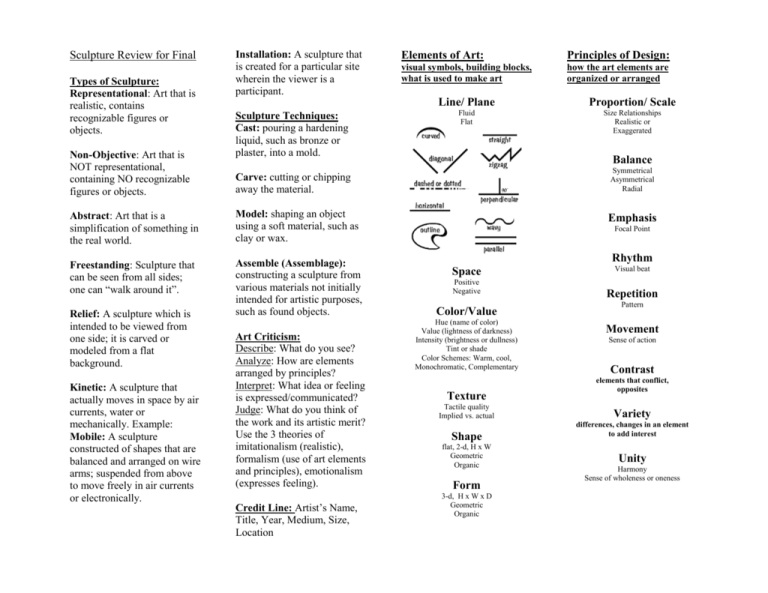
Sculpture Review for Final Types of Sculpture: Representational: Art that is realistic, contains recognizable figures or objects. Non-Objective: Art that is NOT representational, containing NO recognizable figures or objects. Installation: A sculpture that is created for a particular site wherein the viewer is a participant. Sculpture Techniques: Cast: pouring a hardening liquid, such as bronze or plaster, into a mold. Elements of Art: Principles of Design: visual symbols, building blocks, what is used to make art how the art elements are organized or arranged Line/ Plane Proportion/ Scale Fluid Flat Size Relationships Realistic or Exaggerated Balance Carve: cutting or chipping away the material. Symmetrical Asymmetrical Radial Abstract: Art that is a simplification of something in the real world. Model: shaping an object using a soft material, such as clay or wax. Emphasis Freestanding: Sculpture that can be seen from all sides; one can “walk around it”. Assemble (Assemblage): constructing a sculpture from various materials not initially intended for artistic purposes, such as found objects. Relief: A sculpture which is intended to be viewed from one side; it is carved or modeled from a flat background. Kinetic: A sculpture that actually moves in space by air currents, water or mechanically. Example: Mobile: A sculpture constructed of shapes that are balanced and arranged on wire arms; suspended from above to move freely in air currents or electronically. Art Criticism: Describe: What do you see? Analyze: How are elements arranged by principles? Interpret: What idea or feeling is expressed/communicated? Judge: What do you think of the work and its artistic merit? Use the 3 theories of imitationalism (realistic), formalism (use of art elements and principles), emotionalism (expresses feeling). Credit Line: Artist’s Name, Title, Year, Medium, Size, Location Focal Point Rhythm Space Positive Negative Visual beat Repetition Color/Value Pattern Hue (name of color) Value (lightness of darkness) Intensity (brightness or dullness) Tint or shade Color Schemes: Warm, cool, Monochromatic, Complementary Movement Texture Tactile quality Implied vs. actual Shape flat, 2-d, H x W Geometric Organic Form 3-d, H x W x D Geometric Organic Sense of action Contrast elements that conflict, opposites Variety differences, changes in an element to add interest Unity Harmony Sense of wholeness or oneness