BP = (age x 2) - WordPress.com
advertisement

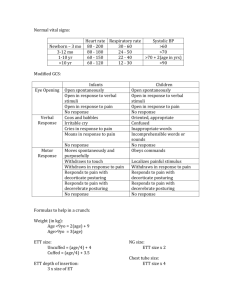
Paediatric and Neonatal Resus (as adults if >8yrs) Epidemiology Most arrests are due to hypoxia, hypotension, acidosis, underlying illness (as opposed to cardiac causes in adults); usually relieved by correction of A+B Most common dysrhtymias are severe bradycardia, asystole; VF 7-15%; ventricular arrhythmia more common if cardiac disease, poisoning, low voltage electrocution; SVT may cause shock; survival to discharge more common in children and adolescents, than infants and adults; 2% survival without severe neuro deficit 5-10% neonate require resus; 1% require intensive resus Weight Newborn: 3.5kg BLS / ALS 1yr: 10kg 1-10yrs: (age + 4) x 2 >10yrs: age x 3 A: Turn on side if drowning; no finger sweep unless solid FB seen; infant = neutral, child = sniff B: look, listen, feel 10secs Do 5x rescue breaths (? Now 2) in children (not adult) RR 10-12 (6-10 in adults) once ETT (every 15 compressions) C: start CPR if unresponsive / not breathing properly ALS provider can do pulse check Use brachial / femoral pulse if <1yr Start CPR if <60bpm with poor perfusion (absent in adults) Pauses should be <10secs; Swap providers Q2min; Depth 1/3 AP diameter; finger <1yr, 1 or 2 hands thereafter; lower ½ sternum (<1yr go 1 finger below internipple line); 100/min (100-120 in children); duty cycle 50%; 5 cycles / 2mins 3:1 in neonate; 15:2 in children; 30:2 in adult / 1 health care provider Paddle size: 4.5cm infant, 8cm child; All shocks 4J/kg; High dose adrenaline not recommended Rhythm check every 2mins (only check pulse if perfusable rhythm) Help 1st as likely cardiac if: witnessed collapse or known cardiac condition in child (and in all adults) BLS 1st as likely respiratory: unwitnessed arrest in child (not in adults) get help after 1min CPR Continue until: breathes normally / impossible to continue / >20mins / no response to 2 doses adrenaline / core T 30deg with hypothermia A B Neutral position if infant, sniffing for children; measure guedel from centre of mouth to angle of mandible Use continuous ETCO2 monitoring; limit intubation attemps to 30secs as can go blue fast; press on larynx not cricoid, but avoid submental digital pressure; aim to have audible leak as otherwise at risk of oedema; use Macintosh blade once >6yrs; bradycardia common during ETT so consider atropine; jaw thrust may be superior to chin lift; NPA less useful in children and may cause bleeding from adenoid tissue BVM size: round mask 000-2 for infants / young child; shaped mask 3-5 for young child / adult Bag size: 250ml in prem / 500ml in neonate or infant / 1500ml in child ETT: Mm: (age / 4) + 4 (uncuffed) + 3.5 (cuffed) Decr size by 0.5mm if severe croup / epiglottitis Length: (age / 2) + 12 or 15 Weight ETT width ETT length Crico tube LMA Larngoscope RR TV PIP PEEP I:E ICC (4x ETT) <28/40 34-38/40 2.5mm 6.5-7cm 3.5mm 7-8cm 0 Miller 0 Miller 20ml/kg >38/40 3.5kg 3.5-4mm 9cm 3.5mm 1 1 Miller 30-60 10ml/kg 15 3-5 1:2 8-12F 1yr 10kg 4mm 11cm 1.5-2 20-30 10ml/kg 3-5 1:2 14-20F 5yr 20kg 5mm 15cm 4mm 2-2.5 2 Miller 12-20 10ml/kg 20-25 3-5 1:2 20-28F 10yr . 