Unit 2- Part 2 Reading Assessment Study Guide
advertisement
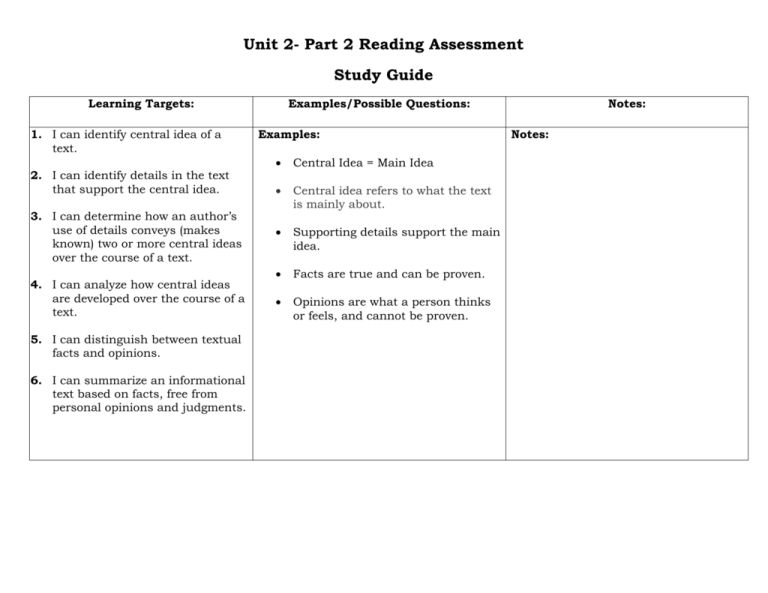
Unit 2- Part 2 Reading Assessment Study Guide Learning Targets: 1. I can identify central idea of a text. 2. I can identify details in the text that support the central idea. 3. I can determine how an author’s use of details conveys (makes known) two or more central ideas over the course of a text. 4. I can analyze how central ideas are developed over the course of a text. 5. I can distinguish between textual facts and opinions. 6. I can summarize an informational text based on facts, free from personal opinions and judgments. Examples/Possible Questions: Notes: Examples: Notes: 1. Central Idea = Main Idea Central idea refers to what the text is mainly about. Supporting details support the main idea. Facts are true and can be proven. Opinions are what a person thinks or feels, and cannot be proven. 7. I can determine the meaning of words or phrases (figurative/literal; connotative/denotative). Examples: Tone- how the author feels about a topic. 8. I can analyze the impact of a specific word choice on meaning (why did the author choose to use that word or phrase). Connotation- the suggested or implied meaning or emotion associated with a word, beyond its literal definition. 9. I can analyze the impact of a specific word choice on tone (why did the author choose to use that word or phrase). Denotation- the dictionary definition or the literal meaning. 10. I can identify a claim or type of argument. 11. I can identify and follow the pattern of an argument. 12. I can determine the credibility of the author and his/her purpose (who wrote it, when it was written and why it was written). 13. I can classify evidence that supports an argument or specific claim and evidence that does not support an argument or specific claim. Examples: Claim- a statement that can be argued. Counterclaim- a claim made by someone with an opposing opinion on an issue. Credibility- Can you trust the author? Source? Notes: Literal- following words closely or exactly, true/fact, not exaggerated. Figurative- figure of speech, representing a different meaning Notes: 14. I can evaluate a claim or argument based on its support (e.g. is the evidence necessary; irrelevant). 15. I can evaluate evidence to determine if the evidence is sound, relevant, and/or sufficient. Examples: Patterns of persuasion- sequence, cause and effect, problem/solution, compare/contrast Types of Persuasion- Logos, Ethos, Pathos Notes: