File
advertisement
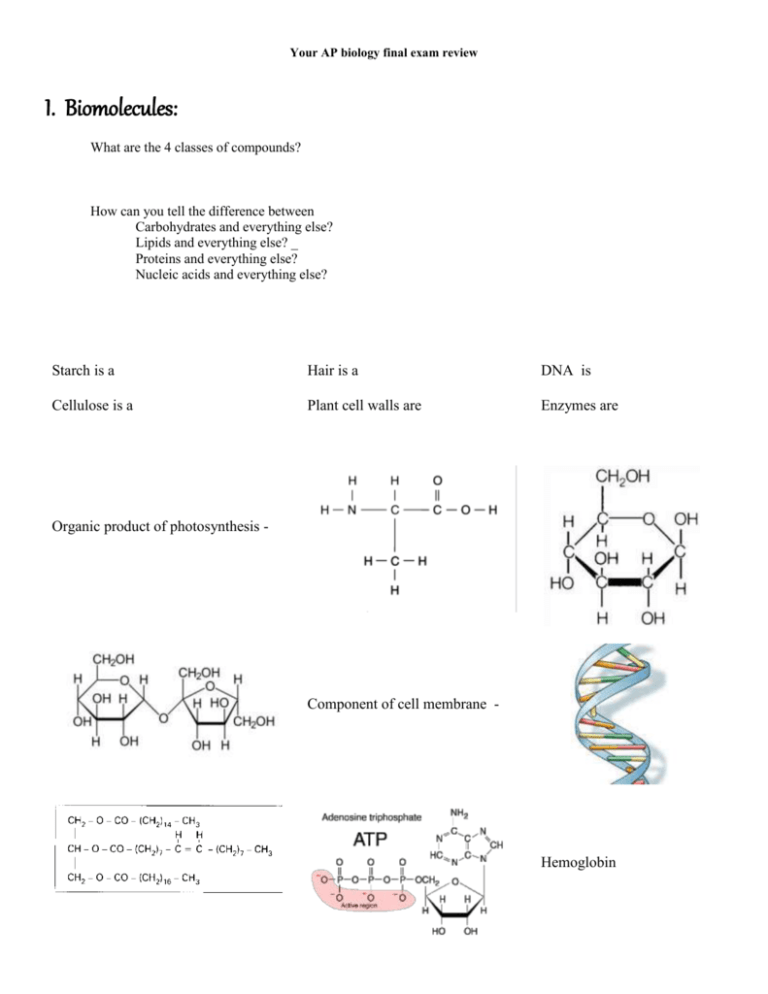
Your AP biology final exam review I. Biomolecules: What are the 4 classes of compounds? How can you tell the difference between Carbohydrates and everything else? Lipids and everything else? _ Proteins and everything else? Nucleic acids and everything else? Starch is a Hair is a DNA is Cellulose is a Plant cell walls are Enzymes are Organic product of photosynthesis - Component of cell membrane - Hemoglobin Unsaturated fat Saturated fat Structure Solid at room temp Examples How many different amino acids are possible? __ What determines the order of the amino acids in your proteins? ___ II. Cells: Prokaryote Eukaryote Size Age Nucleus Organelles Examples Part Nucleus Function Part Smooth ER Cytoplasm Golgi Body Ribosomes Vacuoles Rough ER Lysosome Plasma membrane Mitochondria Chloroplasts Cell wall Function Plant cell and Animal cell comparison and contrast Plant only Both Animal only III. Transport Label the parts of a phospholipid: (polar, nonpolar, phosphate, lipid, hydrophilic, hydrophobic) Label the parts of a bilayer: (polar, nonpolar, phosphate, lipid, hydrophilic, hydrophobic) Use the drawing below to indicate the location of inside the cell, outside of the cell, polar and nonpolar Using the image of a cell membrane below: Color the proteins red Color the polar part green Color the non polar part yellow Add in a channel (transport) protein. Add in a carbohydrate marker on one of the proteins When we say that a lipid bilayer is semipermeable, what do we mean? \ Passive transport Requires energy Moves molecules Active Transport From low concentration to high concentration Moves molecules With (down) the concentration gradient Define osmosis: Label the following drawings as hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic and draw an arrow to indicate the direction water will move. (The cell membrane is semipermeable but will not allow the particles to move thru…only water) Here are some more examples: Great website activity to review what happens to a human cell (blood cell), a plant cell (elodea) and protist (paramecium) in different solutions: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html Indicate which of the following is endocytosis and which is exocytosis. Below each one give an example of a type of substance moved in that manner Indicate which side is hypertonic, hypotonic and the direction water will move. Draw a prediction of what it will look like after sitting for a few hours: before Prediction 5% NaCl 2% NaCl 20% sucrose 50% sucrose 70% NaCl 40% NaCl IV. Energy: Is this reaction exergonic or endergonic? How can you tell? Give an example of endergonic and exergonic reactions: What is activation energy? What do the following letters represent in the diagram Which line (solid or dashed) represents a reaction with an enzyme? Give some characteristics of an enzyme: Give 3 examples of digestive enzymes and the reactions they catalyze: What’s an easy way to tell if a chemical named is an enzyme? Name 4 things that can affect an enzyme functioning Label the structure of ATP using the following terms: phosphate, bonds with high stored energy, sugar, and adenine What does ATP become when it loses one phosphate? two phosphates? All of our energy originates from the The first living things to take incoming energy and transform it to chemical energy (glucose) are called __ or ______ The energy flows from those organisms to __________ or __________ that must eat to obtain energy Give 3 kinds of organisms that are photosynthetic: What is fermentation? When does it occur and what are the byproducts? Bacteria can only conduct the first part of cellular respiration. What is