Binder Page 2- The Science of Human Origins
advertisement

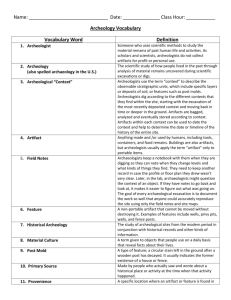
Name: _____________________ Binder Number: ______ The Science of Human Origins Introduction History is the study of people and events through the course of time. It tells us what they did and what happened to them. Historians are people who study and write about the human past. But what about the time before people developed writing? This is an important question to ask since most of human history has occurred without the invention of handwriting. How do current-day historians know and understand the lives of people who lived before people first began to write? Define: Prehistory Humans first appeared on Earth around 150,000 years ago How do we find out about human origins? What we know about the earliest humans comes from the things they left behind and from the hard work of scientists who have worked to uncover these clues. By discovering and interpreting these items, scientists can piece together a large amount of information such as the animals they hunted, the weapons they used, and the homes they ate at. Let’s find out more about the 3 main types of scientists who work in the field of human origins: Archaeologists Excavate sites in search of artifacts that help determine the way people once lived. Anthropologists Humans first invented writing around 5,200 years ago Paleontologists Study the____________________ of a people. Study __________________ and ___________________ life. Excavate Culture- Culture includes items such as: o Food o o o o Study __________________. Fossils- the naturally preserved Artifact- Artifact examples: o Tools o o remains of animals or plants. How we know old something is? ancient fossils and artifacts is called radiocarbon dating. One do method thathow scientists use to date Here’s how it works: All living things on Earth are made up of carbon. Most carbon on Earth is not radioactive, but a very small percentage is. As a result, as living things take in carbon, they also take in a small amount of radioactive carbon. When these life forms die, they stop taking in carbon. The carbon in their bodies at the time of their death will remain in their bodies until they decompose or become fossilized. The radioactive carbon in their body, however, will begin to decay and disappear at a very consistent rate. This allows scientists to compare the normal carbon to the decaying radioactive carbon that is disappearing, giving us the precise age of the item. Radiocarbon dating can accurately tells us the age of items such as bone, cloth, wood, and plant fibers. Simply put, Radiocarbon dating…. Layering Another technique scientists use to find out how old an artifact may be is called layering. Have you ever thought "how do artifacts become buried so far underground?" The answer is not that the artifacts sink, but that the ground builds up in layers over time. In the picture to the right, the soil resembles a layer cake, with the oldest layers on the bottom and more recent deposits on top. The accumulation of soil is a natural process that results from items dying like grass and leaves, and the deposit of blowing dust. Household waste such as ashes from kitchen fires, food remains, and broken glass and ceramics also contribute to the accumulation of layers. Why is this important? Soil layers are the most basic tools available for measuring the passing of time because the deepest layers of soil are older than the layers on top. For this reason, archaeologists excavate one layer at a time, removing all soil from one time period before excavating the layers that preceded it. Old Older Oldest Simply put, layering is…