30kg . 6mm 16-17cm . . 2.5-3 . 2 Mac . 10-12 10ml/kg 3-5 1:2 28-32F Cuffed and uncuffed tubes equally safe, except in neonates; remember to place NGT LMA: <5kg =1; 5-10kg = 1.5; 10-20kg = 2; 20-30kg = 2.5; 30-50kg = 3; 50-70kg = 4; 70-100kg = 5; >100kg = 6 Surgical: use cricothyroid puncture if <12yrs Ventilator: have small air leak; NG mandatory; use p control ventilatory for infants C D E 2Y survey Post-resus mng BP = (age x 2) + 85 UO = 2ml/kg/hr in infant, 1ml/kg/hr in child IVA: use IO if can’t get IVL in <90 secs if critically ill child IO: insert in antmedial prox tibia 1 finger (2-3cm) beneath tibial tuberosity sup to med malleolus antlat distal femur 3cm above lateral condyle Will not be able to aspirate from tibia if >5yrs due to fatty marrow; not reliable for PO2, PCO2, LFT; same onset of drugs; can give up to 10-15ml/min; flush all drugs with 10ml N saline; CI = OP, osteogenesis imperfecta, #, recent same bone IO, cellulitis, burns; complications rare (<1%; tibial #, growth retardation, compartment syndrome, cellulitis, OM, extravasation of fluid) Shock: 20ml/kg IVF if still shocked after 40ml/kg, use inotropes / blood products 4ml/kg PRBC incr Hb 1 10ml/kg plt incr plt 50 Fluids: avoid 5% dex (worsens neuro outcome, causes 2Y diuresis; hypoNa) Maintenance: use 0.45% saline + 2.5-5% dex in children Use 0.18% saline + 10% dex in neonates Shocks: unstable SVT: 0.5-1J/kg; pulsatile VT 0.5-2J/kg Check: LOC, pupils, posture, glu Beware T loss Head to toe B: aim SaO2 94-98% (PaO2 60-80mmHg); aim normocarbia C: maintain adequate perfusion D: therapeutic hypothermia (32-34) within 6hrs of cardiac arrest, and maintain up to 72hrs; avoid hypo/hyperG Neonatal resus Epidemiology: required in 10% births; extensive resus in 1%; in >50% VLBW Causes: iNborn errors of metabolism, Electrolytes, OD, Seizures, Enteric, Cardiac, Recipe (formula etc…), Endocrine, Trauma, Sepsis Cyanosis causes: airway obstruction (eg. Laryngeal web), congenital heart disease, pul disorders (eg. Aspiration, pneumonia, diaphragmatic hernia), CNS (ICH), hypoG, sepsis/shock, metHb Perinatal asphyxia: umbilical artery pH <7; 5min Apgar <4; neuro probs; MOF Apgar score: `; if <7 at 5mins, continue Q5minly until >7; @ 1min, correlates with acidosis and survival; @5mins correlates with neuro outcome; based on HR, resp effort, muscle tone, reflex irritability, colour If >8, no resus needed If 4-7 IPPV intubate if no improvement at 30secs If <4 intubate Colour HR Reflex irritability Tone Respiration 0 Blue/pale Absent No response Limp Absent 1 Acrocyanotic <100/min Grimace Some flexion Weak cry / hypoV 2 Completely pink >100/min Cry / active withdrawal Active motion Good, crying Fluid requirements in neonate: D1-2: 60-80ml/kg/day; D3-7: 100-150ml/kg/day; D 8-28: 120-180ml/kg/day Meconium aspiration: staining occurs in 12-20%, but aspiration rare; 25-50% require mechanical ventilation; 5% die; due to in utero fetal distress; if