that called? How many ATP does it produce? What Cellular respiration Taking glucose and breaking it down to get energy to make ADP into ATP Where Mitochondria of all eukaryotes Who All eukaryotes (prokaryotes only do the first part) What goes in (reactant) Oxygen Glucose What comes out (product) Water sunlight Carbon dioxide 6O2 + C6H12O6 6H2O + 6CO2 Reaction (balanced) Photosynthesis Taking carbon dioxide and building it up to glucose by adding energy captured from sunlight Chloroplasts of plants and algae All Autotrophs (plants, algae, photosynthetic bacteria … bacteria use cell wall instead of chloroplast Water ATP and heat Carbon dioxide Oxygen Glucose 6H2O + 6CO2 6O2 + C6H12O6 V. Cell Reproduction: What is a gene? What is a chromosome? What is chromatin? Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: G1, G2, S, cytokinesis, mitosis, interphase *Notice I am giving you more than one diagram so that you can get used various formats. Who knows what I will put on the final (and Rick Perry is the only one that knows what they’re putting on the STAAR) What happens in each of these phases? G1 - normal cellular activities G2 - growth and prep for mitosis S – DNA replication Mitosis – division of the cell’s nucleus Cytokinesis – division of the cytoplasm What kind of cell never leaves G1 – nerve cell What happens when the cell cycle loses control and begins to rapidly repeat itself? – cancer (a tumor) results How does cytokinesis differ between a plant cell and an animal cell? Label each of the steps in mitosis: A (before mitosis begins) interphase B - prophase C - metaphase D - anaphase E - telophase F (after cytokinesis) - interphase Is there a difference between the two cells labeled F? no. They are identical Is there a difference between the cell labeled A and the two labeled F? No, they are identical What is structure #6? Spindle fibers What is structure #13? Nuclear membrane (reforming) What is structure #1 - centrioles What is structure #8? - centromere You have 22 pairs of chromosomes called __autosomes_. The 23rd set are called __sex__ chromosomes and are either X and X if you are a girl or X and Y if you are a boy. X chromosome is necessary and everyone has one they got from their mother. Y chromosome only codes for male sex characteristics and boys get that chromosome from their father_. Girls get their other X from their dads. What is meiosis? the process by which cells are made that are haploid in number. They are gametes and not identical to each other Characteristic Parent cell Mitosis Diploid Meiosis Diploid Where Somatic cells – all cells in the body except gametes Testicles and ovaries # of daughter cells 2 4 Chromosome # in daughter cells Dipoid (46) Haploid (23) Are they clones? Yes No What is a karyotype? A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell lined up from longest to shortest and paired up Identify the following karyotypes as male or female and indicate if there are any chromosomal disorders Male, with Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21) Female, no disorders VI. Genetics: Who was Gregor Mendel? – What is an allele? What is purebred? What is homozygous? What is heterozygous? What is genotype What is phenotype? Work the following examples of genetic crosses using these traits: Trait Dominant Plant height Tall Seed color brown Flower color Purple Location of flowers Axial Recessive Short White Yellow Terminal A brown seeded plant is crossed with a white seeded plant and all the offspring have brown seeds. What was the genotype of the parents? What is the genotype of the offspring? Two heterozygous axial plants are crossed. What is the genotype and phenotype of the offspring? A heterozygous tall