Directed Reading 2.1 B
advertisement

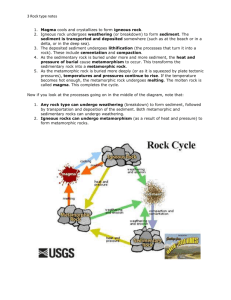
Name________________________________ Chapter 2; Section 1 Pages 26-35 Directed Reading B 1. What is a solid mixture of crystals of one or more minerals called? ___________________________________ 2. What is the process called that forms new rock from old rock? ______________________________________ 3. Early humans made arrowheads from which rock? ________________________________ Circle the answer that best completes the question or statement 4. In the rock cycle, which factor determines which forces will change a rock? a. Location c. Pressure b. Heat d. Time 5. What forces work on rocks at Earth’s surface? a. Heat and pressure b. Weathering and erosion c. Compaction and cementation d. Melting and cooling 6. What affects rocks inside the Earth? a. Heat and pressure c. Erosion b. Weathering d. Deposition 7. What material is formed when metamorphic rock melts? a. Igneous Rock c. Metamorphic Rock b. Sedimentary Rock d. Magma 8. What kind of rock is formed by the weathering and erosion of igneous rocks? a. Magma c. Metamorphic Rock b. Sedimentary Rock d. Igneous Rock 9. What kind of rock is formed when sedimentary rock is subjected to heat and pressure? a. Igneous Rock c. Metamorphic Rock b. Sedimentary Rock d. Magma Use the following terms for questions #10-13 Magma Weathering Deposition Sediment 10. During ______________________, sediment is deposited in bodies of water. 11. The process in which water, wind, ice and heat break down rock is called _______________________. 12. Weathering breaks down rock into fragments, or _________________ from which sedimentary rocks are made. 13. Because ___________________ is less dense than surrounding rock, it rises. Circle the answer that best completes the question or statement 14. What moves sediment from one place to another? a. Deposition c. Erosion b. Weathering d. Uplift 15. What is it called when sediment is deposited in a body of water? a. Deposition c. Weathering b. Uplift d. Erosion 16. What rock forms when sediment is squeezed by the weight of the rock above it? a. Igneous Rock c. Metasedimentary Rock b. Sedimentary Rock d. Metamorphic Rock 17. Besides erosion, what else causes rock to be exposed at the Earth’s surface? a. Uplift c. Deposition b. Compaction d. Cementation 18. Which is NOT one of the three main classes of rock? a. Igneous Rock c. Sedimentary Rock b. Volcanic Rock d. Metamorphic Rock 19. How do scientists classify rocks? a. By color b. By composition & texture c. By mass d. Volume 20. What is meant by the composition of rock? a. Chemical makeup c. Grain size b. Grain shape d. Grain positions 21. Besides size and position, what else determines clastic sedimentary rock texture? a. Temperature of the grains b. Length of the grains c. Width of the grains d. Shape of the grains 22. What types of grains determine clastic sedimentary rock texture? a. Round and square c. Small, medium, & large b. Fine, medium, & coarse d. Heavy and light 23. Which rock’s texture is determined by the size of the grains? a. Igneous c. Metasedimentary b. Metamorphic d. Sedimentary 24. Which rocks’ texture is determined by how fast the magma cooled? a. Igneous c. Metasedimentary b. Metamorphic d. Sedimentary 25. Which rock’s texture is determined b y the pressure and temperature the rock was exposed to? a. Metasedimentary c. Igneous b. Metamorphic d. Sedimentary