stained, suction as soon as head delivered do laryngoscopy and tracheal suction through ETT if: meconium staining + not vigorous (decr RR, decr tone, HR <100); repeat until no further meconium withdrawn; if still severely depressed after meconium cleared, start active resus Stimulate, dry, warm (if prem, may need plastic bag) A: open airway, suction mouth and nose; do Apgar after this B: O2 if SaO2 <95% Assess ventilation and HR: IPPV via neopuff PEEP 5 if: Apnoea for 30secs / gasping HR <100 Persistent central cyanosis despite 100% O2 Apgar 4-7 Use RR 30-40; give for 30secs; p 20mmHg (may need inflation p 30-35mmHg briefly, 20-25mmHg in prems) Assess HR again (after 30secs) If HR >100 assess ventilation If HR <100 further 30secs ventilation If HR <60 after 30secs ventilation commence CPR Use 3:1; 1/3 depth of chest; lower ½ sternum, 100/min, will have RR 30 Assess again (after 30secs) If not improving ETT Other Indications for ETT: Prolonged resus / CPR Prem Meconium aspiration Apgar <4 ?congenital diaphragmatic hernia VLBW May need higher airway p and PEEP in prems For umbilical vein: insert catheter 10-12cm Drugs Adrenaline: 10mcg/kg IV/IO (= 0.1ml/kg 1:10,000) 100mcg/kg ETT (= 0.1ml/kg 1:1000) Give after 2nd shock then every 2nd cycle INF: 0.1-1mcg/kg/min Amiodarone: 5mg/kg after 3rd shock rpt dose after 5th shock 5-15mg/kg/min INF Procainamide: 15mg/kg IV over 30-60mins Atropine: 20mcg/kg (max 600mcg) IV rpt at 5mins Adenosine: 50-100mcg/kg 100mcg/kg 240mcg/kg (max 12mg) Sux: 3mg/kg (neonate), 2mg/kg (child), 1.5mg/kg (adult) Vec: 0.1mg/kg Diazepam: 0.25mg/kg IV Midaz: 0.15mg/kg IV Dextrose: 5ml/kg 10% dex HCO3: Naloxone: FB aspiration Prognosis 1mmol/kg if pH <7.1; must have adequate ventilation 0.1mg/kg IM/IV (max 2mg) (give if maternal opiates <4hrs and resp depression after IPPV has Restored normal HR and colour; CI if maternal narcotic addiction) Calcium: 0.2ml/kg 10% CaCl, 0.6-1ml/kg 10% CaGlu; only if hyperK/Mg, hypoCa, Ca channel blocker OD Effective cough: cough Ineffective cough: unconscious CPR, direct laryngoscopy ASAP Conscious 5x back blows 5x chest thrusts (alternate with abdo thrusts in children) Finger sweep if visible material Outcomes from resus worse than in adults; 9% survival to discharge; if arrive to ED pulseless, death in 95%, all survivors have poor neuro outcome If CPR continued for 30mins with no ROSC, then continued resus is futile (may continue longer if arrest was witnessed and CPR immediately) Notes from: Dunn, Starship guidelines Normal vital signs: Age Term 3/12 6/12 1yrs 2yrs 4yrs 5-6yrs 8yrs 10yrs 12yrs 14yrs Weight 3.5kg 6kg 7.5kg 10kg 12kg 16kg 20kg 24kg 30kg 36kg 42kg HR 110 – 170 30 – 40 100 – 160 20 – 30 80 – 130 20 70 – 115 15-20 70 – 110 60 – 100 BP = 85 + (age x 2) Per kg <10 10-20 >20 Neonatal: Per day 100ml/kg 1000 + 50ml/kg 1500 + 20ml/kg Per hour 4ml/kg 40 + 2ml/kg 60 + 1ml/kg 1-2d: 60-80ml/kg/day 3-7d: 100-150ml/kg/day 8-28d: 120-180ml/kg/day tone tone RR 40 – 60 30 – 50 SBP 50 - 90 60 - 90 65 - 90 70 – 100 75 – 110 80 – 110 85 – 120 90 – 120