BIOL 2304 Blood The Circulatory System Anatomy – enclosed
advertisement
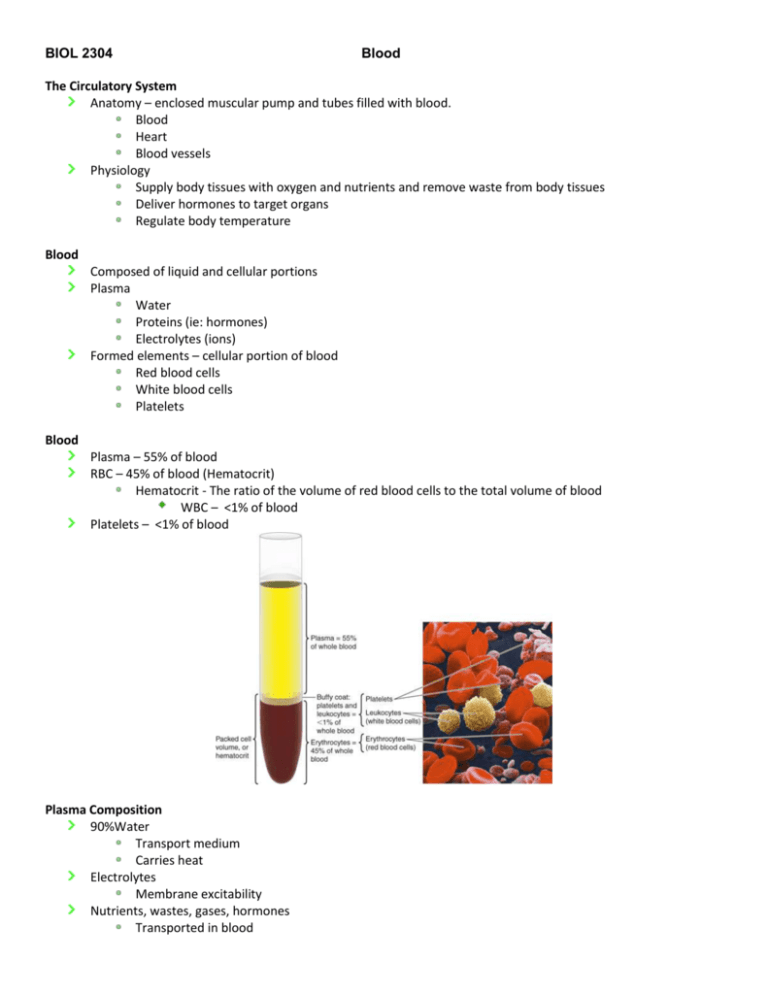
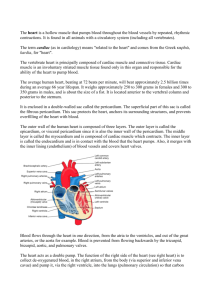
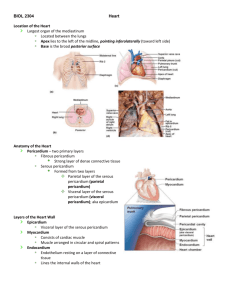
BIOL 2304 Blood The Circulatory System Anatomy – enclosed muscular pump and tubes filled with blood. Blood Heart Blood vessels Physiology Supply body tissues with oxygen and nutrients and remove waste from body tissues Deliver hormones to target organs Regulate body temperature Blood Composed of liquid and cellular portions Plasma Water Proteins (ie: hormones) Electrolytes (ions) Formed elements – cellular portion of blood Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets Blood Plasma – 55% of blood RBC – 45% of blood (Hematocrit) Hematocrit - The ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood WBC – <1% of blood Platelets – <1% of blood Plasma Composition 90%Water Transport medium Carries heat Electrolytes Membrane excitability Nutrients, wastes, gases, hormones Transported in blood 6-8% Plasma proteins Albumins – contribute to osmotic pressure Globulins – clotting factors, antibodies Fibrinogen – inactive precursor for fibrin RBC Structure and Function Biconcave discs Provides larger surface area for diffusion of O2 across the membrane Thinness of cell enables O2 to diffuse rapidly between the exterior and innermost regions of the cell Flexible membrane Allows RBCs to travel through narrow capillaries without rupturing in the process Hemoglobin Iron containing pigment found only in RBCs Consists of 2 parts Globin portion Protein composed of four highly folded polypeptide chains Heme groups Four iron-containing nonprotein groups Each is bound to one of the polypeptides Formation dependent upon Vitamin B12 WBC Structure and Function Colorless and larger than RBCs Protect body from microorganisms 5 different types of circulating leukocytes, either Granulocytes or Agranulocytes Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils Monocytes Lymphocytes Neutrophils Most numerous WBC Phagocytize and destroy bacteria Nucleus—has two to six lobes Granules pick up acidic and basic stains Eosinophils Compose 1–4% of all WBCs Play roles in ending allergic reactions, parasitic infections Basophils About 0.5% of all leukocytes Nucleus—usually two lobes Granules secrete histamines Function in inflammation mediation Similar in function to mast cells Lymphocytes Compose 20–45% of WBCs The most important cells of the immune system Nucleus—stains dark purple Effective in fighting infectious organisms Act against a specific foreign molecule (antigen) Monocytes Compose 4-8% of WBCs The largest leukocytes Nucleus—kidney shaped Transform into macrophages Phagocytic cells Leukocytes Platelets Cell fragments Lack nuclei Have organelles and cytosolic enzymes for generating energy and synthesizing secretory products Involved in blood clotting (thrombosis) Hematopoiesis aka Hemopoiesis Hematopoiesis - the formation of blood cells in the living body (especially in the bone marrow). All blood cells originate in bone marrow. All originate from one cell type. Blood stem cell (pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell) Lymphoid stem cells Give rise to lymphocytes Myeloid stem cells Give rise to all other blood cells Heart - Location of the Heart Largest organ of the mediastinum Located