Progression and Methods in the Four Operations.
advertisement
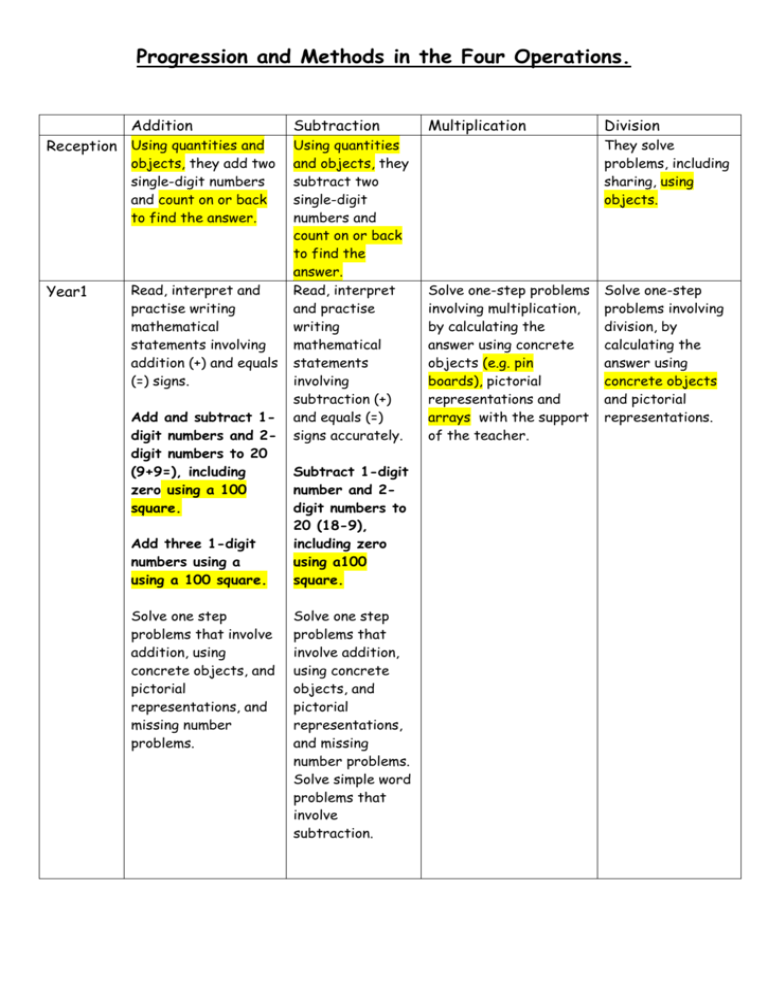
Progression and Methods in the Four Operations. Addition Reception Using quantities and objects, they add two single-digit numbers and count on or back to find the answer. Year1 Read, interpret and practise writing mathematical statements involving addition (+) and equals (=) signs. Add and subtract 1digit numbers and 2digit numbers to 20 (9+9=), including zero using a 100 square. Add three 1-digit numbers using a using a 100 square. Solve one step problems that involve addition, using concrete objects, and pictorial representations, and missing number problems. Subtraction Using quantities and objects, they subtract two single-digit numbers and count on or back to find the answer. Read, interpret and practise writing mathematical statements involving subtraction (+) and equals (=) signs accurately. Subtract 1-digit number and 2digit numbers to 20 (18-9), including zero using a100 square. Solve one step problems that involve addition, using concrete objects, and pictorial representations, and missing number problems. Solve simple word problems that involve subtraction. Multiplication Division They solve problems, including sharing, using objects. Solve one-step problems involving multiplication, by calculating the answer using concrete objects (e.g. pin boards), pictorial representations and arrays with the support of the teacher. Solve one-step problems involving division, by calculating the answer using concrete objects and pictorial representations. Year 2 Add numbers using a 100 square, including: -a two-digit number and ones -a two-digit number and tens -two two-digit numbers -adding three onedigit numbers Begin to use column addition without carrying. Solve problems with addition. Show that addition of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) . Recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and missing number problems. Calculate the value of unknown numbers in a number sentence. Year 3 Add numbers with up to three digits, using column addition. Estimate the answer to a calculation and use inverse operations to check answers. Solve problems, including missing number problems, using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction. Subtract numbers using a 100 square, including: -a two-digit number and ones -a two-digit number and tens -two two-digit numbers -adding three one-digit numbers Calculate mathematical statements for multiplication within the multiplication tables and write them using the multiplication (×),and equals (=) signs. Solve problems with subtraction. Show subtraction cannot be done in any order Solve problems involving multiplication using arraysand multiplication and division facts, including problems in contexts. Solve problems involving division, using the sharing of practical resourcesand division facts, including problems in contexts. Multiply 1-digit and 2-digit numbers by 10 or 100; understanding the effect. (To be taught first) Write and calculate mathematical statements for division using the multiplication tables that they know. Recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and missing number problems. Calculate the value of unknown numbers in a number sentence. Subtract numbers with up to three digits, using column subtraction. Estimate the answer to a calculation and use inverse operations to check answers. Solve problems, including missing number problems, Show that multiplication of two numbers can be done in any order (commutative) . Write and calculate mathematical statements for multiplication, using the multiplication tables that they know. Multiply a two-digit number by a one-digit numbers, using the grid method. Calculate mathematical statements for division within the multiplication tables and write them using the division (÷) and equals (=) signs. Show that division cannot be done in any order. Divide a two-digit number by a onedigit number, using the bus stop method. Solve problems, including missing using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction. Year 4 Add numbers with up to 4 digits using column addition. Estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation. Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. Year 5 Add whole numbers with more than 4 digits, using column addition. Solve addition and subtraction multistep problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. Subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using column subtraction. Estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation. Solve addition and subtraction twostep problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. Subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits, using column subtraction. Solve addition and subtraction multistep problems in contexts, deciding which operations Solve problems, including missing number problems, involving multiplication, including integer scaling problems and correspondence problems in which n objects are connected to m objects. Multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one-digit number, using the grid method. Solve problems involving multiplying and adding, including using the distributive law to multiply two digit numbers by one digit, integer scaling problems and harder correspondence problems such as n objects are connected to m objects. Multiply whole numbers and those involving decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 (To be taught first). Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a oneor two-digit number using the grid method. number problems, involving multiplication and division, including integer scaling problems and correspondence problems in which n objects are connected to m objects. Divide two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one-digit number using the bus stop method. Solve problems involving multiplying and adding, including using the distributive law to multiply two digit numbers by one digit, integer scaling problems and harder correspondence problems such as n objects are connected to m objects. Divide whole numbers and those involving decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 (To be taught first). Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit number using the bus stop method and and methods to use and why. Year 6 Add negative integers (using a number line if required). Use estimation to check answers to calculations and determine in the context of a problem. Carry out combined calculations involving the four operations and state the order of operations. Subtract negative integers (using a number line if required). interpret remainders appropriately for the context. Multiply numbers with at least 4digits by a 2-digit whole number using the grid method. Divide numbers up to 4-digits by a 2-digit number using chunking, and interpret Use estimation to remainders as check answers to Multiply numbers whole number calculations and with up to 2 decimal remainders, determine in the places by 1-digit fractions, context of a and 2-digit whole decimals or by problem. numbers using the rounding. grid method. Carry out Divide numbers combined Use estimation to with up to two calculations check answers to decimal places involving the four calculations and by 1-digit (bus operations and determine in the stop) and 2-digit state the order context of a (chunking) whole of operations. problem. numbers. Use estimation to check answers to calculations and determine in the context of a problem whether an answer should be rounded or written as a fraction or a decimal.








