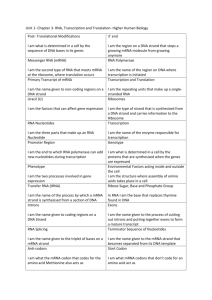
from DNA to be decoded from transcription to translation

Name: _____________________________ Score : _____/39
Self Assessment: RNA Structure and Protein Synthesis
1. – 3. Draw an RNA nucleotide. How is it similar to/different from DNA?
Name each one and tell its function in transcription/translation (protein synthesis)
4. – 5. Describe mRNA. What does it do in transcription/translation?
6. – 7. Describe rRNA. What does it do in transcription/translation?
8. – 9. Describe tRNA. What does it do in transcription/translation?
To the right is a picture of transcription and translation. Label:
A. amino acid
B. anticodon
C. codon
D. DNA
E. mRNA
F. peptide bond
G. polypeptide
H. rRNA
I. tRNA
10. _____
11. _____
16. _____
12. _____
13. _____
14. _____
17. _____
15. _____
18. – 24. Describe transcription by filling in the blank with an appropriate word.
(1 point each)
In the _____________________ of the cell, DNA is copied by _____________________, an enzyme, onto a single strand of _____________. Only one part of a chromosome, called a ___________ is copied and it represents the code for one __________________ that runs a function in your body somewhere. Transcription starts at a region called a ___________________________ and ends at a __________________________ signal.
25. – 36. Describe translation by filling in the blank with an appropriate word.
(1 point each)
A piece of mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm to a
_________________________, which is made out of ___RNA. There, it is “decoded”
_________ nucleotides at a time. A sequence on the mRNA called a ______________ matches a sequence on a ___RNA called an ______________________. When this happens an _____________ ______________ is added to the chain. The result is a
__________________________, which will later be modified into a protein. The three steps are starting the molecule, ___________________________, continuing to make it bigger, ___________________________ and finishing __________________________.
________________ ribosome can decode a single strand of mRNA at one time.
Decode this piece of DNA using the wheel provided.
Here is a DNA strand: G G C T T A C C A T G T A C C
37. The matching RNA strand is:
38. The amino acids would be:
39. There are 64 codons, but only 20 amino acids. Why don’t they match?
Name: __
Answer Key
__ Score : _
39
_/39
Self Assessment: RNA Structure and Protein Synthesis
1. – 3. Draw an RNA nucleotide. How is it similar to/different from DNA?
Similar: Different: sugar ribose nitrogen base uracil (not thymine) phosphate single strand
Name each one and tell its function in transcription/translation (protein synthesis)
4. – 5. Describe mRNA. What does it do in transcription/translation?
Long, single strand; carries code (3 bases … codon) from
DNA to be decoded from transcription to translation
6. – 7. Describe rRNA. What does it do in transcription/translation?
Single strands make up ribosomes (with proteins, too), where polypeptide is made in translation
8. – 9. Describe tRNA. What does it do in transcription/translation?
Single strand, twisted like a clover; matches
(3 bases … anticodon) mRNA and brings 1 and only 1 amino acid in translation
To the right is a picture of transcription and translation. Label:
A. amino acid
B. anticodon
C. codon
D. DNA
E. mRNA
F. peptide bond
G. polypeptide
H. rRNA
I. tRNA
10. _
D
_
11. _
E
_
12. _
C
_
13. _
I
_
16. _
G
_
17. _
A
_
14. _
B
_
15. _
H
_
18. – 24. Describe transcription by filling in the blank with an appropriate word.
(1 point each)
In the __ nucleus
_ of the cell, DNA is copied by _
RNA polymerase
_, an enzyme, onto a single strand of _ mRNA
_. Only one part of a chromosome, called a _ gene
_ is copied and it represents the code for one
_ protein
_ that runs a function in your body somewhere. Transcription starts at a region called a __ promoter
_ and ends at a _ termination
_ signal.
25. – 36. Describe translation by filling in the blank with an appropriate word.
(1 point each)
A piece of mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm to a
__ ribosome
_, which is made out of _ r
_RNA. There, it is “decoded” _
3
_
nucleotides at a time. A sequence on the mRNA called a _ codon
_ matches a sequence on a _ t
_RNA called an _ anticodon
_. When this happens an
_ amino
_ _ acid
_ is added to the chain. The result is a _ polypeptide
_, which will later be modified into a protein. The three steps are starting the molecule,
_ initiation
_, continuing to make it bigger, _ elongation
_ and finishing
_ termination
_. _
>1
_ ribosome can decode a single strand of mRNA at one time.
Decode this piece of DNA using the wheel provided.
Here is a DNA strand: G G C T T A C C A T G T A C C
37. The matching RNA strand is: C C G A A U G G U A C A U G G
38. The amino acids would be: proline–asparagine–glycine–threonine-tryptophan
39. There are 64 codons, but only 20 amino acids. Why don’t they match?
One codon is start
(AUG…methionine), several are stop codons (UAA, UAG,
UGA) and some amino acids have more than one codon (e.g. Valine is UGA, UGC, UGG,
UGU)