between the lungs Apex lies to the left of the midline Base is the broad posterior surface Anatomy of the Heart Pericardium—two primary layers Fibrous pericardium Strong layer of dense connective tissue Serous pericardium Formed from two layers Parietal layer of the serous pericardium Visceral layer of the serous pericardium Layers of the Heart Wall Epicardium Visceral layer of the serous pericardium Myocardium Consists of cardiac muscle Muscle arranged in circular and spiral patterns Endocardium Endothelium resting on a layer of connective tissue Lines the internal walls of the heart Myocardium Forms a thick layer called myocardium Striated like skeletal muscle Contractions pump blood through the heart and into blood vessels Contracts by sliding filament mechanism Cardiac Muscle Tissue Cardiac muscle cells Short, branching, with one or two nuclei Cells join at intercalated discs Complex junctions that connect one cell to the next Intercalated disc - an undulating double membrane separating adjacent cells in cardiac muscle fibers. Intercalated discs support synchronized contraction of cardiac tissue Cells are separated by delicate endomysium Binds adjacent cardiac fibers Contains blood vessels and nerves Gross Anatomy of the Heart Atria - Two thin, upper chambers that receive blood Right atrium receives oxygen poor blood from body Left atrium receives oxygen rich blood from lungs Ventricles - Two thick, lower chambers that pump blood Right ventricle pumps oxygen poor blood to lungs Left ventricle pumps oxygen rich blood to body Left and right sides of heart separated by septa Septa - thin walls or partitions between the internal chambers (interventricular septum) Structure of Heart Wall Left ventricle — three times thicker than right Exerts more pumping force Because it requires more force to send blood to the body than to the lungs Flattens right ventricle into a crescent shape Right Atrium Receives oxygen poor blood from superior and inferior vena cava Pectinate muscles Ridges inside anterior of right atrium Crista terminalis Landmark used to locate veins entering right atrium Fossa ovalis Depression in interatrial septum – a remnant of foramen ovale Right Ventricle Receives blood from right atrium through the tricuspid valve Pumps blood into pulmonary circuit via pulmonary trunk Internal walls of right ventricle Trabeculae carneae Papillary muscles Chordae tendineae Pulmonary semilunar valve Located at opening of right ventricle and pulmonary trunk Left Atrium Makes up heart’s posterior surface Receives oxygen-rich blood from lungs through pulmonary veins Opens into the left ventricle through Mitral valve (left atrioventricular valve/bicuspid valve) Left Ventricle Forms apex of the heart Internal walls of left ventricle Trabeculae carneae Papillary muscles Chordae tendineae Pumps blood through systemic circuit via Aortic semilunar valve (aortic valve) Heart Valves Each valve composed of Endocardium with connective tissue core Atrioventricular (AV) valves Between atria and ventricles Aortic and pulmonary valves At junction of ventricles and great arteries (pulmonary and aortic arteries) Vasculature of the Heart Vasculature of the Heart Functional blood supply Coronary arteries Arise from the aorta Located in the coronary sulcus Main branches Left and right coronary arteries