02A What is Science LP - Educational Excellence
advertisement

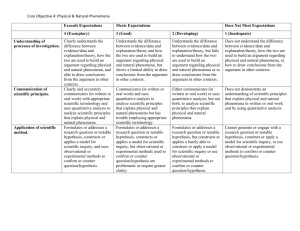
Course Title: Advanced Animal Science Lesson Title: What is Science? TEKS Addressed in Lesson: 130.7 c 2 a b c d http://ritter.tea.state.tx.us/rules/tac/chapter130/index.html Lesson Objectives. The student will be able to: – – – – – Summarize the definition and importance of science Describe a hypothesis Describe a scientific theory Compare hypotheses and theories Synthesize a hypothesis for given situations Tools and Equipment PowerPoint: What is Science? Projector Key Terms / Vocabulary Science: "use of evidence to construct testable explanations and predictions of natural phenomena, as well as the knowledge generated through this process." Scientific Method: a system of observation and experimentation used to answer questions about natural phenomena. Hypothesis: a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation Scientific Theory: refers to a comprehensive explanation of some aspect of nature that is supported by a vast body of evidence. Many scientific theories are so well established that no new evidence is likely to alter them substantially Engage / Interest Approach/Anticipatory Set Facilitate classroom discussion on how they perceive science. Do they feel it is irrelevant? Do they feel it has little effect on what they do every day? Bring up examples of science and why it is an important subject to understand. Discuss how it affects every day life: the fuel we drive, the food we eat, the electricity we all use every day has come from scientific advancements. Science isn’t just limited to chemistry and biology – it’s a way of thinking. Today we will uncover that method of thinking. Explore & Explain / Teaching Plan and Strategy / Presentation of New Material Lecture Format. Review over the “What is Science?” PowerPoint in class. How do we define science? • Science, as defined by the National Academy of Sciences, is the "use of evidence to construct testable explanations and predictions of natural phenomena, as well as the knowledge generated through this process." What does it really mean? • Science is a tool to understand how the universe works around us. • Science is a system of acquiring knowledge. • A system of observation and experimentation used to describe and explain phenomena. • Scientific discovery takes a long time, and is the interconnection of many different studies and existing knowledge Why? Why is it important? • Through explanations and knowledge gained through science, we are able to improve our lives. • What has science done for you? • Electricity • Observations and experimentation by Ben Franklin and Alessandro Volta in the 1700s pioneered the way for harnessing the power of electricity. • Modern Medicine • Through science, we enjoy the benefits of: • Vaccines • Eradication of diseases such as smallpox • Extended lives through the treatment of once deadly diseases • Many people alive today are here because of the benefits that modern medicine provided them. • Modern Agriculture • Science has played a key role in developing a safe and abundant food supply in developed countries. • Specialized biologists (plant breeders) started developing high-yielding varieties of crops through new techniques in breeding. • Today biotechnology plays an essential role in further transforming our food system, ensuring we have a plentiful and safe food supply for future generations. Impact of Science on Society • Those were some examples of products of modern science. Almost everything we enjoy today is the result of science. • Science also enables us to make informed personal and policy decisions concerning health, agriculture, economics, etc. • As a result, it is extremely important to understand science and distinguish between “bad science” and “good science”. • Groups can take advantage of ignorance to push their agenda. The Scientific Method • As we discussed, science is a system of observation and experimentation. • This system of observation and experimentation is the scientific method. The scientific method is the engine behind science. • List out what you feel are the steps of the scientific process. Define a Question “How do I synthesize a pesticide to attack a specific pest?” Observe Information gathering (literature review) Forming of a Hypothesis “Getting pimples is unaffected by eating greasy food” Test the Hypothesis Perform an experiment and collect data. The experiment must be reproducible. Data Analysis Perform statistical analysis. Interpret the Data and its Implications This will provide a starting point for further hypotheses. Publish Results This allows others to learn about your discovery and develop further advanced research. Retest An important part of the scientific process is testing the work of others to ensure you get the same results. Hypothesis • After your observations/researching existing information about issue, you will form an educated guess to answer your question. • Hypothesis is defined as: “a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation”. • Basically, it is a suggested solution for an unexplained occurrence that does not fit into current accepted scientific theory. • It must be worded so that it can be tested, and subsequently answered. • This is called falsifiability and testability. • In order to make it testable, you express your hypothesis using an independent variable and dependent variable. • Independent Variable (IV): variable you change • Dependent Variable (DV): you observe changes of this variable with the changes of the IV. Example Scientific Experiment • Define a Question: “What happens if I water a plant with different liquids?” • Information gathering: research on the methods water is absorbed through the plant • Hypothesis: “Normal water with little to no additives is the most effective liquid to water”. Types of Variables: Independent: This is the variable you change. Give example. Dependent: You collect data on this variable based off of the changes you make to the independent variable. Control: Unchanged, constant Implications/Conclusion: What would your conclusion be given for this data? o Water is the best method of watering your plant. Recommendations? o Water only with water. Theories: • A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation for natural phenomena. – Theory is the result of repeatedly testing and confirming hypotheses with the use of the scientific method. • Theory Examples: – Heliocentric Theory – Germ theory of disease – Cell theory Elaborate / Activity/Application/ Student Engagement /Laboratory • In groups, develop a plan for a scientific experiment. • Draw out and explain all the steps for the scientific theory for your experiment. • Remember: the scientific process is methodical and intricate. It’s important to make sure the experiment is accurate. Evaluation / Summary Classroom questioning: • What is a scientific hypothesis? • What are the steps of the scientific theory? • Describe each step of the scientific theory – Provide examples • Compare and contrast hypotheses and theories References/Additional Materials / Extended Learning Opportunities/ Enrichment University of California, Berkeley: Understanding Science http://undsci.berkeley.edu/index.php Livescience: What is a Scientific Theory? http://www.livescience.com/21491-what-is-ascientific-theory-definition-of-theory.html College & Career Readiness Standard Science IV 1 a ©Texas Education Agency, 2015