and heterozygous purple flowered plant is crossed with a short yellow flowered plant. What is the phenotypic ratios expected in the offspring? An axial white seeded plant is crossed with an axial brown plant. The offspring are half axial white and half axial brown. What is the probably genotype of the axial white plant? What about the axial brown plant? In the case of incomplete dominance, a black hen and a white rooster produce speckled offspring. What if two speckled chickens cross? What are the expected phenotypes of the offspring? If a gene is sex linked recessive found on the X chromosome and a mother that is a carrier mates with a father that does not have the disorder, what is the expected genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? A mother that is type O marries a man who is type AB. What are the expected genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? If one of their type B children marries a person that is AB, what are the expected genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? If one of their type A children marries someone that is type O, what are the expected genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring? VII. DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis Who won the Nobel prize for finding the structure of DNA? Who was Chargaff? Who was R. Franklin? If a DNA molecule is 27% guanine, what percent makes up the other 3 bases? What is antiparallel mean? What two bases are purines? A and G What two bases are pyrimidines? Which ones are bigger? What is replication? When does it take place? Where does it take place? Why does it take place? What does semiconservative mean? Draw an RNA nucleotide: Compare and contrast DNA and RNA Number of strands Nitrogen bases Where it’s found Sugar Kinds DNA 2 ATCG In the nucleus only Deoxyribose One RNA 1 ACUG In the cytoplasm Ribose Many (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) What is the central dogma of molecular biology? What is the purpose of transcription? What is the purpose of translation? Fill out the following chart: DNA (template) Complementary DNA Triplet ATC AAA GAA ATG ACC TAG TTT CTT TAC TGG mRNA (From template) Codon UAG UUU CUU UAC UGG tRNA Amino acid Anticodon AUC AAA GAA AUG ACC Stop Phe Leu Tyr tryptophan What do we mean when we say that the genetic code is universal? How do we use the universality of the genetic code in gene technology? Where does transcription take place? Where does translation take place? What is a mutation? Why is a frameshift mutation nearly always very bad…resulting in a non functional protein. VIII. Evolution What is the definition of evolution? Who was Charles Darwin? What book did he publish? What is artificial selection? What is natural selection? What is natural selection also called? What are the three conditions that must be met for natural selection to take place? Proof of evolution Fossil record: transitional fossils Define Fossils that show a link between two divergent species Example Vestigial structures Homologous structures Amino acid sequences Embryology Structures or organs that have no use but did at one time Structures that are similar between two or more divergent species Similarities in DNA will be apparent by comparing amino acid sequences Similarities in embryos of vertebrates Pelvic bone in snakes and whales Wisdom teeth in humans The forearm of many vertebrates: one large bone, two small bones and bunch of tiny bones Cytochrome C in vertebrates All vertebrate embryos (including humans) have gill slits and a tail Draw a flower and label the following parts: sepal, petals, carpel, stamen, filament, anther, ovule, style, stigma Which parts are female? Which parts are male?